Color naming, lens aging, and grue: what the optics of the aging eye can teach us about color language
- PMID: 15828980
- PMCID: PMC2586906
- DOI: 10.1111/j.0956-7976.2005.01534.x
Color naming, lens aging, and grue: what the optics of the aging eye can teach us about color language
Abstract
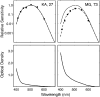
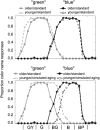
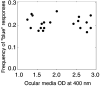
Many languages without separate terms for green and blue are or were spoken in locations receiving above-average exposure to ultraviolet-B (UV-B) radiation. It has been proposed that this correlation is caused by premature lens aging. This conclusion was supported by an experiment in which younger observers used the term "blue" less often when they described simulated paint chips filtered through the equivalent of an older observer's lens-removing much short-wavelength light-than when they described the unfiltered versions of the same paint chips. Some stimuli that were called "blue" without simulated aging were called "green" when filtered. However, in the experiment reported here, we found that the proportion of "blue" color-name responses did not differ between younger subjects and older observers with known ocular media optical densities. Color naming for stimuli that were nominally green, blue-green, or blue was virtually identical for older and younger observers who viewed the same (unfiltered) stimuli. Our results are inconsistent with the lens-brunescence hypothesis.
Figures
References
-
- Berlin B, Kay P. Basic color terms: Their universality and evolution. University of California Press; Berkeley: 1969.
-
- Davidoff J, Davies I, Roberson D. Colour categories in a stone-age tribe. Nature. 1999;398:203–204. - PubMed
-
- Ember M. Size of color lexicon: Interaction of cultural and biological factors. American Anthropologist. 1978;80:364–367.
-
- Hays DG, Margolis E, Naroll R, Perkins DR. Color term salience. American Anthropologist. 1972;74:1107–1121.

