Sequence-specific DNA binding by the alphaNAC coactivator is required for potentiation of c-Jun-dependent transcription of the osteocalcin gene
- PMID: 15831452
- PMCID: PMC1084295
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.9.3452-3460.2005
Sequence-specific DNA binding by the alphaNAC coactivator is required for potentiation of c-Jun-dependent transcription of the osteocalcin gene
Abstract
Since the c-Jun coactivator alphaNAC was initially identified in a differential screen for genes expressed in differentiated osteoblasts, we examined whether the osteocalcin gene, a specific marker of terminal osteoblastic differentiation, could be a natural target for the coactivating function of alphaNAC. We had also previously shown that alphaNAC can specifically bind DNA in vitro, but it remained unclear whether the DNA-binding function of alphaNAC is expressed in vivo or if it is required for coactivation. We have identified an alphaNAC binding site within the murine osteocalcin gene proximal promoter region and demonstrated that recombinant alphaNAC or alphaNAC from ROS17/2.8 nuclear extracts can specifically bind this element. Using transient transfection assays, we have shown that alphaNAC specifically potentiated the c-Jun-dependent transcription of the osteocalcin promoter and that this activity specifically required the DNA-binding domain of alphaNAC. Chromatin immunoprecipitation confirmed that alphaNAC occupies its binding site on the osteocalcin promoter in living osteoblastic cells expressing osteocalcin. Inhibition of the expression of endogenous alphaNAC in osteoblastic cells by use of RNA interference provoked a decrease in osteocalcin gene transcription. Our results show that the osteocalcin gene is a target for the alphaNAC coactivating function, and we propose that alphaNAC is specifically targeted to the osteocalcin promoter through its DNA-binding activity as a means to achieve increased specificity in gene transcription.
Figures

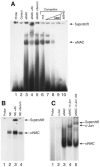
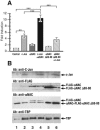


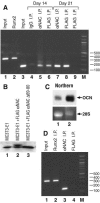

References
-
- Ait-Si-Ali, S., D. Carlisi, S. Ramirez, L. C. Upegui-Gonzalez, A. Duquet, P. Robin, B. Rudkin, A. Harel-Bellan, and D. Trouche. 1999. Phosphorylation by p44 MAP kinase/ERK1 stimulates CBP histone acetyl transferase activity in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 262:157-162. - PubMed
-
- Aslam, F., L. McCabe, B. Frenkel, A. J. van Wijnen, G. S. Stein, J. B. Lian, and J. L. Stein. 1999. AP-1 and vitamin D receptor (VDR) signaling pathways converge at the rat osteocalcin VDR element: requirement for the internal activating protein-1 site for vitamin D-mediated trans-activation. Endocrinology 140:63-70. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1993. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley and Sons, New York, N.Y.
-
- Banerjee, C., J. L. Stein, A. J. Van Wijnen, B. Frenkel, J. B. Lian, and G. S. Stein. 1996. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 responsiveness of the rat osteocalcin gene is mediated by an activator protein-1 binding site. Endocrinology 137:1991-2000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
