The concentration of apolipoprotein A-I decreases during experimentally induced acute-phase processes in pigs
- PMID: 15845530
- PMCID: PMC1087351
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.5.3184-3187.2005
The concentration of apolipoprotein A-I decreases during experimentally induced acute-phase processes in pigs
Abstract
In this work, apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I) was purified from pig sera. The responses of this protein after sterile inflammation and in animals infected with Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae or Streptococcus suis were investigated. Decreases in the concentrations of ApoA-I, two to five times lower than the initial values, were observed at 2 to 4 days. It is concluded that ApoA-I is a negative acute-phase protein in pigs.
Figures
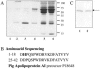

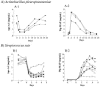
References
-
- Alava, M. A., N. Gonzalez-Ramón, P. Heegaard, S. Guzylack, M. J. M. Toussaint, C. Lipperheide, F. Madec, E. Gruys, P. D. Eckersall, F. Lampreave, and A. Piñeiro. 1997. Pig-MAP, porcine acute phase proteins and standardisation of assays in Europe. Comp. Haematol. Int. 7:208-213.
-
- Angelo, M., C. E. Scanu, and P. Keim. 1975. Serum lipoproteins, p. 317-391. In F. W. Putnam (ed.), The plasma proteins, vol. 1. Academic Press, New York, N.Y.
-
- Avrameas, S., and T. Ternynck. 1969. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry 6:53-66. - PubMed
-
- Baumann, H., and J. Gauldie. 1994. The acute phase response. Immunol. Today 15:74-80. - PubMed
-
- Burger, D., and J. M. Dayer. 2002. High-density lipoprotein-associated apolipoprotein A-I: the missing link between infection and chronic inflammation? Autoimmun. Rev. 1:111-117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

