Many accurate small-discriminatory feature subsets exist in microarray transcript data: biomarker discovery
- PMID: 15826317
- PMCID: PMC1090559
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-97
Many accurate small-discriminatory feature subsets exist in microarray transcript data: biomarker discovery
Abstract
Background: Molecular profiling generates abundance measurements for thousands of gene transcripts in biological samples such as normal and tumor tissues (data points). Given such two-class high-dimensional data, many methods have been proposed for classifying data points into one of the two classes. However, finding very small sets of features able to correctly classify the data is problematic as the fundamental mathematical proposition is hard. Existing methods can find "small" feature sets, but give no hint how close this is to the true minimum size. Without fundamental mathematical advances, finding true minimum-size sets will remain elusive, and more importantly for the microarray community there will be no methods for finding them.
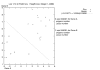
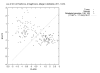
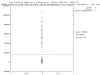
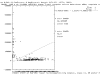
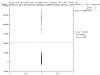
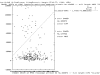
Results: We use the brute force approach of exhaustive search through all genes, gene pairs (and for some data sets gene triples). Each unique gene combination is analyzed with a few-parameter linear-hyperplane classification method looking for those combinations that form training error-free classifiers. All 10 published data sets studied are found to contain predictive small feature sets. Four contain thousands of gene pairs and 6 have single genes that perfectly discriminate.
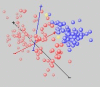
Conclusion: This technique discovered small sets of genes (3 or less) in published data that form accurate classifiers, yet were not reported in the prior publications. This could be a common characteristic of microarray data, thus making looking for them worth the computational cost. Such small gene sets could indicate biomarkers and portend simple medical diagnostic tests. We recommend checking for small gene sets routinely. We find 4 gene pairs and many gene triples in the large hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC, Liver cancer) data set of Chen et al. The key component of these is the "placental gene of unknown function", PLAC8. Our HMM modeling indicates PLAC8 might have a domain like part of lP59's crystal structure (a Non-Covalent Endonuclease lii-Dna Complex). The previously identified HCC biomarker gene, glypican 3 (GPC3), is part of an accurate gene triple involving MT1E and ARHE. We also find small gene sets that distinguish leukemia subtypes in the large pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia cancer set of Yeoh et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In silico microdissection of microarray data from heterogeneous cell populations.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Mar 14;6:54. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-54. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15766384 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression analysis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma using gene set enrichment analysis for biostatistical management.BJU Int. 2011 Jul;108(2 Pt 2):E29-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09794.x. Epub 2011 Mar 16. BJU Int. 2011. PMID: 21435154
-
Regularized Least Squares Cancer classifiers from DNA microarray data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Dec 1;6 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-S4-S2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 16351746 Free PMC article.
-
Microarrays--identifying molecular portraits for prostate tumors with different Gleason patterns.Methods Mol Med. 2008;141:131-51. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-148-6_8. Methods Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18453088 Review.
-
Statistical considerations for analysis of microarray experiments.Clin Transl Sci. 2011 Dec;4(6):466-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-8062.2011.00309.x. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Clin Transl Sci. 2011. PMID: 22212230 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An integrated approach for identifying wrongly labelled samples when performing classification in microarray data.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46700. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046700. Epub 2012 Oct 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23082127 Free PMC article.
-
Rough set soft computing cancer classification and network: one stone, two birds.Cancer Inform. 2010 Jul 15;9:139-45. doi: 10.4137/cin.s4874. Cancer Inform. 2010. PMID: 20706619 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis and computational dissection of molecular signature multiplicity.PLoS Comput Biol. 2010 May 20;6(5):e1000790. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000790. PLoS Comput Biol. 2010. PMID: 20502670 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaced roles of PLAC8 in cancer.Biomark Res. 2021 Oct 9;9(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s40364-021-00329-1. Biomark Res. 2021. PMID: 34627411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overlapping gene expression profiles of cell migration and tumor invasion in human bladder cancer identify metallothionein 1E and nicotinamide N-methyltransferase as novel regulators of cell migration.Oncogene. 2008 Nov 6;27(52):6679-89. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.264. Epub 2008 Aug 25. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18724390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moler E, Chow M, Mian I. Analysis of molecular profile data using generative and discriminative methods. Physiological Genomics. 2000;4:109–126. - PubMed
-
- Ramaswamy S, Tamayo P, Rifkin R, Mukherjee S, Yeang CH, Angelo M, Ladd C, Reich M, Latulippe E, Mesirov J, Poggio T, Gerald W, Loda M, Lander E, Golub T. Multiclass cancer diagnosis using tumor gene expression signatures. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2001;98:15149–15154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.211566398. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

