Ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 controls osteoblast activity and bone homeostasis by targeting MEKK2 for degradation
- PMID: 15820682
- PMCID: PMC3314294
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.01.035
Ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 controls osteoblast activity and bone homeostasis by targeting MEKK2 for degradation
Abstract
Bone is constantly resorbed and formed throughout life by coordinated actions of osteoclasts and osteoblasts. Here we show that Smurf1, a HECT domain ubiquitin ligase, has a specific physiological role in suppressing the osteogenic activity of osteoblasts. Smurf1-deficient mice are born normal but exhibit an age-dependent increase of bone mass. The cause of this increase can be traced to enhanced activities of osteoblasts, which become sensitized to bone morphogenesis protein (BMP) in the absence of Smurf1. However, loss of Smurf1 does not affect the canonical Smad-mediated intracellular TGFbeta or BMP signaling; instead, it leads to accumulation of phosphorylated MEKK2 and activation of the downstream JNK signaling cascade. We demonstrate that Smurf1 physically interacts with MEKK2 and promotes the ubiquitination and turnover of MEKK2. These results indicate that Smurf1 negatively regulates osteoblast activity and response to BMP through controlling MEKK2 degradation.
Figures
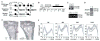
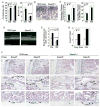
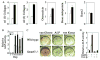
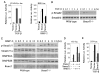


Comment in
-
Ubiquitin-mediated degradation a mechanism for fine-tuning TGF-beta signaling.Cell. 2005 Apr 8;121(1):2-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.03.017. Cell. 2005. PMID: 15820671
References
-
- Bakin AV, Rinehart C, Tomlinson AK, Arteaga CL. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for TGFβ-mediated fibroblastic transdifferentiation and cell migration. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:3193–3206. - PubMed
-
- Balemans W, Van Hul W. Extracellular regulation of BMP signaling in vertebrates: a cocktail of modulators. Dev Biol. 2002;250:231–250. - PubMed
-
- Bhargava U, Bar-Lev M, Bellows CG, Aubin JE. Ultrastructural analysis of bone nodules formed in vitro by isolated fetal rat calvaria cells. Bone. 1988;9:155–163. - PubMed
-
- Brown JD, DiChiara MR, Anderson KR, Gimbrone MA, Jr, Topper JN. MEKK-1, a component of the stress (stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase) pathway, can selectively activate Smad2-mediated transcriptional activation in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:8797–8805. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

