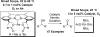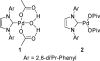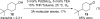Development and comparison of the substrate scope of Pd-catalysts for the aerobic oxidation of alcohols
- PMID: 15844968
- PMCID: PMC2692733
- DOI: 10.1021/jo0482211
Development and comparison of the substrate scope of Pd-catalysts for the aerobic oxidation of alcohols
Abstract
[reaction: see text] Three catalysts for aerobic oxidation of alcohols are discussed and the effectiveness of each is evaluated for allylic, benzylic, aliphatic, and functionalized alcohols. Additionally, chiral nonracemic substrates as well as chemoselective and diastereoselective oxidations are investigated. In this study, the most convenient system for the Pd-catalyzed aerobic oxidation of alcohols is Pd(OAc)(2) in combination with triethylamine. This system functions effectively for the majority of alcohols tested and uses mild conditions (3 to 5 mol % of catalyst, room temperature). Pd(IiPr)(OAc)(2)(H(2)O) (1) also successfully oxidizes the majority of alcohols evaluated. This system has the advantage of significantly lowering catalyst loadings but requires higher temperatures (0.1 to 1 mol % of catalyst, 60 degrees C). A new catalyst is also disclosed, Pd(IiPr)(OPiv)(2) (2). This catalyst operates under very mild conditions (1 mol %, room temperature, and air as the O(2) source) but with a more limited substrate scope.
References
-
- Collins JC, Hess WW, Frank FJ. Tetrahedron Lett. 1968:3363–3363.
-
- Dess DB, Martin JC. J. Org. Chem. 1983;48:4155–4156.
-
- Harding KE, May LM, Dick KF. J. Org. Chem. 1975;40:1664–1665.
-
- Pfitzner KE, Moffatt JG. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1965;87:5661–5670.
-
- Parikh JR, Doering WE. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967;89:5505–5507.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources