Adipocyte-derived collagen VI affects early mammary tumor progression in vivo, demonstrating a critical interaction in the tumor/stroma microenvironment
- PMID: 15841211
- PMCID: PMC1077173
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI23424
Adipocyte-derived collagen VI affects early mammary tumor progression in vivo, demonstrating a critical interaction in the tumor/stroma microenvironment
Abstract
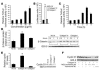
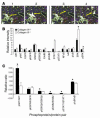
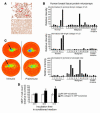
The interactions of transformed cells with the surrounding stromal cells are of importance for tumor progression and metastasis. The relevance of adipocyte-derived factors to breast cancer cell survival and growth is well established. However, it remains unknown which specific adipocyte-derived factors are most critical in this process. Collagen VI is abundantly expressed in adipocytes. Collagen(-/-) mice in the background of the mouse mammary tumor virus/polyoma virus middle T oncogene (MMTV-PyMT) mammary cancer model demonstrate dramatically reduced rates of early hyperplasia and primary tumor growth. Collagen VI promotes its growth-stimulatory and pro-survival effects in part by signaling through the NG2/chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan receptor expressed on the surface of malignant ductal epithelial cells to sequentially activate Akt and beta-catenin and stabilize cyclin D1. Levels of the carboxyterminal domain of collagen VIalpha3, a proteolytic product of the full-length molecule, are dramatically upregulated in murine and human breast cancer lesions. The same fragment exerts potent growth-stimulatory effects on MCF-7 cells in vitro. Therefore, adipocytes play a vital role in defining the ECM environment for normal and tumor-derived ductal epithelial cells and contribute significantly to tumor growth at early stages through secretion and processing of collagen VI.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Adipocyte-secreted factors synergistically promote mammary tumorigenesis through induction of anti-apoptotic transcriptional programs and proto-oncogene stabilization.Oncogene. 2003 Sep 25;22(41):6408-23. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206737. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 14508521
-
Adipocyte-derived endotrophin promotes malignant tumor progression.J Clin Invest. 2012 Nov;122(11):4243-56. doi: 10.1172/JCI63930. Epub 2012 Oct 8. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 23041627 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 gene disruption promotes mammary tumorigenesis and dramatically enhances lung metastasis in vivo. Role of Cav-1 in cell invasiveness and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-2/9) secretion.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 3;279(49):51630-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409214200. Epub 2004 Sep 7. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15355971
-
Beta-catenin and Tcfs in mammary development and cancer.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2003 Apr;8(2):145-58. doi: 10.1023/a:1025944723047. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2003. PMID: 14635791 Review.
-
Collagen VI in cancer and its biological mechanisms.Trends Mol Med. 2013 Jul;19(7):410-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2013.04.001. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Trends Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23639582 Review.
Cited by
-
Adipocytes cause leukemia cell resistance to daunorubicin via oxidative stress response.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 8;7(45):73147-73159. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12246. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27705905 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix Metalloprotease Generated Fragments of Type VI Collagen Have Serum Biomarker Potential in Cancer - A Proof of Concept Study.Transl Oncol. 2019 May;12(5):693-698. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2019.02.004. Epub 2019 Mar 9. Transl Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30856553 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose Stroma Accelerates the Invasion and Escape of Human Breast Cancer Cells from an Engineered Microtumor.Cell Mol Bioeng. 2021 Aug 24;15(1):15-29. doi: 10.1007/s12195-021-00697-6. eCollection 2022 Feb. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2021. PMID: 35096184 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic dysregulation and adipose tissue fibrosis: role of collagen VI.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Mar;29(6):1575-91. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01300-08. Epub 2008 Dec 29. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19114551 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen VI sustains cell stemness and chemotherapy resistance in glioblastoma.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Jul 28;80(8):233. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04887-5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37505240 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elenbaas B, Weinberg RA. Heterotypic signaling between epithelial tumor cells and fibroblasts in carcinoma formation. Exp. Cell Res. 2001;264:169–184. - PubMed
-
- Klausner RD. The fabric of cancer cell biology: weaving together the strands. Cancer Cell. 2002;1:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Iyengar P, et al. Adipocyte secreted factors synergistically promote mammary tumorigenesis through induction of anti-apoptotic transcriptional programs and proto-oncogene stabilization. Oncogene. 2003;22:6408–6423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

