MR Imaging of pial melanosis secondary to a posterior fossa melanotic ependymoma
- PMID: 15814924
- PMCID: PMC7977103
MR Imaging of pial melanosis secondary to a posterior fossa melanotic ependymoma
Abstract
A 36-year-old man presented with trouble speaking and bilateral progressive hearing loss. MR imaging and histopathologic results revealed a posterior fossa melanotic ependymoma. Pial surfaces appeared hyperintense on T1-weighted images and hypointense on T2-weighted images. Histopathologic examination revealed that tumor cells and interstitial spaces had abundant melanin accumulation. There was no evidence of hemosiderin in tumor cells and in interstitial spaces. Pial melanin accumulation secondary to a posterior fossa melanotic ependymoma explained our MR findings.
Figures

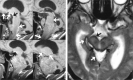

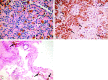
References
-
- Chan AC, Ho LC, Yip WW, Cheung FC. Pigmented ependymoma with lipofuscin and neuromelanin production. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:872–875 - PubMed
-
- Kakkar N, Vasishta RK, Banerjee AK. Pathology teach and tell: melanotic ependymoma. Pediatr Pathol Mol Med 2003;22:171–174 - PubMed
-
- McCloskey JJ, Parker JC Jr, Brooks WH, Blacker HM. Melanin as a component of cerebral gliomas: the melanotic cerebral ependymoma. Cancer 1976;37:2373–2379 - PubMed
-
- Rosenblum MK, Erlandson RA, Aleksic SN, Budzilovich GN. Melanotic ependymoma and subependymoma. Am J Surg Pathol 1990;14:729–736 - PubMed
-
- Panyathanya R, Chantarakul N. Melanotic ependymoma with distant metastases. J Med Assoc Thai 1982;65:454–458 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
