Relationship of brain and skull in pre- and postoperative sagittal synostosis
- PMID: 15817105
- PMCID: PMC1571486
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00397.x
Relationship of brain and skull in pre- and postoperative sagittal synostosis
Erratum in
- J Anat. 2006 Feb;208(2):259
Abstract
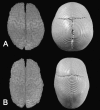
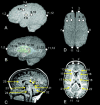
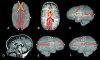
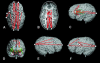
Models of vertebrate skull evolution stress the coordinated developmental relationship between the skull and the brain that it houses. This study investigates the relationship between altered skull morphology and brain morphology in premature fusion of the cranial sagittal suture (isolated sagittal synostosis; ISS), a condition associated with dysmorphology of both neurocranium and brain. Although the skull displays a more normal shape following reconstructive cranial vault surgery, effects of this surgery on the brain have not been investigated. Landmark coordinate data were collected from three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging reconstructions of the brain in a sample of ISS patients and an age-matched unaffected cohort. These data were analysed using Euclidean distance matrix analysis (EDMA). Results show that the brain in ISS is dysmorphic preoperatively, displaying a posteriorly directed neural expansion that does not 'worsen' with growth. Postoperatively, the brain in ISS displays a more globular shape overall as compared with the preoperative morphology, but differs from normal in its subcortical morphology. These results show that the ISS brain is altered following neurocranial surgery, but does not more closely approximate that of unaffected individuals. This suggests that although the brain is affected by manipulation of the skull, it retains a growth pattern that is, at least in part, independent of the skull.
Figures

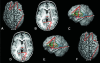
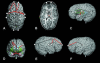
References
-
- Aldridge K, Barta P, Pearlson G, Richtsmeier J. Brain morphology, MRI data, and landmark-based analyses of form. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. Suppl. 2000;30:94.
-
- Aylward E, Augustine A, Li Q, Barta P, Pearlson G. Measurement of frontal lobe volume on magnetic resonance imaging scans. Psych. Res. 1997;75:23–30. - PubMed
-
- Barritt J, Brooksbank M, Simpson D. Scaphocephaly: aesthetic and psychosocial considerations. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1981;23:183–191. - PubMed
-
- Barta P, Dhingra L, Royall R, Schwartz E. Improving stereological estimates for the volume of structures identified in three-dimensional arrays of spatial data. J. Neurosci. Meth. 1997;75:111–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

