Dok-R mediates attenuation of epidermal growth factor-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase and Akt activation through processive recruitment of c-Src and Csk
- PMID: 15831486
- PMCID: PMC1084282
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.9.3831-3841.2005
Dok-R mediates attenuation of epidermal growth factor-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase and Akt activation through processive recruitment of c-Src and Csk
Abstract
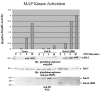
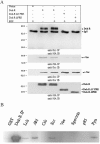
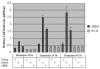
Dok-R has previously been shown to associate with the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and become tyrosine phosphorylated in response to EGF stimulation. The recruitment of Dok-R to the EGFR, which is mediated through its phosphotyrosine binding (PTB) domain, results in attenuation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation. Dok-R's ability to attenuate EGF-driven MAPK activation is independent of its ability to recruit rasGAP, a known attenuator of MAPK activity, suggesting an alternate Dok-R-mediated pathway. Herein, we have determined the structural determinants within Dok-R that are required for its ability to attenuate EGF signaling and to associate with c-Src and with the Src family kinase (SFK)-inhibitory kinase, Csk. We demonstrate that Dok-R associates constitutively with c-Src through an SH3-dependent interaction and that this association is essential to Dok-R's ability to attenuate c-Src activity and diminish MAPK and Akt/PKB activity. We further illustrate that EGF-dependent phosphorylation of Dok-R requires SFK activity and, more specifically, that SFK-dependent phosphorylation of tyrosine 402 on Dok-R facilitates the inducible recruitment of Csk. We propose that recruitment of Csk to Dok-R serves to bring Csk to c-Src and down-regulate its activity, resulting in a concomitant attenuation of MAPK and Akt/PKB activity. Furthermore, we demonstrate that Dok-R can abrogate c-Src's ability to protect the breast cancer cell line SKBR3 from anoikis and that an association with c-Src and Csk is required for this activity. Collectively these results demonstrate that Dok-R acts as an EGFR-recruited scaffolding molecule that processively assembles c-Src and Csk to attenuate signaling from the EGFR.
Figures




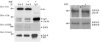


Similar articles
-
Csk-binding protein (Cbp) negatively regulates epidermal growth factor-induced cell transformation by controlling Src activation.Oncogene. 2006 Sep 7;25(40):5495-506. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209554. Epub 2006 Apr 24. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16636672
-
Bradykinin-induced p42/p44 MAPK phosphorylation and cell proliferation via Src, EGF receptors, and PI3-K/Akt in vascular smooth muscle cells.J Cell Physiol. 2005 Jun;203(3):538-46. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20250. J Cell Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15573401
-
H2O2-induced transactivation of EGF receptor requires Src and mediates ERK1/2, but not Akt, activation in renal cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004 May;286(5):F858-65. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00282.2003. Epub 2004 Feb 10. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15075181
-
Src family kinases: regulation of their activities, levels and identification of new pathways.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Jan;1784(1):56-65. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.08.012. Epub 2007 Aug 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 17905674 Review.
-
Src protein-tyrosine kinase structure, mechanism, and small molecule inhibitors.Pharmacol Res. 2015 Apr;94:9-25. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2015.01.003. Epub 2015 Feb 3. Pharmacol Res. 2015. PMID: 25662515 Review.
Cited by
-
Global phosphoproteomics reveals crosstalk between Bcr-Abl and negative feedback mechanisms controlling Src signaling.Sci Signal. 2011 Mar 29;4(166):ra18. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2001314. Sci Signal. 2011. PMID: 21447799 Free PMC article.
-
Introduction to DOK2 and its potential role in cancer.Physiol Res. 2021 Nov 29;70(5):671-685. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934710. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Physiol Res. 2021. PMID: 34505522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Migfilin interacts with Src and contributes to cell-matrix adhesion-mediated survival signaling.J Biol Chem. 2009 Dec 4;284(49):34308-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.045021. Epub 2009 Oct 15. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19833732 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Receptor Dimerization as a Novel Negative Feedback Mechanism of EGFR Signaling.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 14;10(10):e0139971. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139971. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26465157 Free PMC article.
-
CD5 signalosome coordinates antagonist TCR signals to control the generation of Treg cells induced by foreign antigens.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jun 9;117(23):12969-12979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1917182117. Epub 2020 May 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32434911 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belsches, A. P., M. D. Haskell, and S. J. Parsons. 1997. Role of c-Src tyrosine kinase in EGF-induced mitogenesis. Front. Biosci. 2:d501-d518. - PubMed
-
- Belsches-Jablonski, A. P., J. S. Biscardi, D. R. Peavy, D. A. Tice, D. A. Romney, and S. J. Parsons. 2001. Src family kinases and HER2 interactions in human breast cancer cell growth and survival. Oncogene 20:1465-1475. - PubMed
-
- Carpino, N., D. Wisniewski, A. Strife, D. Marshak, R. Kobayashi, B. Stillman, and B. Clarkson. 1997. p62(dok): a constitutively tyrosine-phosphorylated, GAP-associated protein in chronic myelogenous leukemia progenitor cells. Cell 88:197-204. - PubMed
-
- Coll, M. L., K. Rosen, V. Ladeda, and J. Filmus. 2002. Increased Bcl-xL expression mediates v-Src-induced resistance to anoikis in intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogene 21:2908-2913. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
