Multiplex PCR for typing strains of Toxoplasma gondii
- PMID: 15815026
- PMCID: PMC1081364
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.4.1940-1943.2005
Multiplex PCR for typing strains of Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
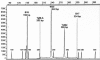
A multiplex PCR assay was designed for multilocus strain typing of Toxoplasma gondii based on length polymorphism of five microsatellite markers. Eight T. gondii strains already sequenced at these five markers were used as control isolates. This method is simple, rapid, reproducible, and adapted to a large set of isolates.
Figures

References
-
- Ajzenberg, D., N. Cogné, L. Paris, M. H. Bessieres, P. Thulliez, D. Filisetti, H. Pelloux, P. Marty, and M. L. Dardé. 2002. Genotype of 86 Toxoplasma gondii isolates associated with human congenital toxoplasmosis, and correlation with clinical findings. J. Infect. Dis. 186:684-689. - PubMed
-
- Ajzenberg, D., A. L. Bañuls, C. Su, A. Dumètre, M. Demar, B. Carme, and M. L. Dardé. 2004. Genetic diversity, clonality and sexuality in Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 34:1185-1196. - PubMed
-
- Burnett, A. J., S. G. Short, J. Isaac-Renton, A. King, D. Werker, and W. R. Bowie. 1998. Multiple cases of acquired toxoplasmosis retinitis presenting in an outbreak. Ophthalmology 105:1032-1037. - PubMed
-
- Dardé, M. L., B. Bouteille, and M. Pestre-Alexandre. 1988. Isoenzymic characterization of seven isolates of Toxoplasma gondii by isoelectrofocusing in polyacrylamide gels. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 39:551-558. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

