Bistability in the Bacillus subtilis K-state (competence) system requires a positive feedback loop
- PMID: 15819619
- PMCID: PMC3831615
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04592.x
Bistability in the Bacillus subtilis K-state (competence) system requires a positive feedback loop
Abstract
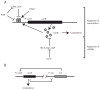
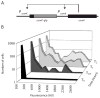
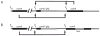
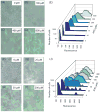
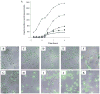
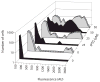
High expression of the transcriptional activator ComK occurs in 10-20% of the cells in stationary phase cultures of Bacillus subtilis strain 168. ComK drives the expression of more than 100 genes constituting the semidormant K-state, distinct from sporulation and vegetative growth. Among the genes so activated are those that permit competence for genetic transformation. We have addressed the origin of bistability in expression of ComK. We show that bistability requires positive autoregulation at the promoter of comK, but not a potential toggle switch, in which ComK represses the promoter of rok and Rok represses the promoter of comK. We further address the source of the noise that results in the stochastic selection of cells that will express comK. A revised model for the regulation of comK expression is proposed that partially explains bistability.
Figures
References
-
- Balaban NQ, Merrin J, Chait R, Kowalik L, Leibler S. Bacterial persistence as a phenotypic switch. Science. 2004;305:1622–1625. - PubMed
-
- Berka RM, Hahn J, Albano M, Draskovic I, Persuh M, Cui X, et al. Microarray analysis of the Bacillus subtilis K-state: genome-wide expression changes dependent on ComK. Mol Microbiol. 2002;43:1331–1345. - PubMed
-
- Elowitz MB, Levine AJ, Siggia ED, Swain PS. Stochastic gene expression in a single cell. Science. 2002;297:1183–1186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

