Escherichia coli K1 RS218 interacts with human brain microvascular endothelial cells via type 1 fimbria bacteria in the fimbriated state
- PMID: 15845498
- PMCID: PMC1087349
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.5.2923-2931.2005
Escherichia coli K1 RS218 interacts with human brain microvascular endothelial cells via type 1 fimbria bacteria in the fimbriated state
Abstract
Escherichia coli K1 is a major gram-negative organism causing neonatal meningitis. E. coli K1 binding to and invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMEC) are a prerequisite for E. coli penetration into the central nervous system in vivo. In the present study, we showed using DNA microarray analysis that E. coli K1 associated with HBMEC expressed significantly higher levels of the fim genes compared to nonassociated bacteria. We also showed that E. coli K1 binding to and invasion of HBMEC were significantly decreased with its fimH deletion mutant and type 1 fimbria locked-off mutant, while they were significantly increased with its type 1 fimbria locked-on mutant. E. coli K1 strains associated with HBMEC were predominantly type 1 fimbria phase-on (i.e., fimbriated) bacteria. Taken together, we showed for the first time that type 1 fimbriae play an important role in E. coli K1 binding to and invasion of HBMEC and that type 1 fimbria phase-on E. coli is the major population interacting with HBMEC.
Figures

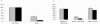

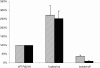
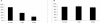

Similar articles
-
Role of S fimbriae in Escherichia coli K1 binding to brain microvascular endothelial cells in vitro and penetration into the central nervous system in vivo.Microb Pathog. 2004 Dec;37(6):287-93. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2004.09.002. Epub 2004 Dec 9. Microb Pathog. 2004. PMID: 15619424
-
Effects of ompA deletion on expression of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli K1 strain RS218 and on the association of E. coli with human brain microvascular endothelial cells.Infect Immun. 2006 Oct;74(10):5609-16. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00321-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16988236 Free PMC article.
-
Flagella promote Escherichia coli K1 association with and invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells.Infect Immun. 2007 Jun;75(6):2937-45. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01543-06. Epub 2007 Mar 19. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17371850 Free PMC article.
-
Current concepts on Escherichia coli K1 translocation of the blood-brain barrier.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2004 Nov 1;42(3):271-9. doi: 10.1016/j.femsim.2004.09.001. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15477040 Review.
-
Invasion processes of pathogenic Escherichia coli.Int J Med Microbiol. 2005 Oct;295(6-7):463-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2005.07.004. Int J Med Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16238020 Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of Escherichia coli K1 ibeT in bacterial adhesion that is associated with the entry into human brain microvascular endothelial cells.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2008 Dec;197(4):337-44. doi: 10.1007/s00430-007-0065-y. Epub 2007 Nov 27. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18040715
-
Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Activation of EGFR As a Novel Target for Meningitic Escherichia coli Penetration of the Blood-Brain Barrier.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Oct 6;12(10):e1005926. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005926. eCollection 2016 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27711202 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogen interactions with endothelial cells and the induction of innate and adaptive immunity.Eur J Immunol. 2018 Oct;48(10):1607-1620. doi: 10.1002/eji.201646789. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Eur J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30160302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome profiling of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli and the mouse microvascular endothelial cell line bEnd.3 during interaction.PeerJ. 2020 May 21;8:e9172. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9172. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32509459 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor-1 (CNF1) does not promote E. coli infection in a murine model of ascending pyelonephritis.BMC Microbiol. 2017 May 25;17(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s12866-017-1036-0. BMC Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28545489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander, W. A., A. B. Hartman, E. V. Oaks, and M. M. Venkatesan. 1996. Construction and characterization of virG (icsA)-deleted Escherichia coli K12-Shigella flexneri hybrid vaccine strains. Vaccine 14:1053-1061. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

