Coupling aggressive mass removal with microbial reductive dechlorination for remediation of DNAPL source zones: a review and assessment
- PMID: 15811838
- PMCID: PMC1278488
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.6932
Coupling aggressive mass removal with microbial reductive dechlorination for remediation of DNAPL source zones: a review and assessment
Abstract
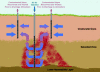
The infiltration of dense non-aqueous-phase liquids (DNAPLs) into the saturated subsurface typically produces a highly contaminated zone that serves as a long-term source of dissolved-phase groundwater contamination. Applications of aggressive physical-chemical technologies to such source zones may remove > 90% of the contaminant mass under favorable conditions. The remaining contaminant mass, however, can create a rebounding of aqueous-phase concentrations within the treated zone. Stimulation of microbial reductive dechlorination within the source zone after aggressive mass removal has recently been proposed as a promising staged-treatment remediation technology for transforming the remaining contaminant mass. This article reviews available laboratory and field evidence that supports the development of a treatment strategy that combines aggressive source-zone removal technologies with subsequent promotion of sustained microbial reductive dechlorination. Physical-chemical source-zone treatment technologies compatible with posttreatment stimulation of microbial activity are identified, and studies examining the requirements and controls (i.e., limits) of reductive dechlorination of chlorinated ethenes are investigated. Illustrative calculations are presented to explore the potential effects of source-zone management alternatives. Results suggest that, for the favorable conditions assumed in these calculations (i.e., statistical homogeneity of aquifer properties, known source-zone DNAPL distribution, and successful bioenhancement in the source zone), source longevity may be reduced by as much as an order of magnitude when physical-chemical source-zone treatment is coupled with reductive dechlorination.
Figures




References
-
- AATDF 1997. Technology Practices Manual for Surfactants and Cosolvents. Houston, TX:Advanced Applied Technology Demonstration Facility, Rice University.
-
- Abelson PH. Volatile contaminants of drinking water [Editorial] Science. 1990;247:141. - PubMed
-
- Abriola LM, Drummond CD, Hahn EJ, Hayes KF, Kibbey TCG, Lemke LD, et al. 2005. Pilot-scale demonstration of surfactant-enhanced PCE solubilization at the Bachman Road Site. 1. site characterization and test design. Environ Sci Technol [ 10.1021/es0495819]. - PubMed
-
- Adamson DT, Lyon DY, Hughes JB. Flux and product distribution during biological treatment of tetrachloroethene dense non-aqueous-phase liquid. Environ Sci Technol. 2004;38:2021–2028. - PubMed
-
- Adamson DT, McDade JM, Hughes JB. Inoculation of a DNAPL source zone to initiate reductive dechlorination of PCE. Environ Sci Technol. 2003;37:2525–2533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

