Gastric motor effects of peptide and non-peptide ghrelin agonists in mice in vivo and in vitro
- PMID: 15843418
- PMCID: PMC1774892
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2005.065896
Gastric motor effects of peptide and non-peptide ghrelin agonists in mice in vivo and in vitro
Abstract
Background and aims: The gastroprokinetic activities of ghrelin, the natural ligand of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHS-R), prompted us to compare the effect of ghrelin with that of synthetic peptide (growth hormone releasing peptide 6 (GHRP-6)) and non-peptide (capromorelin) GHS-R agonists both in vivo and in vitro.
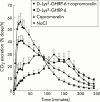
Methods: In vivo, the dose dependent effects (1-150 nmol/kg) of ghrelin, GHRP-6, and capromorelin on gastric emptying were measured by the 14C octanoic breath test which was adapted for use in mice. The effect of atropine, N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride (L-NAME), or D-Lys3-GHRP-6 (GHS-R antagonist) on the gastroprokinetic effect of capromorelin was also investigated. In vitro, the effect of the GHS-R agonists (1 microM) on electrical field stimulation (EFS) induced responses was studied in fundic strips in the absence and presence of L-NAME.
Results: Ghrelin, GHRP-6, and capromorelin accelerated gastric emptying in an equipotent manner, with bell-shaped dose-response relationships. In the presence of atropine or l-NAME, which delayed gastric emptying, capromorelin failed to accelerate gastric emptying. D-Lys3-GHRP-6 also delayed gastric emptying but did not effectively block the action of the GHS-R agonists, but this may be related to interactions with other receptors. EFS of fundic strips caused frequency dependent relaxations that were not modified by the GHS-R agonists. L-NAME turned EFS induced relaxations into cholinergic contractions that were enhanced by ghrelin, GHRP-6, and capromorelin.
Conclusion: The 14C octanoic breath test is a valuable technique to evaluate drug induced effects on gastric emptying in mice. Peptide and non-peptide GHS-R agonists accelerate gastric emptying of solids in an equipotent manner through activation of GHS receptors, possibly located on local cholinergic enteric nerves.
Figures



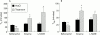
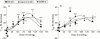
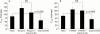

Similar articles
-
Comparison of the gastroprokinetic effects of ghrelin, GHRP-6 and motilin in rats in vivo and in vitro.Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 May 16;515(1-3):160-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.04.008. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15890336
-
Gastric motor effects of ghrelin and growth hormone releasing peptide 6 in diabetic mice with gastroparesis.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Mar 7;14(9):1419-24. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1419. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18322959 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect and mechanism of ghrelin and its synthetic peptide growth hormone releasing peptide 6 on gastric motor in mice].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2008 Mar;11(2):172-6. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18344088 Chinese.
-
Growth hormone secretagogue receptor family members and ligands.Endocrine. 2001 Feb;14(1):9-14. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:14:1:009. Endocrine. 2001. PMID: 11322507 Review.
-
Insights on discovery, efficacy, safety and clinical applications of ghrelin receptor agonist capromorelin in veterinary medicine.Vet Res Commun. 2024 Feb;48(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s11259-023-10184-0. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Vet Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 37493940 Review.
Cited by
-
Decreased gastric motility in type II diabetic patients.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:894087. doi: 10.1155/2014/894087. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25147821 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of different surgical traumas on postoperative ileus in rats and the mechanisms involved.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Sep 15;8(9):16778-86. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26629220 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Pre-Endoscopic Metoclopramide Does Not Prevent the Need for Repeat Endoscopy: A U.S. Based Retrospective Cohort Study.Life (Basel). 2024 Apr 19;14(4):526. doi: 10.3390/life14040526. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672796 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of motilin and ghrelin in gastrointestinal motility.Int J Pept. 2010;2010:820794. doi: 10.1155/2010/820794. Epub 2010 Feb 3. Int J Pept. 2010. PMID: 20798893 Free PMC article.
-
Ghrelin prevents levodopa-induced inhibition of gastric emptying and increases circulating levodopa in fasted rats.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012 May;24(5):e235-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2012.01904.x. Epub 2012 Mar 23. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012. PMID: 22443313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howard AD, Feighner SD, Cully DF, et al. A receptor in pituitary and hypothalamus that functions in growth hormone release. Science 1996;273:974–7. - PubMed
-
- Bowers CY, Chang J, Momany F, et al. Effects of enkephalins, enkephalins analogs on release of pituitary hormones in vitro In: MacIntyre I, Szelke H, eds. Molecular endocrinology. Amsterdam/North Holland: Elsevier, 1977:287–92.
-
- Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, et al. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999;402:656–60. - PubMed
-
- Hosoda H, Kojima M, Matsuo H, et al. Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin: two major forms of rat ghrelin peptide in gastrointestinal tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000;279:909–13. - PubMed
-
- Tschop M, Smiley DL, Heiman ML. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature 2000;407:908–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
