Determinants for the occurrence of acute exacerbation of hepatitis B virus infection in Chinese patients after HBeAg seroclearance
- PMID: 15814971
- PMCID: PMC1081372
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.4.1594-1599.2005
Determinants for the occurrence of acute exacerbation of hepatitis B virus infection in Chinese patients after HBeAg seroclearance
Abstract
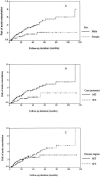
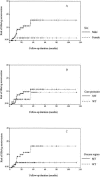
This study was performed to determine the factors for predicting the occurrence of acute exacerbation of hepatitis B virus infection in HBeAg-negative patients. Two hundred and sixteen patients with known times of HBeAg seroclearance were recruited. Liver biochemistry and virologic markers were monitored. Precore and core promoter mutations were determined by a line probe assay. The median age at HBeAg seroclearance was 34.5 years. The median follow-up duration was 26.4 months. Fifty-six (27.9%) patients had acute exacerbations. By Cox regression analysis, male gender, older age, and core promoter mutations at the time of HBeAg seroclearance were independently associated with the occurrence of acute exacerbation after HBeAg seroclearance (P = 0.025, 0.018, and 0.001, respectively). Fourteen (7.0%) patients had HBeAg seroreversion within a median follow-up period of 11.6 months after HBeAg seroclearance. By Cox regression analysis, older age at HBeAg seroclearance was independently associated with the chance of HBeAg seroreversion (P = 0.01). We concluded that male patients with core promoter mutations and delayed HBeAg seroclearance had a higher cumulative chance of acute exacerbation in the HBeAg-negative phase. Patients with delayed HBeAg seroclearance had a higher frequency of HBeAg seroreversion.
Figures
References
-
- Brunetto, M. R., F. Oliveri, B. Coco, G. Leandro, P. Colombatto, J. M. Gorin, and F. Bonino. 2002. Outcome of anti-HBe positive chronic hepatitis B in alpha-interferon treated and untreated patients: a long term cohort study. J. Hepatol. 36:263-270. - PubMed
-
- Buckwold, V. E., Z. Xu, T. S. Yen, and J. H. Ou. 1997. Effects of a frequent double-nucleotide basal core promoter mutation and its putative single-nucleotide precursor mutations on hepatitis B virus gene expression and replication. J. Gen. Virol. 78:2055-2065. - PubMed
-
- Chan, H. L., Y. Hui, N. W. Leung, J. Y. Ching, F. K. Chan, and J. J. Sung. 2000. Risk factors for active liver disease in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B virus-infected patients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 95:3547-3551. - PubMed
-
- Chang, M. H., H. Y. Hsu, H. C. Hsu, Y. H. Ni, J. S. Chen, and D. S. Chen. 1995. The significance of spontaneous hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in childhood with special emphasis on the clearance of hepatitis B e antigen before 3 years of age. Hepatology 22:1387-1392. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

