Indomethacin-induced activation of the death receptor-mediated apoptosis pathway circumvents acquired doxorubicin resistance in SCLC cells
- PMID: 15812552
- PMCID: PMC2361992
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602516
Indomethacin-induced activation of the death receptor-mediated apoptosis pathway circumvents acquired doxorubicin resistance in SCLC cells
Abstract
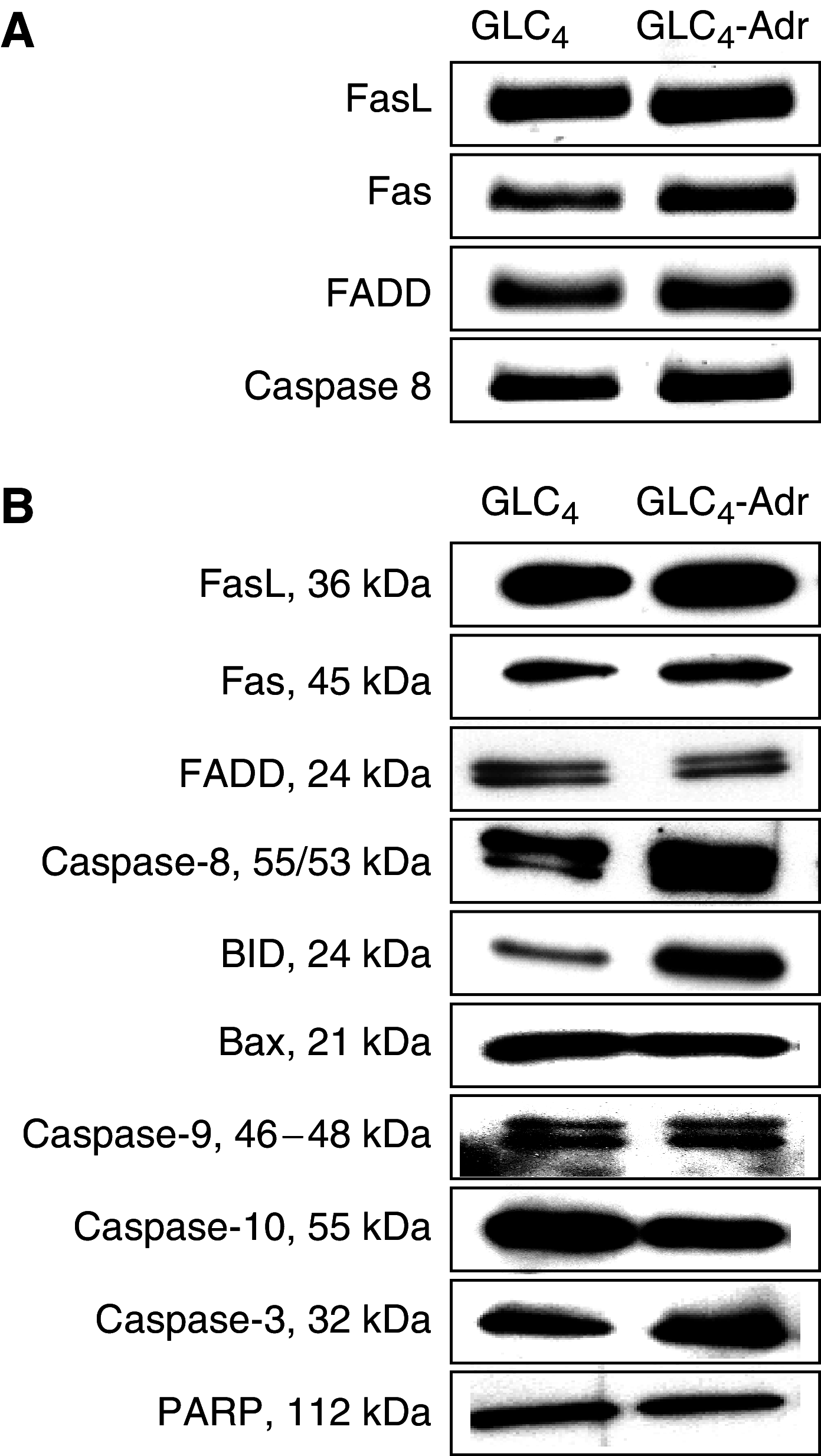
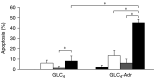
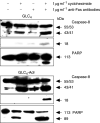
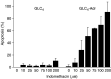
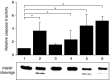
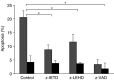
Small-cell lung cancers (SCLCs) initially respond to chemotherapy but are often resistant at recurrence. A potentially new method to overcome resistance is to combine classical chemotherapeutic drugs with apoptosis induction via tumour necrosis factor (TNF) death receptor family members such as Fas. The doxorubicin-resistant human SCLC cell line GLC4-Adr and its parental doxorubicin-sensitive line GLC4 were used to analyse the potential of the Fas-mediated apoptotic pathway and the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway to modulate doxorubicin resistance in SCLC. Western blotting showed that all proteins necessary for death-inducing signalling complex formation and several inhibitors of apoptosis were expressed in both lines. The proapototic proteins Bid and caspase-8, however, were higher expressed in GLC4-Adr. In addition, GLC4-Adr expressed more Fas (3.1x) at the cell membrane. Both lines were resistant to anti-Fas antibody, but plus the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide anti-Fas antibody induced 40% apoptosis in GLC4-Adr. Indomethacin, which targets the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, induced apoptosis in GLC4-Adr but not in GLC4 cells. Surprisingly, in GLC4-Adr indomethacin induced caspase-8 and caspase-9 activation as well as Bid cleavage, while both caspase-8 and caspase-9 specific inhibitors blocked indomethacin-induced apoptosis. In GLC4-Adr, doxorubicin plus indomethacin resulted in elevated caspase activity and a 2.7-fold enhanced sensitivity to doxorubicin. In contrast, no effect of indomethacin on doxorubicin sensitivity was observed in GLC4. Our findings show that indomethacin increases the cytotoxic activity of doxorubicin in a doxorubicin-resistant SCLC cell line partly via the death receptor apoptosis pathway, independent of Fas.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Indomethacin induces apoptosis via a MRP1-dependent mechanism in doxorubicin-resistant small-cell lung cancer cells overexpressing MRP1.Br J Cancer. 2007 Oct 22;97(8):1077-83. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604010. Epub 2007 Oct 16. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17940500 Free PMC article.
-
[Modulation of human small cell lung cancer cell line GLC4/ADR multidrug resistance in the inhibition of multidrug resistance-associated protein and its antisense].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2001 Sep;23(5):355-8. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2001. PMID: 11810759 Chinese.
-
High cytotoxic sensitivity of the human small cell lung doxorubicin-resistant carcinoma (GLC4/ADR) cell line to prodigiosin through apoptosis activation.Anticancer Drugs. 2005 Apr;16(4):393-9. doi: 10.1097/00001813-200504000-00005. Anticancer Drugs. 2005. PMID: 15746575
-
Bid, a critical mediator for apoptosis induced by the activation of Fas/TNF-R1 death receptors in hepatocytes.J Mol Med (Berl). 2000;78(4):203-11. doi: 10.1007/s001090000099. J Mol Med (Berl). 2000. PMID: 10933582 Review.
-
Role of RLIP76 in doxorubicin resistance in lung cancer.Int J Oncol. 2009 Jun;34(6):1505-11. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000279. Int J Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19424567 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Indomethacin-enhanced anticancer effect of arsenic trioxide in A549 cell line: involvement of apoptosis and phospho-ERK and p38 MAPK pathways.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:237543. doi: 10.1155/2013/237543. Epub 2013 Nov 10. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24312908 Free PMC article.
-
Early Gβγ-GRK2 Inhibition Ameliorates Osteoarthritis Development by Simultaneous Anti-Inflammatory and Chondroprotective Effects.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 19;23(14):7933. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147933. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887281 Free PMC article.
-
Functional chlorin gold nanorods enable to treat breast cancer by photothermal/photodynamic therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Nov 29;13:8119-8135. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S186974. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30555230 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigation of indomethacin-induced gastrointestinal damages in fat-1 transgenic mice via gate-keeper action of ω-3-polyunsaturated fatty acids.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 23;6:33992. doi: 10.1038/srep33992. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27658533 Free PMC article.
-
Inhaled Indomethacin-Loaded Liposomes as Potential Therapeutics against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Pharm Res. 2022 Nov;39(11):2801-2815. doi: 10.1007/s11095-022-03392-x. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Pharm Res. 2022. PMID: 36109463
References
-
- Altorki NK, Keresztes RS, Port JL, Libby DM, Korst RJ, Flieder DB, Ferrara CA, Yankelevitz DF, Subbaramaiah K, Pasmantier MW, Dannenberg AJ (2003) Celecoxib, a selective cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitor, enhances the response to preoperative paclitaxel and carboplatin in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. JClin Oncol 21: 2645–2650 - PubMed
-
- Bagrij T, Klokouzas A, Hladky SB, Barrand MA (2001) Influences of glutathione on anionic substrate efflux in tumour cells expressing the multidrug resistance-associated protein, MRP1. Biochem Pharmacol 62: 199–206 - PubMed
-
- Bennett M, Macdonald K, Chan SW, Luzio JP, Simari R, Weissberg P (1998) Cell surface trafficking of Fas: a rapid mechanism of p53-mediated apoptosis. Science 282: 290–293 - PubMed
-
- Broxterman HJ, Pinedo HM, Kuiper CM, Schuurhuis GJ, Lankelma J (1989) Glycolysis in P-glycoprotein-overexpressing human tumor cell lines. Effects of resistance-modifying agents. FEBS Lett 247: 405–410 - PubMed
-
- Crosby CG, DuBois RN (2003) The cyclooxygenase-2 pathway as a target for treatment or prevention of cancer. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 8: 1–7 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

