Ligand-induced dimerization of Drosophila peptidoglycan recognition proteins in vitro
- PMID: 15843462
- PMCID: PMC1088352
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0407559102
Ligand-induced dimerization of Drosophila peptidoglycan recognition proteins in vitro
Abstract
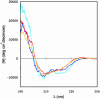
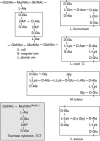
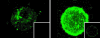
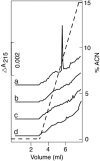
Drosophila knockout mutants have placed peptidoglycan recognition proteins (PGRPs) in the two major pathways controlling immune gene expression. We now examine PGRP affinities for peptidoglycan. PGRP-SA and PGRP-LCx are bona fide pattern recognition receptors, and PGRP-SA, the peptidoglycan receptor of the Toll/Dif pathway, has selective affinity for different peptidoglycans. PGRP-LCx, the default peptidoglycan receptor of the Imd/Relish pathway, has strong affinity for all polymeric peptidoglycans tested and for monomeric peptidoglycan. PGRP-LCa does not have affinity for polymeric or monomeric peptidoglycan. Instead, PGRP-LCa can form heterodimers with LCx when the latter is bound to monomeric peptidoglycan. Hence, PGRP-LCa can be said to function as an adaptor, thus adding a new function to a member of the PGRP family.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of Drosophila PGRP-SD suggests binding to DAP-type but not lysine-type peptidoglycan.Mol Immunol. 2008 May;45(9):2521-30. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.01.015. Epub 2008 Mar 4. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18304640
-
Peptidoglycan recognition protein LF: a negative regulator of Drosophila immunity.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 Dec;37(12):1309-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2007.08.003. Epub 2007 Aug 21. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17967349
-
Downregulation of the Drosophila immune response by peptidoglycan-recognition proteins SC1 and SC2.PLoS Pathog. 2006 Feb;2(2):e14. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020014. Epub 2006 Feb 24. PLoS Pathog. 2006. PMID: 16518472 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian PGRPs: novel antibacterial proteins.Cell Microbiol. 2006 Jul;8(7):1059-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2006.00726.x. Cell Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16819960 Review.
-
Peptidoglycan recognition proteins of the innate immune system.Trends Microbiol. 2007 Mar;15(3):127-34. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2007.01.006. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Trends Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17275309 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune pathways and defence mechanisms in honey bees Apis mellifera.Insect Mol Biol. 2006 Oct;15(5):645-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2006.00682.x. Insect Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 17069638 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappaB in the immune response of Drosophila.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009 Dec;1(6):a000232. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000232. Epub 2009 Oct 7. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009. PMID: 20457557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular and intracellular pathogen recognition by Drosophila PGRP-LE and PGRP-LC.Int Immunol. 2010 Mar;22(3):143-8. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxp128. Epub 2010 Jan 20. Int Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20089584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Drosophila peptidoglycan-recognition protein LF interacts with peptidoglycan-recognition protein LC to downregulate the Imd pathway.EMBO Rep. 2011 Apr;12(4):327-33. doi: 10.1038/embor.2011.19. Epub 2011 Mar 4. EMBO Rep. 2011. PMID: 21372849 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial homeostasis and the underlying molecular mechanisms in the gut of the insect model Drosophila melanogaster.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011 Nov;68(22):3651-60. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0828-x. Epub 2011 Oct 2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21964927 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akira, S. & Takeda, K. (2004) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4, 499-511. - PubMed
-
- Hultmark, D. (2003) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 15, 12-19. - PubMed
-
- Kaneko, T., Goldman, W. E., Mellroth, P., Steiner, H., Fukase, K., Kusumoto, S., Harley, W., Fox, A., Golenbock, D. & Silverman, N. (2004) Immunity 20, 637-649. - PubMed
-
- Leulier, F., Parquet, C., Pili-Floury, S., Ryu, J. H., Caroff, M., Lee, W. J., Mengin-Lecreulx, D. & Lemaitre, B. (2003) Nat. Immunol. 4, 478-484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

