Dissection of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis pathology in 1-month-abstinent alcohol-dependent men, part 2: response to ovine corticotropin-releasing factor and naloxone
- PMID: 15834217
- PMCID: PMC1906932
- DOI: 10.1097/01.alc.0000158939.25531.ee
Dissection of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis pathology in 1-month-abstinent alcohol-dependent men, part 2: response to ovine corticotropin-releasing factor and naloxone
Abstract
Background: Pituitary and adrenal responsiveness is suppressed in abstinent alcohol-dependent individuals. To clarify the specific organizational disruption in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal functioning during early abstinence, the authors separately assessed each level of the stress-response axis. In this second of a two-part study, ovine corticotropin-releasing factor (oCRH) was used to stimulate the pituitary corticotrophs, and naloxone was used to activate the axis at the hypothalamic level. In addition, pulsatile characteristics of corticotropin and cortisol were assessed over a 12-hr period (0800 to 2000 hr).
Methods: Eleven abstinent alcohol-dependent men and 10 healthy comparison participants were assessed. All participants were between the ages of 30 and 50 years, and alcohol-dependent patients were abstinent from 4 to 6 weeks. Basal concentrations of corticotropin and cortisol were obtained every 10 min from 0800 to 2000 hr and subjected to pulsatile analysis. Plasma corticotropin and cortisol concentrations were then obtained every 5 to 10 min after low-dose, intravenously administered doses of oCRH (0.4 microg/kg) or naloxone (0.125 mg/kg). Medications were administered at 2000 hr and the two challenge studies were separated by 48 hr.
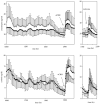
Results: Pulsatile analysis revealed that the mean corticotropin amplitude was increased in alcohol-dependent patients relative to controls (p <0.05). Other pulsatile characteristics of corticotropin and all cortisol pulsatile measures were not significantly different between the two groups. The integrated cortisol response to oCRH was significantly lower in alcohol-dependent patients compared with controls (p <0.01), but the integrated corticotropin response was not significantly different. In contrast, neither the corticotropin nor the cortisol response to naloxone was significantly different between groups.
Conclusions: Adrenocorticoid hyposensitivity persists after oCRH infusion for at least 1 month after cessation of drinking, whereas hyporesponsiveness of the pituitary corticotrophs to CRH seems to resolve with continued abstinence. The authors suggest that adrenocortical hyporesponsiveness during prolonged abstinence may impact relapse risk.
Figures
References
-
- Adinoff B, Martin PR, Bone GHA, Eckardt MJ, Roehrich L, George DT, Moss HB, Eskay R, Linnoila M, Gold PW. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis functioning and cerebrospinal fluid corticotropin releasing hormone and corticotropin levels in alcoholics after recent and long-term abstinence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1990;47:325–330. - PubMed
-
- Adinoff B, Risher-Flowers D, De Jong J, Ravitz B, Bone GHA, Nutt DJ, Roehrich L, Martin PR, Linnoila M. Disturbances of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis functioning during ethanol withdrawal in six men. Am J Psychiatry. 1991;148:1023–1025. - PubMed
-
- Adinoff B, Ruether K, Krebaum S, Iranmanesh A, Williams MJ. Increased salivary cortisol concentrations during chronic alcohol intoxication in a naturalistic clinical sample of men. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2003;27:1420–1427. - PubMed

