Use of an educational computer program before genetic counseling for breast cancer susceptibility: effects on duration and content of counseling sessions
- PMID: 15834239
- PMCID: PMC1201432
- DOI: 10.1097/01.gim.0000159905.13125.86
Use of an educational computer program before genetic counseling for breast cancer susceptibility: effects on duration and content of counseling sessions
Abstract
Purpose: Patients seeking genetic testing for inherited breast cancer risk are typically educated by genetic counselors; however, the growing demand for cancer genetic testing will likely exceed the availability of counselors trained in this area. We compared the effectiveness of counseling alone versus counseling preceded by use of a computer-based decision aid among women referred to genetic counseling for a family or personal history of breast cancer.
Methods: We developed and evaluated an interactive computer program that educates women about breast cancer, heredity, and genetic testing. Between May 2000 and September 2002, women at six study sites were randomized into either: Counselor Group (n = 105), who received standard genetic counseling, or Computer Group (n = 106), who used the interactive computer program before counseling. Clients and counselors both evaluated the effectiveness of counseling sessions, and counselors completed additional measures for the Computer Group. Counselors also recorded the duration of each session.
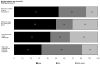
Results: Baseline characteristics did not differ significantly between groups. Participants and counselors both rated the counseling sessions as highly effective, whether or not the sessions were preceded by computer use. Computer use resulted in significantly shorter counseling sessions among women at low risk for carrying BRCA1/2 mutations. In approximately half of the sessions preceded by clients' computer use, counselors indicated that clients' use of the computer program affected the way they used the time, shifting the focus away from basic education toward personal risk and decision-making.
Conclusion: This study shows that the interactive computer program "Breast Cancer Risk and Genetic Testing" is a valuable adjunct to genetic counseling. Its use before counseling can shorten counseling sessions and allow counselors to focus more on the clients' individual risks and specific psychological concerns. As the demand for counseling services increases, a program such as this can play a valuable role in enhancing counseling efficiency.
Figures
References
-
- International Consortium Completes Human Genome Project: All goals achieved; New vision for genome research unveiled, 2004. National Human Genome Research Institute, National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services, and Office of Science U.S. Department of Energy; 2003.
-
- Eng C, Hampel H, de la Chapelle A. Genetic testing for cancer predisposition. Annu Rev Med. 2001;52:371–400. - PubMed
-
- Collins F. Shattuck lecture: Medical and societal consequences of the Human Genome Project. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:28–37. - PubMed
-
- Petersen GM. Genetic testing. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2000;14:939–52. - PubMed
-
- Biesecker BB. Future directions in genetic counseling: Practical and ethical considerations. Kennedy Institute of Ethics Journal. 1998;8:145–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous