Lamin A/C-dependent localization of Nesprin-2, a giant scaffolder at the nuclear envelope
- PMID: 15843432
- PMCID: PMC1165422
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-11-1009
Lamin A/C-dependent localization of Nesprin-2, a giant scaffolder at the nuclear envelope
Abstract
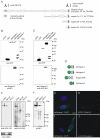
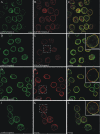
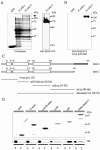
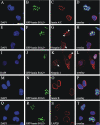
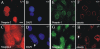
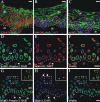
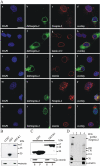
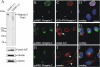
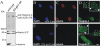
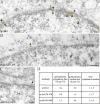
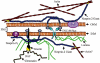
The vertebrate proteins Nesprin-1 and Nesprin-2 (also referred to as Enaptin and NUANCE) together with ANC-1 of Caenorhabditis elegans and MSP-300 of Drosophila melanogaster belong to a novel family of alpha-actinin type actin-binding proteins residing at the nuclear membrane. Using biochemical techniques, we demonstrate that Nesprin-2 binds directly to emerin and the C-terminal common region of lamin A/C. Selective disruption of the lamin A/C network in COS7 cells, using a dominant negative lamin B mutant, resulted in the redistribution of Nesprin-2. Furthermore, using lamin A/C knockout fibroblasts we show that lamin A/C is necessary for the nuclear envelope localization of Nesprin-2. In normal skin where lamin A/C is differentially expressed, strong Nesprin-2 expression was found in all epidermal layers, including the basal layer where only lamin C is present. This indicates that lamin C is sufficient for proper Nesprin-2 localization at the nuclear envelope. Expression of dominant negative Nesprin-2 constructs and knockdown studies in COS7 cells revealed that the presence of Nesprin-2 at the nuclear envelope is necessary for the proper localization of emerin. Our data imply a scaffolding function of Nesprin-2 at the nuclear membrane and suggest a potential involvement of this multi-isomeric protein in human disease.
Figures

References
-
- Apel, E. D., Lewis, R. M., Grady, R. M., and Sanes, J. R. (2000). Syne-1, a dystrophin- and Klarsicht-related protein associated with synaptic nuclei at the neuromuscular junction. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 31986–31995. - PubMed
-
- Bengtsson, L., and Wilson, K. L. (2004). Multiple and surprising new functions for emerin, a nuclear membrane protein. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 16, 1–7. - PubMed
-
- Burke, B., and Stewart, C. L. (2002). Life at the edge: the nuclear envelope and human disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 3, 575–585. - PubMed
-
- Ellis, D. J., Jenkins, H. E., Whitfield, W.G.F., and Hutchison, C. J. (1997). GST-lamin fusion proteins act as dominant negative mutants in Xenopus egg extract and reveal the function of the lamina in DNA replication. J. Cell Sci. 110, 2507–2518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

