Buruli ulcer (M. ulcerans infection): new insights, new hope for disease control
- PMID: 15839744
- PMCID: PMC1087202
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0020108
Buruli ulcer (M. ulcerans infection): new insights, new hope for disease control
Erratum in
- PLoS Med. 2005 May;2(5):e173
Abstract
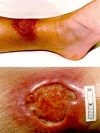
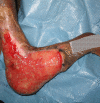
Buruli ulcer is a disease of skin and soft tissue caused by Mycobacterium ulcerans. It can leave affected people scarred and disabled. What are the prospects for disease control?
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- MacCallum P, Tolhurst JC, Buckle G, Sissons HA. A new mycobacterial infection in man. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1948;60:93–122. - PubMed
-
- Meyers WM. Mycobacterial infections of the skin. In: Seifert G, editor. Tropical dermatology. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 1994.
-
- Smith JH. Epidemiologic observations on cases of Buruli ulcer seen in a hospital in the Lower Congo. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1970;19:657–663. - PubMed
-
- Epidemiology of Mycobacterium ulcerans infection (Buruli ulcer) at Kinyara, Uganda. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1971;65:763–775. - PubMed
-
- Oluwasanmi JO, Solankee TF, Olurin EO, Itayemi SO, Alabi GO, et al. Mycobacterium ulcerans (Buruli) skin ulceration in Nigeria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976;25:122–128. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

