Downregulation of activating transcription factor 5 is required for differentiation of neural progenitor cells into astrocytes
- PMID: 15829641
- PMCID: PMC6724921
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3447-04.2005
Downregulation of activating transcription factor 5 is required for differentiation of neural progenitor cells into astrocytes
Abstract
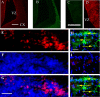
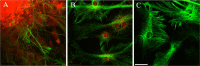
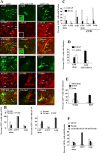
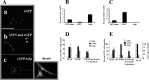
The mechanisms that regulate neural progenitor cell differentiation are primarily unknown. The transcription factor activating transcription factor 5 (ATF5) is expressed in neural progenitors of developing brain but is absent from mature astrocytes and neurons. Here, we demonstrate that ATF5 regulates the conversion of ventricular zone (VZ) and subventricular zone (SVZ) neural progenitors into astrocytes. Constitutive ATF5 expression maintains neural progenitor cell proliferation and blocks their in vitro and in vivo differentiation into astrocytes. Conversely, loss of ATF5 function promotes cell-cycle exit and allows astrocytic differentiation in vitro and in vivo. CNTF, a promoter of astrocytic differentiation, downregulates endogenous ATF5, whereas constitutively expressed ATF5 suppresses CNTF-promoted astrocyte genesis. Unexpectedly, constitutive ATF5 expression in neonatal SVZ cells both in vitro and in vivo causes them to acquire properties and anatomic distributions of VZ cells. These findings identify ATF5 as a key regulator of astrocyte formation and potentially of the VZ to SVZ transition.
Figures


References
-
- Arlotta P, Magavi SS, Macklis JD (2003) Induction of adult neurogenesis: molecular manipulation of neural precursors in situ. Ann NY Acad Sci 991: 229-236. - PubMed
-
- Bylund M, Andersson E, Novitch BG, Muhr J (2003) Vertebrate neurogenesis is counteracted by Sox1-3 activity. Nat Neurosci 6: 1162-1168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
