Abnormal cortical complexity and thickness profiles mapped in Williams syndrome
- PMID: 15843618
- PMCID: PMC6724948
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0165-05.2005
Abnormal cortical complexity and thickness profiles mapped in Williams syndrome
Abstract
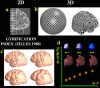
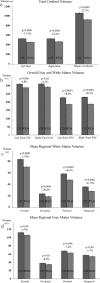
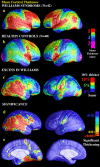
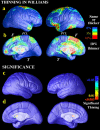
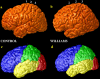
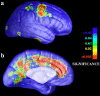
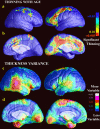
We identified and mapped an anatomically localized failure of cortical maturation in Williams syndrome (WS), a genetic condition associated with deletion of approximately 20 contiguous genes on chromosome 7. Detailed three-dimensional (3D) maps of cortical thickness, based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of 164 brain hemispheres, identified a delimited zone of right hemisphere perisylvian cortex that was thicker in WS than in matched controls, despite pervasive gray and white matter deficits and reduced total cerebral volumes. 3D cortical surface models were extracted from 82 T1-weighted brain MRI scans (256 x 192 x 124 volumes) of 42 subjects with genetically confirmed WS (mean +/- SD, 29.2 +/- 9.0 years of age; 19 males, 23 females) and 40 age-matched healthy controls (27.5 +/- 7.4 years of age; 16 males, 24 females). A cortical pattern-matching technique used 72 sulcal landmarks traced on each brain as anchors to align cortical thickness maps across subjects, build group average maps, and identify regions with altered cortical thickness in WS. Cortical models were remeshed in frequency space to compute their fractal dimension (surface complexity) for each hemisphere and lobe. Surface complexity was significantly increased in WS (p < 0.0015 and p < 0.0014 for left and right hemispheres, respectively) and correlated with temporoparietal gyrification differences, classified via Steinmetz criteria. In WS, cortical thickness was increased by 5-10% in a circumscribed right hemisphere perisylvian and inferior temporal zone (p < 0.002). Spatially extended cortical regions were identified with increased complexity and thickness; cortical thickness and complexity were also positively correlated in controls (p < 0.03). These findings visualize cortical zones with altered anatomy in WS, which merit additional study with techniques to assess function and connectivity.
Figures


References
-
- Annese J, Pitiot A, Dinov ID, Toga AW (2004) A myelo-architectonic method for the structural classification of cortical areas. NeuroImage 21: 15-26. - PubMed
-
- Barth E, Zetzsche C, Ferraro M, Rentschler I (1993) Fractal properties from 2D-curvature on multiple scales. In: Geometric methods in computer vision (Vemuri B, ed), pp 87-99. Bellingham, WA: The International Society for Optical Engineering.
-
- Bartley AJ, Jones DW, Weinberger DR (1997) Genetic variability of human brain size and cortical gyral patterns. Brain 120: 257-269. - PubMed
-
- Bartzokis G, Sultzer D, Lu PH, Nuechterlein KH, Mintz J, Cummings JL (2004) Heterogeneous age-related breakdown of white matter structural integrity: implications for cortical “disconnection” in aging and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 25: 843-851. - PubMed
-
- Bellugi U, Lichtenberger L, Jones W, Lai Z, St George M (2000) I. The neurocognitive profile of Williams syndrome: a complex pattern of strengths and weaknesses. J Cogn Neurosci 12[Suppl 1]: 7-29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
