The intriguing biology of the tumour necrosis factor/tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily: players, rules and the games
- PMID: 15819693
- PMCID: PMC1782125
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02143.x
The intriguing biology of the tumour necrosis factor/tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily: players, rules and the games
Abstract
The members of the tumour necrosis factor (TNF)/tumour necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily are critically involved in the maintenance of homeostasis of the immune system. The biological functions of this system encompass beneficial and protective effects in inflammation and host defence as well as a crucial role in organogenesis. At the same time, members of this superfamily are responsible for host damaging effects in sepsis, cachexia, and autoimmune diseases. This review summarizes recent progress in the immunobiology of the TNF/TNFR superfamily focusing on results obtained from animal studies using gene targeted mice. The different modes of signalling pathways affecting cell proliferation, survival, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune organ development as well as host defence are reviewed. Molecular and cellular mechanisms that demonstrate a therapeutic potential by targeting individual receptors or ligands for the treatment of chronic inflammatory or autoimmune diseases are discussed.
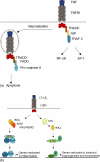
Figures

References
-
- Aggarwal BB, Schwarz L, Hogan ME, Rando RF. Triple helix-forming oligodeoxyribonucleotides targeted to the human tumor necrosis factor (TNF) gene inhibit TNF production and block the TNF-dependent growth of human glioblastoma tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1996;56:5156–64. - PubMed
-
- Granger GA, Shacks SJ, Williams TW, Kolb WP. Lymphocyte in vitro cytotoxicity. specific release of lymphotoxin-like materials from tuberculin-sensitive lymphoid cells. Nature. 1969;221:1155–7. - PubMed
-
- Helson L, Green S, Carswell E, Old LJ. Effect of tumour necrosis factor on cultured human melanoma cells. Nature. 1975;258:731–2. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B, Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor: an endogenous mediator of shock and inflammation. Immunol Res. 1986;5:281–93. - PubMed
-
- Locksley RM, Killeen N, Lenardo MJ. The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology. Cell. 2001;104:487–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

