Amphotropic murine leukaemia virus envelope protein is associated with cholesterol-rich microdomains
- PMID: 15840168
- PMCID: PMC1087893
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-2-36
Amphotropic murine leukaemia virus envelope protein is associated with cholesterol-rich microdomains
Abstract
Background: Cholesterol-rich microdomains like lipid rafts were recently identified as regions within the plasma membrane, which play an important role in the assembly and budding of different viruses, e.g., measles virus and human immunodeficiency virus. For these viruses association of newly synthesized viral proteins with lipid rafts has been shown.
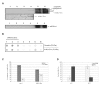
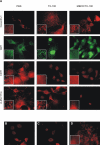
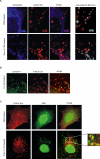
Results: Here we provide evidence for the association of the envelope protein (Env) of the 4070A isolate of amphotropic murine leukaemia virus (A-MLV) with lipid rafts. Using density gradient centrifugation and immunocytochemical analyses, we show that Env co-localizes with cholesterol, ganglioside GM1 and caveolin-1 in these specific regions of the plasma membrane.
Conclusions: These results show that a large amount of A-MLV Env is associated with lipid rafts and suggest that cholesterol-rich microdomains are used as portals for the exit of A-MLV.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amphotropic murine leukemia virus is preferentially attached to cholesterol-rich microdomains after binding to mouse fibroblasts.Virol J. 2006 Apr 2;3:21. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-3-21. Virol J. 2006. PMID: 16579862 Free PMC article.
-
Caveola-dependent endocytic entry of amphotropic murine leukemia virus.J Virol. 2005 Aug;79(16):10776-87. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.16.10776-10787.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16051869 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of R peptide of murine leukemia virus envelope glycoproteins in syncytium formation and entry.Arch Virol. 2007;152(12):2169-82. doi: 10.1007/s00705-007-1054-6. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Arch Virol. 2007. PMID: 17851730
-
Modulation of entry of enveloped viruses by cholesterol and sphingolipids (Review).Mol Membr Biol. 2003 Jul-Sep;20(3):243-54. doi: 10.1080/0968768031000104944. Mol Membr Biol. 2003. PMID: 12893532 Review.
-
Antibodies against heat shock proteins and cholesterol in HIV infection.Mol Immunol. 2005 Jan;42(1):79-85. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2004.07.003. Mol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15488946 Review.
Cited by
-
Cholesterol depletion inactivates XMRV and leads to viral envelope protein release from virions: evidence for role of cholesterol in XMRV infection.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e48013. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048013. Epub 2012 Oct 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23110160 Free PMC article.
-
Arenavirus entry occurs through a cholesterol-dependent, non-caveolar, clathrin-mediated endocytic mechanism.Virology. 2007 Dec 5;369(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.07.014. Epub 2007 Aug 14. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17698159 Free PMC article.
-
Lipids and membrane microdomains in HIV-1 replication.Virus Res. 2009 Aug;143(2):162-76. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2009.04.007. Epub 2009 Apr 19. Virus Res. 2009. PMID: 19383519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caveolin-1 interacts with the Gag precursor of murine leukaemia virus and modulates virus production.Virol J. 2006 Sep 6;3:73. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-3-73. Virol J. 2006. PMID: 16956408 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of critical serine residues in HIV-1 matrix result in an envelope incorporation defect which can be rescued by truncation of the gp41 cytoplasmic tail.Virology. 2009 Feb 5;384(1):233-41. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.10.047. Epub 2008 Dec 6. Virology. 2009. PMID: 19059618 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

