Monitoring standing wheelchair use after spinal cord injury: a case report
- PMID: 15823996
- PMCID: PMC3151726
- DOI: 10.1080/09638280400009337
Monitoring standing wheelchair use after spinal cord injury: a case report
Abstract
Purpose: An important issue in spinal cord injury (SCI) research is whether standing can yield positive health benefits. However, quantifying dose of standing and establishing subject compliance with a standing protocol is difficult. This case report describes a method to monitor dose of standing outside the laboratory, describes the standing patterns of one subject, and describes this subject's satisfaction with the standing protocol.
Method: A man with T-10 complete paraplegia agreed to have his commercially available standing wheelchair instrumented with a custom-designed logging device for a 2-year period. The micro-controller-based logger, under custom software control, was mounted to the standing wheelchair. The logger recorded date, duration, angle of standing, and start/stop times.
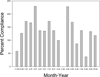
Results: The client exceeded a suggested minimum dosage of standing per month (130.4% of goal), choosing to stand for short bouts (mean = 11.57 min) at an average angle of 61 degrees, on an average 3.86 days per calendar week. He was generally very satisfied with the standing device and provided subjective reports of improved spasticity and bowel motility.
Conclusion: This case report describes a standing and surveillance system that allow quantification of standing dose. Future controlled studies are needed to evaluate whether standing can be beneficially affect secondary complications after SCI.
Figures

References
-
- Eichenholtz SN. Management of long-bone fractures in paraplegic patients. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery - American Volume. 1963;45-A:299–310.
-
- Issekutz B, Jr, Blizzard JJ, Birkhead NC, Rodahl K. Effect of prolonged bed rest on urinary calcium output. Journal of Applied Physiology. 1966;21:1013–1020. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan PE, Roden W, Gilbert E, Richards L, Goldschmidt JW. Reduction of hypercalciuria in tetraplegia after weight-bearing and strengthening exercises. Paraplegia. 1981;19:289–293. - PubMed
-
- Uebelhart D, Demiaux-Domenech B, Roth M, Chantraine A. Bone metabolism in spinal cord injured individuals and in others who have prolonged immobilisation. A review. Paraplegia. 1995;33:669–673. - PubMed
-
- Abramson AS. Bone disturbances in injuries to the spinal cord and cauda equina (paraplegia) The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 1948;30-A:982–987. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
