Single copy shRNA configuration for ubiquitous gene knockdown in mice
- PMID: 15831785
- PMCID: PMC1079974
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gni065
Single copy shRNA configuration for ubiquitous gene knockdown in mice
Abstract
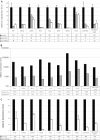
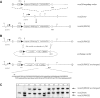
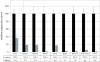
RNA interference through the expression of small hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules has become a very promising tool in reverse mouse genetics as it may allow inexpensive and rapid gene function analysis in vivo. However, the prerequisites for ubiquitous and reproducible shRNA expression are not well defined. Here we show that a single copy shRNA-transgene can mediate body-wide gene silencing in mice when inserted in a defined locus of the genome. The most commonly used promoters for shRNA expression, H1 and U6, showed a comparably broad activity in this configuration. Taken together, the results define a novel approach for efficient interference with expression of defined genes in vivo. Moreover, we provide a rapid strategy for the production of gene knockdown mice combining recombinase mediated cassette exchange and tetraploid blastocyst complementation approaches.
Figures


References
-
- Fire A., Xu S., Montgomery M.K., Kostas S.A., Driver S.E., Mello C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp T.R., Bernards R., Agami R. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science. 2002;296:550–553. - PubMed
-
- Tuschl T. Expanding small RNA interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002;20:446–448. - PubMed
-
- Kunath T., Gish G., Lickert H., Jones N., Pawson T., Rossant J. Transgenic RNA interference in ES cell-derived embryos recapitulates a genetic null phenotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003;21:559–561. - PubMed
-
- Rubinson D.A., Dillon C.P., Kwiatkowski A.V., Sievers C., Yang L., Kopinja J., Rooney D.L., Ihrig M.M., McManus M.T., Gertler F.B., et al. A lentivirus-based system to functionally silence genes in primary mammalian cells, stem cells and transgenic mice by RNA interference. Nature Genet. 2003;33:401–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

