European multicenter study of the LIAISON automated diagnostic system for determination of Toxoplasma gondii-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM and the IgG avidity index
- PMID: 15814967
- PMCID: PMC1081322
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.4.1570-1574.2005
European multicenter study of the LIAISON automated diagnostic system for determination of Toxoplasma gondii-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM and the IgG avidity index
Abstract
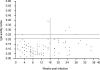
The LIAISON system is a fully automated system based on chemiluminescence and antigen bound to magnetic microparticles. The system allows fast and precise measurement of Toxoplasma-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM antibody levels and measurement of the IgG avidity index even at low levels of Toxoplasma-specific IgG antibodies in a single step without manual interference. Seven European centers participated in a multicenter evaluation of the LIAISON system. The sensitivity and specificity of the LIAISON system compared to the Sabin-Feldman dye test were 99.3 and 96.8%, respectively. In a comparison of the LIAISON Toxoplasma-specific IgM assay with an immunosorbent agglutination assay, the LIAISON assay had a sensitivity of 96.7% and a specificity of 95.4%. The LIAISON IgG assay showed agreements of 91, 100, and 100% with the AXSYM IgG (Abbott), VIDAS IgG (bioMerieux), and Platelia IgG (Bio-Rad) assays, respectively. The LIAISON IgM assay showed agreements of 95% with the AXSYM IgM and Platelia IgM assays, 96% with the ISAGA IgM assay (bioMerieux), and 97% with the VIDAS IgM assay. The coefficient of correlation between the LIAISON system and the VIDAS Toxoplasma-specific IgG avidity index was 0.81. By use of the Toxoplasma-specific IgG avidity index assay with specific IgM-positive samples, the diagnosis of infection with Toxoplasma gondii in early pregnancy has been improved significantly. The LIAISON avidity assay is a valuable assay for the exclusion of recently acquired infection with T. gondii (less than 4 months) in pregnant women, and it decreases significantly the necessity for follow-up testing.
Figures

References
-
- Alvarado-Esquivel, C., S. Sethi, K. Janitschke, H. Hahn, and O. Liesenfeld. 2002. Comparison of two commercially available avidity tests for Toxoplasma-specific IgG antibodies. Arch. Med. Res. 33:520-523. - PubMed
-
- Beghetto, E., W. Buffolano, A. Spadoni, M. Del Pezzo, M. Di Cristina, O. Minenkova, E. Petersen, F. Filici, and N. Gargano. 2003. Use of an immunoglobulin G avidity assay based on recombinant antigens for diagnosis of primary Toxoplasma gondii infection during pregnancy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41:5414-5418. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

