TFIIIB subunit Bdp1p is required for periodic integration of the Ty1 retrotransposon and targeting of Isw2p to S. cerevisiae tDNAs
- PMID: 15833918
- PMCID: PMC1080134
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1299105
TFIIIB subunit Bdp1p is required for periodic integration of the Ty1 retrotransposon and targeting of Isw2p to S. cerevisiae tDNAs
Abstract
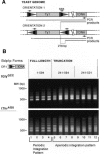
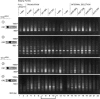
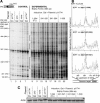
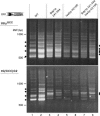
Retrotransposons are RNA elements that reverse transcribe their RNA genomes and make a cDNA copy that is inserted back into a new genomic location by the element-encoded integrase protein. Ty1 is a long terminal repeat (LTR) retrotransposon in Saccharomyces cerevisiae that inserts into an approximately 700-bp integration window upstream of tRNA genes with a periodicity of approximately 80 bp. ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling by Isw2 upstream of tRNA genes leads to changes in chromatin structure and Ty1 integration site selection. We show that the N terminus of Bdp1p, a component of the RNA polymerase III transcription factor TFIIIB, is required for periodic integration of Ty1 into the integration window. Deletion of the Bdp1p N terminus and mutation of ISW2 result in similar disruption of nucleosome positioning upstream of some tRNA genes, and the N-terminal domain of Bdp1p is required for targeting of Isw2 complex to tRNA genes. This study provides the first example for recruitment of an ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling factor by a general transcription factor in vivo.
Figures


References
-
- Alen C., Kent, N.A., Jones, H.S., O'Sullivan, J., Aranda, A., and Proudfoot, N.J. 2002. A role for chromatin remodeling in transcriptional termination by RNA polymerase II. Mol. Cell 10: 1441-1452. - PubMed
-
- Beck P., Dingermann, T., and Winckler, T. 2002. Transfer RNA gene-targeted retrotransposition of Dictyostelium TRE5-A into a chromosomal UMP synthase gene trap. J. Mol. Biol. 318: 273-285. - PubMed
-
- Boeke J.D. and Devine, S.E. 1998. Yeast retrotransposons: Finding a nice quiet neighborhood. Cell 93: 1087-1089. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
