Complementary structural information from a tryptic N-linked glycopeptide via electron transfer ion/ion reactions and collision-induced dissociation
- PMID: 15822944
- PMCID: PMC1350609
- DOI: 10.1021/pr049770q
Complementary structural information from a tryptic N-linked glycopeptide via electron transfer ion/ion reactions and collision-induced dissociation
Abstract
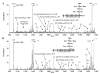
Glycosylation is an important post-translational modification. Analysis of glycopeptides is difficult using collision-induced dissociation, as it typically yields only information about the glycan structure, without any peptide sequence information. We demonstrate here how a 3D-quadrupole ion trap, using the complementary techniques of collision induced dissociation (CID) and electron-transfer dissociation (ETD), can be used to elucidate the glycan structure and peptide sequence of the N-glycosylated peptide from a fractionated tryptic digest of the lectin from the coral tree, Erythina cristagalli. CID experiments on the multiply protonated glycopeptide ions yield, almost exclusively, cleavage at glycosidic bonds, with little peptide backbone fragmentation. ETD reactions of the triply charged glycopeptide cations with either sulfur dioxide or nitrobenzene anions yield cleavage of the peptide backbone with no loss of the glycan structure. These results show that a 3D-quadrupole ion trap can be used to provide glycopeptide amino acid sequence information as well as information about the glycan structure.
Figures

References
-
- Apweiler R, Hermjakob H, Sharon N. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1473:4–8. - PubMed
-
- Harvey DJ. Proteomics. 2001;1:311–328. - PubMed
-
- Demelbauer UM, Zehl M, Plematl A, Allmaier G, Rizzi A. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2004;18:1575–1582. - PubMed
-
- Wada Y, Tajiri M, Yoshida S. Anal Chem. 2004;76:6560–6565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

