Functional characterization of WaaL, a ligase associated with linking O-antigen polysaccharide to the core of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 15838026
- PMCID: PMC1082828
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.9.3002-3012.2005
Functional characterization of WaaL, a ligase associated with linking O-antigen polysaccharide to the core of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
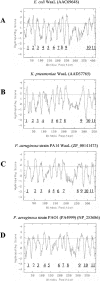
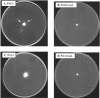
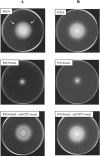
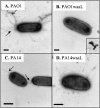
The O antigen of Pseudomonas aeruginosa B-band lipopolysaccharide is synthesized by assembling O-antigen-repeat units at the cytoplasmic face of the inner membrane by nonprocessive glycosyltransferases, followed by polymerization on the periplasmic face. The completed chains are covalently attached to lipid A core by the O-antigen ligase, WaaL. In P. aeruginosa the process of ligating these O-antigen molecules to lipid A core is not clearly defined, and an O-antigen ligase has not been identified until this study. Using the sequence of waaL from Salmonella enterica as a template in a BLAST search, a putative waaL gene was identified in the P. aeruginosa genome. The candidate gene was amplified and cloned, and a chromosomal knockout of PAO1 waaL was generated. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from this mutant is devoid of B-band O-polysaccharides and semirough (SR-LPS, or core-plus-one O-antigen). The mutant PAO1waaL is also deficient in the production of A-band polysaccharide, a homopolymer of D-rhamnose. Complementation of the mutant with pPAJL4 containing waaL restored the production of both A-band and B-band O antigens as well as SR-LPS, indicating that the knockout was nonpolar and waaL is required for the attachment of O-antigen repeat units to the core. Mutation of waaL in PAO1 and PA14, respectively, could be complemented with waaL from either strain to restore wild-type LPS production. The waaL mutation also drastically affected the swimming and twitching motilities of the bacteria. These results demonstrate that waaL in P. aeruginosa encodes a functional O-antigen ligase that is important for cell wall integrity and motility of the bacteria.
Figures


References
-
- Abeyrathne, P. D., and R. N. Nazar. 2000. Plasmid-enhanced strategy for PCR-mediated mutagenesis with difficult DNA templates. BioTechniques 29:1172-1176. - PubMed
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F., R. Brent, R. Kingston, D. Moore, J. seidman, J. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1997. Preparation of genomic DNA from bacteria. In K. Struhl (ed.), Short protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley and Sons, New York, N.Y.
-
- Bengoechea, J. A., H. Najdenski, and M. Skurnik. 2004. Lipopolysaccharide O antigen status of Yersinia enterocolitica O:8 is essential for virulence and absence of O antigen affects the expression of other Yersinia virulence factors. Mol. Microbiol. 52:451-469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

