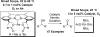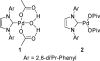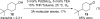Development and comparison of the substrate scope of Pd-catalysts for the aerobic oxidation of alcohols
- PMID: 15844968
- PMCID: PMC2692733
- DOI: 10.1021/jo0482211
Development and comparison of the substrate scope of Pd-catalysts for the aerobic oxidation of alcohols
Abstract
[reaction: see text] Three catalysts for aerobic oxidation of alcohols are discussed and the effectiveness of each is evaluated for allylic, benzylic, aliphatic, and functionalized alcohols. Additionally, chiral nonracemic substrates as well as chemoselective and diastereoselective oxidations are investigated. In this study, the most convenient system for the Pd-catalyzed aerobic oxidation of alcohols is Pd(OAc)(2) in combination with triethylamine. This system functions effectively for the majority of alcohols tested and uses mild conditions (3 to 5 mol % of catalyst, room temperature). Pd(IiPr)(OAc)(2)(H(2)O) (1) also successfully oxidizes the majority of alcohols evaluated. This system has the advantage of significantly lowering catalyst loadings but requires higher temperatures (0.1 to 1 mol % of catalyst, 60 degrees C). A new catalyst is also disclosed, Pd(IiPr)(OPiv)(2) (2). This catalyst operates under very mild conditions (1 mol %, room temperature, and air as the O(2) source) but with a more limited substrate scope.
Similar articles
-
Scope of enantioselective palladium(II)-catalyzed aerobic alcohol oxidations with (-)-sparteine.J Org Chem. 2003 May 30;68(11):4600-3. doi: 10.1021/jo0269161. J Org Chem. 2003. PMID: 12762783
-
Using mechanistic and computational studies to explain ligand effects in the palladium-catalyzed aerobic oxidation of alcohols.J Am Chem Soc. 2005 Jun 15;127(23):8499-507. doi: 10.1021/ja050949r. J Am Chem Soc. 2005. PMID: 15941285
-
A convenient palladium-catalyzed aerobic oxidation of alcohols at room temperature.Chem Commun (Camb). 2002 Dec 21;(24):3034-5. doi: 10.1039/b209344h. Chem Commun (Camb). 2002. PMID: 12536803
-
Palladium oxidase catalysis: selective oxidation of organic chemicals by direct dioxygen-coupled turnover.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2004 Jun 28;43(26):3400-20. doi: 10.1002/anie.200300630. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2004. PMID: 15221827 Review.
-
Practical aerobic oxidations of alcohols and amines with homogeneous copper/TEMPO and related catalyst systems.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014 Aug 18;53(34):8824-38. doi: 10.1002/anie.201403110. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014. PMID: 25044821 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Studies Toward the Synthesis of (-)-Zampanolide: Preparation of the Macrocyclic Core.Adv Synth Catal. 2008 Aug 4;350(11-12):1701-1711. doi: 10.1002/adsc.200800247. Epub 2008 Jul 9. Adv Synth Catal. 2008. PMID: 23543877 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the ligand linkers on stability of mixed-valence Cu(I)Cu(II) and catalytic aerobic alcohol oxidation activity.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 5;14(1):15497. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66227-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38969824 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling Pd-Catalyzed Alcohol Oxidation to Olefin Functionalization: Hydrohalogenation/Hydroalkoxylation of Styrenes.Organometallics. 2007 Nov 5;26(23):5680-5686. doi: 10.1021/om700675z. Organometallics. 2007. PMID: 19779575 Free PMC article.
-
Ru(ii)-N-heterocyclic carbene complexes: synthesis, characterization, transfer hydrogenation reactions and biological determination.RSC Adv. 2019 Oct 25;9(59):34406-34420. doi: 10.1039/c9ra05605j. eCollection 2019 Oct 23. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35529977 Free PMC article.
-
The influential IPr: 25 years after its discovery.Chem Sci. 2025 Jan 9;16(5):2062-2082. doi: 10.1039/d4sc07009g. eCollection 2025 Jan 29. Chem Sci. 2025. PMID: 39811009 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Collins JC, Hess WW, Frank FJ. Tetrahedron Lett. 1968:3363–3363.
-
- Dess DB, Martin JC. J. Org. Chem. 1983;48:4155–4156.
-
- Harding KE, May LM, Dick KF. J. Org. Chem. 1975;40:1664–1665.
-
- Pfitzner KE, Moffatt JG. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1965;87:5661–5670.
-
- Parikh JR, Doering WE. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967;89:5505–5507.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources