Expression of heat shock proteins (HSP27, HSP60, HSP70, HSP90, GRP78, GRP94) in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinomas and dysplastic nodules
- PMID: 15810071
- PMCID: PMC4305774
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i14.2072
Expression of heat shock proteins (HSP27, HSP60, HSP70, HSP90, GRP78, GRP94) in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinomas and dysplastic nodules
Abstract
Aim: Expression of heat shock proteins (HSPs) is frequently up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which evolves from dysplastic nodule (DN) and early HCC to advanced HCC. However, little is known about the differential expression of HSPs in multistep hepatocarcinogenesis. It was the purpose of this study to monitor the expression of HSPs in multistep hepatocarcinogenesis and to evaluate their prognostic significance in hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related HCC.
Methods: Thirty-eight HCC and 19 DN samples were obtained from 52 hepatitis B surface antigen-positive Korean patients. Immunohistochemical and dot immunoblot analyses of HSP27, HSP60, HSP70, HSP90, glucose regulated protein (GRP)78, and GRP94 were performed and their expression at different stages of HCC development was statistically analyzed.
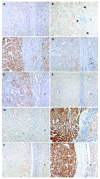
Results: Expression of HSP27, HSP70, HSP90, GRP78, and GRP94 increased along with the stepwise progression of hepatocarcinogenesis. Strong correlation was found only in GRP78 (Spearman's r = 0.802). There was a positive correlation between the expressions of GRP78, GRP94, HSP90, or HSP70 and prognostic factors of HCC. Specifically, the expression of GRP78, GRP94, or HSP90 was associated significantly with vascular invasion and intrahepatic metastasis.
Conclusion: The expressions of HSPs are commonly up-regulated in HBV-related HCCs and GRP78 might play an important role in the stepwise progression of HBV-related hepatocarcinogenesis. GRP78, GRP94, and HSP90 may be important prognostic markers of HBV-related HCC, strongly suggesting vascular invasion and intrahepatic metastasis.
Figures

References
-
- Anthony PP. Hepatocellular carcinoma: an overview. Histopathology. 2001;39:109–118. - PubMed
-
- Terminology of nodular hepatocellular lesions. Hepatology. 1995;22:983–993. - PubMed
-
- Hirohashi S, Ishak KG, Kojiro M, Wanless IR, Theise ND, Tsukama H, Blum HE, Deugnier Y, Laurent Puig P, Fischer HP, et al. Tumors of the liver and intrahepatic bile ducts. Hepatocellular carcinoma. In: Hamilton SR, Aaltonen LA, eds , editors. WHO classification. Tumours of the digestive system. 2nd ed. Lyon: IARC; 2000. p. 167.
-
- Kojiro M. Pathological evolution of early hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology. 2002;62 Suppl 1:43–47. - PubMed
-
- Sakamoto M, Hirohashi S, Shimosato Y. Early stages of multistep hepatocarcinogenesis: adenomatous hyperplasia and early hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 1991;22:172–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

