Presynaptically silent GABA synapses in hippocampus
- PMID: 15843605
- PMCID: PMC6724942
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4969-04.2005
Presynaptically silent GABA synapses in hippocampus
Abstract
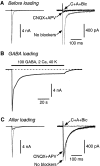
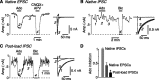
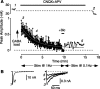
Mammalian central synapses commonly specialize in one fast neurotransmitter, matching the content of their presynaptic vesicles with the appropriate receptors in their postsynaptic membrane. Here, I show that hippocampal cultures contain autaptic glutamatergic synapses that contravene this rule: in addition to postsynaptic glutamate receptors, they also express clusters of functional postsynaptic GABA(A) receptors yet lack presynaptic GABA. Hence, these synapses are presynaptically silent with respect to GABA. They can be unsilenced by loading GABA into presynaptic vesicles by endocytosis, after which a postload IPSC appears. This IPSC is similar to native IPSCs recorded from GABAergic interneurons in the same cultures. Thus, these "mistargeted" GABA(A) receptors, which apparently lack a signal that confers synaptic specificity, function almost normally. After GABA loading, glutamatergic miniature postsynaptic currents acquire a slow tail that is mediated by GABA(A) receptors, showing that synaptic vesicles can accommodate both the usual concentration of native glutamate and a saturating concentration of loaded GABA. After brief Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis, endocytosis of GABA can proceed in low-Ca(2+) external solution. The amplitude of the postload IPSC declines exponentially with repetitive stimulation as the endocytosed GABA passes through the presynaptic vesicle cycle and is depleted. Hence, by using GABA as an exogenous but physiological tracer, the properties of these presynaptically silent synapses can provide novel insights into the content and cycling of vesicles in presynaptic terminals.
Figures

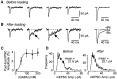

Similar articles
-
GABAB receptors in the medial septum/diagonal band slice from 16-25 day rat.Neuroscience. 2005;132(3):789-800. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.01.027. Neuroscience. 2005. PMID: 15837139
-
Distinct mechanisms of presynaptic inhibition at GABAergic synapses of the rat substantia nigra pars compacta.J Neurophysiol. 2005 Sep;94(3):1992-2003. doi: 10.1152/jn.00171.2005. Epub 2005 Jun 8. J Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 15944237
-
Inhibitory synapses in the developing auditory system are glutamatergic.Nat Neurosci. 2005 Mar;8(3):332-8. doi: 10.1038/nn1397. Epub 2005 Jan 30. Nat Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15746915
-
Modulation of allopregnanolone on excitatory transmitters release from single glutamatergic terminal.Brain Res Bull. 2013 Apr;93:39-46. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2012.11.002. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Brain Res Bull. 2013. PMID: 23174309 Review.
-
GABA vesicles at synapses: are there 2 distinct pools?Neuroscientist. 2009 Jun;15(3):218-24. doi: 10.1177/1073858408326431. Neuroscientist. 2009. PMID: 19436074 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Distinctive quantal properties of neurotransmission at excitatory and inhibitory autapses revealed using variance-mean analysis.J Neurosci. 2008 Dec 10;28(50):13563-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3350-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19074030 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression in accumbens GABA neurons from inbred rats with different drug-taking behavior.Genes Brain Behav. 2011 Oct;10(7):778-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2011.00716.x. Epub 2011 Aug 1. Genes Brain Behav. 2011. PMID: 21745336 Free PMC article.
-
Heterosynaptic GABAergic plasticity bidirectionally driven by the activity of pre- and postsynaptic NMDA receptors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Aug 30;113(35):9898-903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1601194113. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27531957 Free PMC article.
-
GABAergic signaling at mossy fiber synapses in neonatal rat hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2006 Jan 11;26(2):597-608. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4493-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16407558 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic inhibition of synaptic release with chromophore-assisted light inactivation (CALI).Neuron. 2013 Jul 24;79(2):241-53. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.05.022. Neuron. 2013. PMID: 23889931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aravanis AM, Pyle JL, Tsien RW (2003) Single synaptic vesicles fusing transiently and successively without loss of identity. Nature 423: 643-647. - PubMed
-
- Axmacher N, Stemmler M, Engel D, Draguhn A, Ritz R (2004) Transmitter metabolism as a mechanism of synaptic plasticity: a modeling study. J Neurophysiol 91: 25-39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
