Random insertional mutagenesis of Leptospira interrogans, the agent of leptospirosis, using a mariner transposon
- PMID: 15838053
- PMCID: PMC1082815
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.9.3255-3258.2005
Random insertional mutagenesis of Leptospira interrogans, the agent of leptospirosis, using a mariner transposon
Abstract
The recent availability of the complete genome sequences of Leptospira interrogans, the agent of leptospirosis, has allowed the identification of several putative virulence factors. However, to our knowledge, attempts to carry out gene transfer in pathogenic Leptospira spp. have failed so far. In this study, we show that the Himar1 mariner transposon permits random mutagenesis in the pathogen L. interrogans. We have identified genes that have been interrupted by Himar1 insertion in 35 L. interrogans mutants. This approach of transposon mutagenesis will be useful for understanding the spirochetal physiology and the pathogenic mechanisms of Leptospira, which remain largely unknown.
Figures
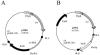

References
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Bauby, H., I. Saint Girons, and M. Picardeau. 2003. Construction and complementation of the first auxotrophic mutant in the spirochaete Leptospira meyeri. Microbiology 149:689-693. - PubMed
-
- Cashel, M., D. R. Gentry, V. J. Hernandez, and D. Vinella. 1996. The stress response, p. 1458-1496. In F. C. Neidhart, R. Curtiss III, J. L. Ingraham, E. C. C. Lin, K. B. Low, B. Magasanik, W. S. Reznikoff, M. Riley, M. Schaechter, and H. E. Umbarger (ed.), Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology. ASM Press, Washington, D.C.
-
- Chiang, S. L., and E. J. Rubin. 2002. Construction of a mariner-based transposon for epitope-tagging and genomic targeting. Gene 296:179-185. - PubMed
-
- Ellinghausen, H. C., and W. G. McCullough. 1965.. Nutrition of Leptospira pomona and growth of 13 other serotypes: fractionation of oleic albumin complex and a medium of bovine albumin and polysorbate 80. Am. J. Vet. Res. 26:45-51. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

