Biphasic behavior of anammox regulated by nitrite and nitrate in an estuarine sediment
- PMID: 15812021
- PMCID: PMC1082541
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.4.1923-1930.2005
Biphasic behavior of anammox regulated by nitrite and nitrate in an estuarine sediment
Abstract
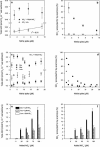
The production of N2 gas via anammox was investigated in sediment slurries at in situ NO2- concentrations in the presence and absence of NO3-. With single enrichment above 10 microM 14NO2- or 14NO3- and 15NH4+, anammox activity was always linear (P < 0.05), in agreement with previous findings. In contrast, anammox exhibited a range of activity below 10 microM NO2- or NO3-, including an elevated response at lower concentrations. With 100 microM NO3-, no significant transient accumulation of NO2- could be measured, and the starting concentration of NO2- could therefore be regulated. With dual enrichment (1 to 20 microM NO2- plus 100 microM NO3-), there was a pronounced nonlinear response in anammox activity. Maximal activity occurred between 2 and 5 microM NO2-, but the amplitude of this peak varied across the study (November 2003 to June 2004). Anammox accounted for as much as 82% of the NO2- added at 1 microM in November 2003 but only for 15% in May 2004 and for 26 and 5% of the NO2- added at 5 microM for these two months, respectively. Decreasing the concentration of NO3- but holding NO2- at 5 microM decreased the significance of anammox as a sink for NO2-. The behavior of anammox was explored by use of a simple anammox-denitrification model, and the concept of a biphasic system for anammox in estuarine sediments is proposed. Overall, anammox is likely to be regulated by the availability of NO3- and NO2- and the relative size or activity of the anammox population.
Figures



References
-
- Dalsgaard, T., D. E. Canfield, J. Petersen, B. Thamdrup, and J. Acuna-González. 2003. N2 production by the anammox reaction in the anoxic water column of Golfo Dulce, Costa Rica. Nature 422:606-608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

