Dissection of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis pathology in 1-month-abstinent alcohol-dependent men, part 1: adrenocortical and pituitary glucocorticoid responsiveness
- PMID: 15834216
- PMCID: PMC2584970
- DOI: 10.1097/01.alc.0000158940.05529.0a
Dissection of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis pathology in 1-month-abstinent alcohol-dependent men, part 1: adrenocortical and pituitary glucocorticoid responsiveness
Abstract
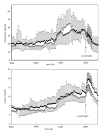
Background: Long-term ingestion of alcohol produces marked alterations in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity. The authors engaged in a series of studies to determine the distinct role of the hypothalamus and the pituitary and adrenal glands in the disturbances observed in abstinent alcohol-dependent subjects. In this first of a two-part study, the authors report on (1) the basal secretory profile of corticotropin and cortisol from 2000 to 0800 hrs, (2) adrenocortical sensitivity in both the presence and absence of endogenous pituitary activation, and (3) pituitary glucocorticoid sensitivity to dexamethasone.
Methods: Eleven male, 4 to 6 weeks abstinent, alcohol-only-dependent subjects and 10 age-matched male healthy controls were studied. Basal circulating concentrations of corticotropin and cortisol were obtained from 2000 to 0800 hr. A submaximal dose of cosyntropin (0.01 microg/kg), a corticotropin analogue was then administered to assess adrenocortical sensitivity. In a separate session, cosyntropin was administered following high-dose dexamethasone (8 mg iv) to assess adrenocortical sensitivity in the relative absence of endogenous corticotropin. In addition, the corticotropin response to dexamethasone was measured to determine pituitary glucocorticoid responsiveness.
Results: Cortisol, but not corticotropin, pulse amplitude (p < 0.05) and mean concentration (p= 0.05) was significantly lower in alcohol-dependent subjects compared with controls. The cortisol response to cosyntropin was lower in alcohol-dependent subjects following endogenous corticotropin suppression by high-dose dexamethasone (p <0.04) but not without dexamethasone pretreatment. Mean corticotropin (p <0.004) and cortisol (p <0.05) concentrations in response to dexamethasone were attenuated in the patients compared to controls. Basal concentrations of 11-deoxycortisol, the precursor to cortisol, were also decreased in alcohol-dependent subjects (p <0.05).
Conclusion: Attenuated basal and stimulated adrenocortical concentrations in abstinent alcohol-dependent men are coupled with a nonhomeostatic increase in pituitary glucocorticoid inhibition. A decrease in stress-axis responsivity in alcohol dependence may have implications for treatment outcome.
Figures

References
-
- Adinoff B, Martin PR, Bone GHA, Eckardt MJ, Roehrich L, George DT, Moss HB, Eskay R, Linnoila M, Gold PW. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis functioning and cerebrospinal fluid corticotropin releasing hormone and corticotropin levels in alcoholics after recent and long-term abstinence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1990;47:325–330. - PubMed
-
- Adinoff B, Risher-Flowers D, De Jong J, Ravitz B, Bone GHA, Nutt DJ, Roehrich L, Martin PR, Linnoila M. Disturbances of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis functioning during ethanol withdrawal in six men. Am J Psychiatry. 1991;148:1023–1025. - PubMed
-
- Adinoff B, Ruether K, Krebaum S, Iranmanesh A, Williams MJ. Increased salivary cortisol concentrations during chronic alcohol intoxication in a naturalistic clinical sample of men. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2003;27:1420–1427. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4. American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC: 1994.
-
- Anthenelli RM, Maxwell RA, Geracioti TDJ, Hauger R. Stress hormone dysregulation at rest and after serotonergic stimulation among alcohol-dependent men with extended abstinence and controls. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2001;25:692–703. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

