Thyroid hormone induces cardiac myocyte hypertrophy in a thyroid hormone receptor alpha1-specific manner that requires TAK1 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
- PMID: 15831522
- PMCID: PMC1237131
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2004-0503
Thyroid hormone induces cardiac myocyte hypertrophy in a thyroid hormone receptor alpha1-specific manner that requires TAK1 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
Abstract
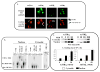
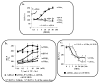
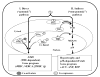
Alterations in TR [thyroid hormone (TH) receptor]1 isoform expression have been reported in models of both physiologic and pathologic cardiac hypertrophy as well as in patients with heart failure. In this report, we demonstrate that TH induces hypertrophy as a direct result of binding to the TRalpha1 isoform and, moreover, that overexpression of TRalpha1 alone is also associated with a hypertrophic phenotype, even in the absence of ligand. The mechanism of TH and TRalpha1-specific hypertrophy is novel for a nuclear hormone receptor and involves the transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase (TAK1) and p38. Mitigating TRalpha1 effects, both TRalpha2 and TRbeta1 attenuate TRalpha1-induced myocardial growth and gene expression by diminishing TAK1 and p38 activities, respectively. These findings refine our previous observations on TR expression in the hypertrophied and failing heart and suggest that manipulation of thyroid hormone signaling in an isoform-specific manner may be a relevant therapeutic target for altering the pathologic myocardial program.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Thyroid hormone receptor alpha 1: a switch to cardiac cell "metamorphosis"?J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008 Jun;59(2):253-69. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18622044
-
Adeno-associated virus-mediated expression of thyroid hormone receptor isoforms-alpha1 and -beta1 improves contractile function in pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy.Endocrinology. 2007 Jun;148(6):2870-7. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0009. Epub 2007 Feb 22. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17317766
-
Transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta)-induced apoptosis of prostate cancer cells involves Smad7-dependent activation of p38 by TGF-beta-activated kinase 1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Feb;14(2):529-44. doi: 10.1091/mbc.02-03-0037. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12589052 Free PMC article.
-
Promotion by thyroid hormone of cytoplasm-to-nucleus shuttling of thyroid hormone receptors.Steroids. 2008 Oct;73(9-10):1013-7. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2007.12.030. Epub 2008 Jan 16. Steroids. 2008. PMID: 18329679 Review.
-
The emerging role of TRα1 in cardiac repair: potential therapeutic implications.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:481482. doi: 10.1155/2014/481482. Epub 2014 Feb 9. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014. PMID: 24683435 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Thyroid hormone receptor function in maturing ovine cardiomyocytes.J Physiol. 2019 Apr;597(8):2163-2176. doi: 10.1113/JP276874. Epub 2019 Mar 20. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30770568 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial and energetic cardiac phenotype in hypothyroid rat. Relevance to heart failure.Pflugers Arch. 2007 Dec;455(3):431-42. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0307-2. Epub 2007 Jul 19. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17638011 Free PMC article.
-
Rebuilding the post-infarcted myocardium by activating 'physiologic' hypertrophic signaling pathways: the thyroid hormone paradigm.Heart Fail Rev. 2010 Mar;15(2):143-54. doi: 10.1007/s10741-008-9111-0. Epub 2008 Sep 5. Heart Fail Rev. 2010. PMID: 18773293 Review.
-
Thyroid hormone and cardiac disease: from basic concepts to clinical application.J Thyroid Res. 2011;2011:958626. doi: 10.4061/2011/958626. Epub 2011 Jun 19. J Thyroid Res. 2011. PMID: 21765997 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine Influence on Cardiac Metabolism in Development and Regeneration.Endocrinology. 2021 Sep 1;162(9):bqab081. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqab081. Endocrinology. 2021. PMID: 33880553 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hamilton MA, Stevenson LW, Luu M, Walden JA. Altered thyroid hormone metabolism in advanced heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990;16:91–5. - PubMed
-
- Opasich C, Pacini F, Ambrosino N, et al. Sick euthyroid syndrome in patients with moderate-to-severe chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 1996;17:1860–6. - PubMed
-
- Fruhwald FM, Ramschak-Schwarzer S, Pichler B, et al. Subclinical thyroid disorders in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Cardiology. 1997;88:156–9. - PubMed
-
- Ascheim DD, Hryniewicz K. Thyroid hormone metabolism in patients with congestive heart failure: the low triiodothyronine state. Thyroid. 2002;12:511–5. - PubMed
-
- Moruzzi P, Doria E, Agostoni PG, Capacchione V, Sganzerla P. Usefulness of L-thyroxine to improve cardiac and exercise performance in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 1994;73:374–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

