Enhanced proliferation of cultured human vascular smooth muscle cells linked to increased function of RNA-binding protein HuR
- PMID: 15824116
- PMCID: PMC1350862
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M501106200
Enhanced proliferation of cultured human vascular smooth muscle cells linked to increased function of RNA-binding protein HuR
Abstract
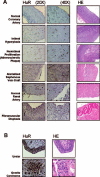
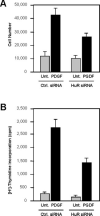
In dividing cells, the RNA-binding protein HuR associates with and stabilizes labile mRNAs encoding proliferative proteins, events that are linked to the increased cytoplasmic presence of HuR. Here, assessment of HuR levels in various vascular pathologies (intimal hyperplasia, atherosclerosis and neointimal proliferation, sclerosis of arterialized saphenous venous graft, and fibromuscular dysplasia) revealed a distinct increase in HuR expression and cytoplasmic abundance within the intima and neointima layers. On the basis of these observations, we postulated a role for HuR in promoting the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. To test this hypothesis directly, we investigated the expression, subcellular localization, and proliferative influence of HuR in human vascular smooth muscle cells (hVSMCs). Treatment of hVSMCs with platelet-derived growth factor increased HuR levels in the cytoplasm, thereby influencing the expression of metabolic, proliferative, and structural genes. Importantly, knockdown of HuR expression by using RNA interference caused a reduction of hVSMC proliferation, both basally and following platelet-derived growth factor treatment. We propose that HuR contributes to regulating hVSMC growth and homeostasis in pathologies associated with vascular smooth muscle proliferation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Influence of the RNA-binding protein HuR in pVHL-regulated p53 expression in renal carcinoma cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Oct;23(20):7083-95. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.20.7083-7095.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14517280 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin A2-mediated stabilization of p21 mRNA through an ERK-dependent pathway requiring the RNA-binding protein HuR.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 19;279(47):49298-306. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407535200. Epub 2004 Sep 14. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15371446
-
Interaction of RNA-binding proteins HuR and AUF1 with the human ATF3 mRNA 3'-untranslated region regulates its amino acid limitation-induced stabilization.J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 14;280(41):34609-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M507802200. Epub 2005 Aug 17. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16109718 Free PMC article.
-
Posttranscriptional orchestration of an anti-apoptotic program by HuR.Cell Cycle. 2007 Jun 1;6(11):1288-92. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.11.4299. Epub 2007 Jun 15. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17534146 Review.
-
RNA-binding proteins and gene regulation in myogenesis.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2011 Nov;32(11):652-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2011.06.004. Epub 2011 Oct 6. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21982546 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HuR regulates phospholamban expression in isoproterenol-induced cardiac remodelling.Cardiovasc Res. 2020 Apr 1;116(5):944-955. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz205. Cardiovasc Res. 2020. PMID: 31373621 Free PMC article.
-
Human iPSC-derived MSCs (iMSCs) from aged individuals acquire a rejuvenation signature.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Mar 18;10(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1209-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30885246 Free PMC article.
-
HuR antagonizes the effect of an intronic pyrimidine-rich sequence in regulating WT1 +/-KTS isoforms.RNA Biol. 2015;12(12):1364-71. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1102831. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 26512748 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of RNA-binding proteins in diabetes and their therapeutic potential in diabetic complications.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2018 Mar;9(2):10.1002/wrna.1459. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1459. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2018. PMID: 29280295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and function of anti-inflammatory interleukins: the other side of the vascular response to injury.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2009 Jul;7(3):267-76. doi: 10.2174/157016109788340721. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19601851 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berk BC. Physiol. Rev. 2001;81:999–1030. - PubMed
-
- Dzau VJ, Braun-Dullaeus RC, Sedding DG. Nat. Med. 2002;8:1249–1256. - PubMed
-
- Boehm M, Nabel EG. Prog. Cell Cycle Res. 2003;23:555–565. - PubMed
-
- Sukhanov S, Song YH, Delafontaine P. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 2003;306:443–449. - PubMed
-
- Campos AH, Zhao Y, Pollman MJ, Gibbons GH. Circ. Res. 2003;92:111–118. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

