Inactivation of a predicted leader peptidase prevents photoautotrophic growth of Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803
- PMID: 15838034
- PMCID: PMC1082817
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.9.3071-3078.2005
Inactivation of a predicted leader peptidase prevents photoautotrophic growth of Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803
Abstract
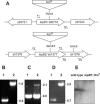
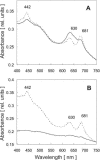
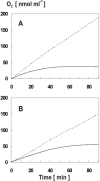
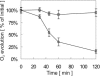
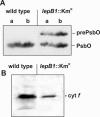
To establish the role of the two putative type I leader peptidases (LepB1 and LepB2) encoded in the genome of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803, we generated independent knockout mutants for both genes by introducing kanamycin resistance cassettes into the two open reading frames (sll0716 [lepB1] and slr1377 [lepB2], respectively). Although the insertion was successful in both instances, it was not possible to select homozygous mutant cells for lepB2, suggesting that the function of this gene is essential for cell viability. In contrast, LepB1 is apparently essential only for photoautotrophic growth, because homozygous lepB1::Km(r) cells could be propagated under heterotrophic conditions. They were even capable to some extent of photosynthetic oxygen evolution. However, the photosynthetic activity decreased gradually with extended incubation in the light and was particularly affected by high light intensities. Both features were indicative of photooxidative damage, which was probably caused by inefficient replacement of damaged components of the photosynthetic machinery due to the lack of a leader peptidase removing the signal peptides from photosynthetic precursor proteins. Indeed, processing of the PsbO precursor polypeptide to the corresponding mature protein was significantly affected in the mutant, and reduced amounts of other proteins that are synthesized as precursors with signal peptides accumulated in the cells. These results strongly suggest that LepB1 is important for removal of the signal peptides after membrane transport of the components of the photosynthetic machinery, which in turn is a prerequisite for the biogenesis of a functional photosynthetic electron transport chain.
Figures

References
-
- Barbrook, A. C., J. C. L. Packer, and C. J. Howe. 1993. Components of the protein translocation machinery in the thermophilic cyanobacterium Phormidium laminosum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 197:874-877. - PubMed
-
- Berghöfer, J., and R. B. Klösgen. 1999. Two distinct translocation intermediates can be distinguished during protein transport by the TAT (delta pH) pathway across the thylakoid membrane. FEBS Lett. 460:328-332. - PubMed
-
- Bonnemain, C., C. Raynaud, H. Reglier-Poupet, I. Dubail, C. Frehel, M. A. Lety, P. Berche, and A. Charbit. 2004. Differential roles of multiple signal peptidases in the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Mol. Microbiol. 51:1251-1266. - PubMed
-
- Burnap, R. L., and L. A. Sherman. 1991. Deletion mutagenesis in Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 indicates that the Mn-stabilizing protein of photosystem II is not essential for O2 evolution. Biochemistry 30:440-446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

