Deletion of presynaptic adenosine A1 receptors impairs the recovery of synaptic transmission after hypoxia
- PMID: 15837119
- PMCID: PMC2259447
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.12.009
Deletion of presynaptic adenosine A1 receptors impairs the recovery of synaptic transmission after hypoxia
Abstract
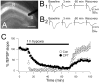
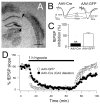
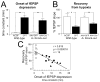
Adenosine protects neurons during hypoxia by inhibiting excitatory synaptic transmission and preventing NMDA receptor activation. Using an adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector containing Cre recombinase, we have focally deleted adenosine A(1) receptors in specific hippocampal regions of adult mice. Recently, we found that deletion of A(1) receptors in the CA1 area blocks the postsynaptic responses to adenosine in CA1 pyramidal neurons, and deletion of A(1) receptors in CA3 neurons abolishes the presynaptic effects of adenosine on the Schaffer collateral input [J Neurosci 23 (2003) 5762]. In the current study, we used this technique to delete A(1) receptors focally from CA3 neurons to investigate whether presynaptic A(1) receptors protect synaptic transmission from hypoxia. We studied the effects of prolonged (1 h) hypoxia on the evoked field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs) in the CA1 region using in vitro slices. Focal deletion of the presynaptic A(1) receptors on the Schaffer collateral input slowed the depression of the fEPSPs in response to hypoxia and impaired the recovery of the fEPSPs after hypoxia. Delayed responses to hypoxia linearly correlated with impaired recovery. These findings provide direct evidence that the neuroprotective role of adenosine during hypoxia depends on the rapid inhibition of synaptic transmission by the activation of presynaptic A(1) receptors.
Figures
References
-
- Boening JA, Kass IS, Cottrell JE, Chambers G. The effect of blocking sodium influx on anoxic damage in the rat hippocampal slice. Neuroscience. 1989;33:263–268. - PubMed
-
- Coelho JE, de Mendonca A, Ribeiro JA. Presynaptic inhibitory receptors mediate the depression of synaptic transmission upon hypoxia in rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 2000;869:158–165. - PubMed
-
- Costenla AR, De Mendonca A, Sebastiao A, Ribeiro JA. An adenosine analogue inhibits NMDA receptor-mediated responses in bipolar cells of the rat retina. Exp Eye Res. 1999;68:367–370. - PubMed
-
- de Mendonca A, Ribeiro JA. Contribution of metabotropic glutamate receptors to the depression of excitatory postsynaptic potentials during hypoxia. Neuroreport. 1997;8:3667–3671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

