Characterization of the Bacillus subtilis GTPase YloQ and its role in ribosome function
- PMID: 15828870
- PMCID: PMC1180735
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20041873
Characterization of the Bacillus subtilis GTPase YloQ and its role in ribosome function
Abstract
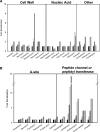
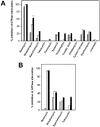
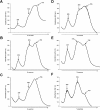
We present an analysis of the cellular phenotype and biochemical activity of a conserved bacterial GTPase of unknown function (YloQ and YjeQ in Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli respectively) using a collection of antibiotics of diverse mechanisms and chemical classes. We created a yloQ deletion strain, which exhibited a slow growth phenotype and formed chains of filamentous cells. Additionally, we constructed a conditional mutant in yloQ, where growth was dependent on inducible expression from a complementing copy of the gene. In phenotypic studies, depletion of yloQ sensitized cells to antibiotics that bind at the peptide channel or peptidyl transferase centre, providing the first chemical genetic evidence linking this GTPase to ribosome function. Additional experiments using these small-molecule probes in vitro revealed that aminoglycoside antibiotics severely affected a previously characterized ribosome-associated GTPase activity of purified, recombinant YjeQ from E. coli. None of the antibiotics tested competed with YjeQ for binding to 30 or 70 S ribosomes. A closer examination of YloQ depletion revealed that the polyribosome profiles were altered and that decreased expression of YloQ led to the accumulation of ribosomal subunits at the expense of intact 70 S ribosomes. The present study provides the first evidence showing that YloQ/YjeQ may be involved in several areas of cellular metabolism, including cell division and ribosome function.
Figures




References
-
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McMormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature (London) 1990;348:125–132. - PubMed
-
- Pandit S. B., Srinivasan N. Survey for G-proteins in the prokaryotic genomes: prediction of functional roles based on classification. Proteins. 2003;52:585–597. - PubMed
-
- Daigle D. M., Rossi L., Berghuis A. M., Aravind L., Koonin E. V., Brown E. D. YjeQ, an essential, conserved, uncharacterized protein from Escherichia coli, is an unusual GTPase with circularly permuted G-motifs and marked burst kinetics. Biochemistry. 2002;41:11109–11117. - PubMed
-
- Levdikov V. M., Blagova E. V., Brannigan J. A., Cladiere L., Antson A. A., Isupov M. N., Seror S. J., Wilkinson A. J. The crystal structure of YloQ, a circularly permuted GTPase essential for Bacillus subtilis. J. Mol. Biol. 2004;340:767–782. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

