Helicobacter pylori binds to CD74 on gastric epithelial cells and stimulates interleukin-8 production
- PMID: 15845476
- PMCID: PMC1087363
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.5.2736-2743.2005
Helicobacter pylori binds to CD74 on gastric epithelial cells and stimulates interleukin-8 production
Abstract
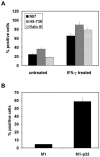
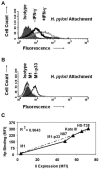
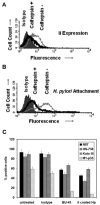
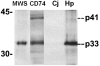
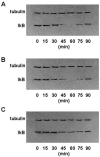
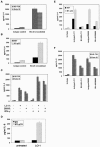
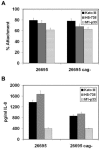
The pathogenesis associated with Helicobacter pylori infection requires consistent contact with the gastric epithelium. Although several cell surface receptors have been suggested to play a role in adhesion, the bacterium-host interactions that elicit host responses are not well defined. This study investigated the interaction of H. pylori with the class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-associated invariant chain (Ii; CD74), which was found to be highly expressed by gastric epithelial cells. Bacterial binding was increased when CD74 surface expression was increased by gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) treatment or by fibroblast cells transfected with CD74, while binding was decreased by CD74 blocking antibodies, enzyme cleavage of CD74, and CD74-coated bacteria. H. pylori was also shown to bind directly to affinity-purified CD74 in the absence of class II MHC. Cross-linking of CD74 and the engagement of CD74 were verified to stimulate IL-8 production by unrelated cell lines expressing CD74 in the absence of class II MHC. Increased CD74 expression by cells increased IL-8 production in response to H. pylori, and agents that block CD74 decreased these responses. The binding of H. pylori to CD74 presents a novel insight into an initial interaction of H. pylori with the gastric epithelium that leads to upregulation of inflammatory responses.
Figures
References
-
- Bamford, K. B., X. Fan, S. E. Crowe, J. F. Leary, W. K. Gourley, G. K. Luthra, E. G. Brooks, D. Y. Graham, V. E. Reyes, and P. B. Ernst. 1998. Lymphocytes in the human gastric mucosa during Helicobacter pylori have a T helper cell 1 phenotype. Gastroenterology 114:482-492. - PubMed
-
- Barrera, C., R. Espejo, and V. E. Reyes. 2002. Differential glycosylation of MHC class II molecules on gastric epithelial cells: implications in local immune responses. Hum. Immunol. 63:384-393. - PubMed
-
- Barrera, C. A., R. J. Almanza, P. L. Ogra, and V. E. Reyes. 1998. The role of the invariant chain in mucosal immunity. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 117:85-93. - PubMed
-
- Beales, I. L., and J. Calam. 1997. Stimulation of IL-8 production in human gastric epithelial cells by Helicobacter pylori, IL-1beta and TNF-alpha requires tyrosine kinase activity, but not protein kinase C. Cytokine 9:514-520. - PubMed
-
- Chu, S. H., H. Kim, J. Y. Seo, J. W. Lim, N. Mukaida, and K. H. Kim. 2003. Role of NF-kappaB and AP-1 on Helicobacter pylori-induced IL-8 expression in AGS cells. Dig. Dis. Sci. 48:257-265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

