Specific and nonspecific hybridization of oligonucleotide probes on microarrays
- PMID: 15834006
- PMCID: PMC1366534
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.055343
Specific and nonspecific hybridization of oligonucleotide probes on microarrays
Abstract
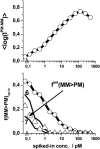
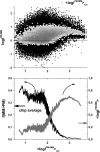
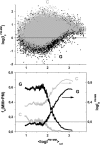
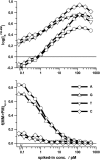
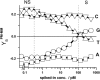
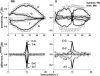
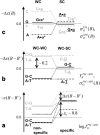
Gene expression analysis by means of microarrays is based on the sequence-specific binding of RNA to DNA oligonucleotide probes and its measurement using fluorescent labels. The binding of RNA fragments involving sequences other than the intended target is problematic because it adds a chemical background to the signal, which is not related to the expression degree of the target gene. The article presents a molecular signature of specific and nonspecific hybridization with potential consequences for gene expression analysis. We analyzed the signal intensities of perfect match (PM) and mismatch (MM) probes of GeneChip microarrays to specify the effect of specific and nonspecific hybridization. We found that these events give rise to different relations between the PM and MM intensities as function of the middle base of the PM, namely a triplet-like (C > G approximately T > A > 0) and a duplet-like (C approximately T > 0 > G approximately A) pattern of the PM-MM log-intensity difference upon binding of specific and nonspecific RNA fragments, respectively. The systematic behavior of the intensity difference can be rationalized on the level of basepairings of DNA/RNA oligonucleotide duplexes in the middle of the probe sequence. Nonspecific binding is characterized by the reversal of the central Watson-Crick (WC) pairing for each PM/MM probe pair, whereas specific binding refers to the combination of a WC and a self-complementary (SC) pairing in PM and MM probes, respectively. The Gibbs free energy contribution of WC pairs to duplex stability is asymmetric for purines and pyrimidines of the PM and decreases according to C > G approximately T > A. SC pairings on the average only weakly contribute to duplex stability. The intensity of complementary MM introduces a systematic source of variation which decreases the precision of expression measures based on the MM intensities.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Base pair interactions and hybridization isotherms of matched and mismatched oligonucleotide probes on microarrays.Langmuir. 2005 Sep 27;21(20):9287-302. doi: 10.1021/la051231s. Langmuir. 2005. PMID: 16171364
-
Tests of rRNA hybridization to microarrays suggest that hybridization characteristics of oligonucleotide probes for species discrimination cannot be predicted.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 May 17;34(9):e66. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl133. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16707658 Free PMC article.
-
Nonspecific hybridization scaling of microarray expression estimates: a physicochemical approach for chip-to-chip normalization.J Phys Chem B. 2009 Mar 5;113(9):2874-95. doi: 10.1021/jp808118m. J Phys Chem B. 2009. PMID: 19708217
-
Mismatch formation in solution and on DNA microarrays: how modified nucleosides can overcome shortcomings of imperfect hybridization caused by oligonucleotide composition and base pairing.Mol Biosyst. 2008 Mar;4(3):232-45. doi: 10.1039/b713259j. Epub 2008 Feb 4. Mol Biosyst. 2008. PMID: 18437266 Review.
-
DNA probes: applications of the principles of nucleic acid hybridization.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;26(3-4):227-59. doi: 10.3109/10409239109114069. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1991. PMID: 1718662 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between gene expression and observed intensities in DNA microarrays--a modeling study.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 May 24;34(9):e70. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl122. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16723429 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous Detection of Nine Key Bacterial Respiratory Pathogens Using Luminex xTAG® Technology.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017 Feb 23;14(3):223. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14030223. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28241513 Free PMC article.
-
Temperature effects on DNA chip experiments from surface plasmon resonance imaging: isotherms and melting curves.Biophys J. 2007 Feb 1;92(3):935-46. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.097790. Epub 2006 Nov 3. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17085497 Free PMC article.
-
G-stack modulated probe intensities on expression arrays - sequence corrections and signal calibration.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Apr 27;11:207. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-207. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20423484 Free PMC article.
-
Washing scaling of GeneChip microarray expression.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 May 28;11:291. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-291. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20509934 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lipshutz, R. J., S. P. A. Fodor, T. R. Gingeras, and D. J. Lockhart. 1999. High density synthetic oligonucleotide arrays. Nat. Genet. 21:20–24. - PubMed
-
- Affymetrix. 2001. Affymetrix Microarray Suite 5.0. In User Guide. Affymetrix, Inc., Santa Clara, CA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

