Differential induction of the toll-like receptor 4-MyD88-dependent and -independent signaling pathways by endotoxins
- PMID: 15845500
- PMCID: PMC1087371
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.5.2940-2950.2005
Differential induction of the toll-like receptor 4-MyD88-dependent and -independent signaling pathways by endotoxins
Erratum in
- Infect Immun. 2006 May;74(5):3077
Abstract
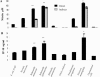
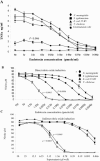
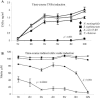
The biological response to endotoxin mediated through the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-MD-2 receptor complex is directly related to lipid A structure or configuration. Endotoxin structure may also influence activation of the MyD88-dependent and -independent signaling pathways of TLR4. To address this possibility, human macrophage-like cell lines (THP-1, U937, and MM6) or murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells were stimulated with picomolar concentrations of highly purified endotoxins. Harvested supernatants from previously stimulated cells were also used to stimulate RAW 264.7 or 23ScCr (TLR4-deficient) macrophages (i.e., indirect induction). Neisseria meningitidis lipooligosaccharide (LOS) was a potent direct inducer of the MyD88-dependent pathway molecules tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1), macrophage inflammatory protein 3alpha (MIP-3alpha), and the MyD88-independent molecules beta interferon (IFN-beta), nitric oxide, and IFN-gamma-inducible protein 10 (IP-10). Escherichia coli 55:B5 and Vibrio cholerae lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) at the same pmole/ml lipid A concentrations induced comparable levels of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, and MIP-3alpha, but significantly less IFN-beta, nitric oxide, and IP-10. In contrast, LPS from Salmonella enterica serovars Minnesota and Typhimurium induced amounts of IFN-beta, nitric oxide, and IP-10 similar to meningococcal LOS but much less TNF-alpha and MIP-3alpha in time course and dose-response experiments. No MyD88-dependent or -independent response to endotoxin was seen in TLR4-deficient cell lines (C3H/HeJ and 23ScCr) and response was restored in TLR4-MD-2-transfected human embryonic kidney 293 cells. Blocking the MyD88-dependent pathway by DNMyD88 resulted in significant reduction of TNF-alpha release but did not influence nitric oxide release. IFN-beta polyclonal antibody and IFN-alpha/beta receptor 1 antibody significantly reduced nitric oxide release. N. meningitidis endotoxin was a potent agonist of both the MyD88-dependent and -independent signaling pathways of the TLR4 receptor complex of human macrophages. E. coli 55:B5 and Vibrio cholerae LPS, at the same picomolar lipid A concentrations, selectively induced the MyD88-dependent pathway, while Salmonella LPS activated the MyD88-independent pathway.
Figures
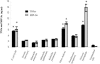

Similar articles
-
The role of MyD88 and TLR4 in the LPS-mimetic activity of Taxol.Eur J Immunol. 2001 Aug;31(8):2448-57. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200108)31:8<2448::aid-immu2448>3.0.co;2-n. Eur J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11500829
-
TLR4, but not TLR2, mediates IFN-beta-induced STAT1alpha/beta-dependent gene expression in macrophages.Nat Immunol. 2002 Apr;3(4):392-8. doi: 10.1038/ni774. Epub 2002 Mar 18. Nat Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11896392
-
Toll-like receptor 4 and Toll-IL-1 receptor domain-containing adapter protein (TIRAP)/myeloid differentiation protein 88 adapter-like (Mal) contribute to maximal IL-6 expression in macrophages.J Immunol. 2002 Nov 15;169(10):5874-80. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.10.5874. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12421970
-
Enhancement of endotoxin activity by muramyldipeptide.J Endotoxin Res. 2002;8(5):337-42. doi: 10.1179/096805102125000669. J Endotoxin Res. 2002. PMID: 12537692 Review.
-
A novel negative regulator for IL-1 receptor and Toll-like receptor 4.Immunol Lett. 2005 Jan 15;96(1):27-31. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2004.07.008. Immunol Lett. 2005. PMID: 15585304 Review.
Cited by
-
Differentiation and classification of bacterial endotoxins based on surface enhanced Raman scattering and advanced machine learning.Nanoscale. 2022 Jun 23;14(24):8806-8817. doi: 10.1039/d2nr01277d. Nanoscale. 2022. PMID: 35686584 Free PMC article.
-
Differential modulation of TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis by Neisseria meningitidis.PLoS Pathog. 2009 May;5(5):e1000405. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000405. Epub 2009 May 1. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19412525 Free PMC article.
-
Toll/IL-1 domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-β (TRIF) mediates innate immune responses in murine peritoneal mesothelial cells through TLR3 and TLR4 stimulation.Cytokine. 2016 Jan;77:127-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.11.010. Epub 2015 Nov 12. Cytokine. 2016. PMID: 26579632 Free PMC article.
-
Vibrio cholerae, classification, pathogenesis, immune response, and trends in vaccine development.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 May 5;10:1155751. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1155751. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37215733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Soluble Uric Acid in Modulating Autophagy Flux and Inflammasome Activation during Bacterial Infection in Macrophages.Biomedicines. 2020 Dec 12;8(12):598. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8120598. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 33322651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira, S., and K. Hoshino. 2003. Myeloid differentiation factor 88-dependent and -independent pathways in toll-like receptor signaling. J Infect. Dis. 187(Suppl. 2):S356-63. - PubMed
-
- Beutler, B. 2004. Innate immunity: an overview. Mol. Immunol. 40:845-859. - PubMed
-
- Beutler, B., K. Hoebe, X. Du, E. Janssen, P. Georgel, and K. Tabeta. 2003. Lps2 and signal transduction in sepsis: at the intersection of host responses to bacteria and viruses. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 35:563-567. - PubMed
-
- Beutler, B., K. Hoebe, X. Du, and R. J. Ulevitch. 2003. How we detect microbes and respond to them: the Toll-like receptors and their transducers. J. Leukoc. Biol. 74:479-485. - PubMed
-
- Blunck, R., O. Scheel, M. Muller, K. Brandenburg, U. Seitzer, and U. Seydel. 2001. New insights into endotoxin-induced activation of macrophages: involvement of a K+ channel in transmembrane signaling. J. Immunol. 166:1009-1015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

