Conversion of Staphylococcus epidermidis strains from commensal to invasive by expression of the ica locus encoding production of biofilm exopolysaccharide
- PMID: 15845531
- PMCID: PMC1087319
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.5.3188-3191.2005
Conversion of Staphylococcus epidermidis strains from commensal to invasive by expression of the ica locus encoding production of biofilm exopolysaccharide
Abstract
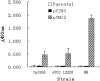
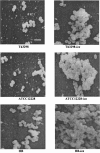
To test if biofilm formation in Staphylococcus epidermidis is dependent on the polysaccharide intercellular adhesin, whose biosynthesis is driven by the ica locus, a plasmid containing the ica locus was transferred to three ica-negative strains. Using in vitro biofilm assays and a rat central venous catheter infection model, we confirmed the importance of the ica locus for biofilm production and pathogenesis of S. epidermidis.
Figures
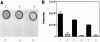
Similar articles
-
Anaerobic conditions induce expression of polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis.Infect Immun. 2001 Jun;69(6):4079-85. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.6.4079-4085.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11349079 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum-sensing control of biofilm factors in Staphylococcus epidermidis.J Infect Dis. 2003 Sep 1;188(5):706-18. doi: 10.1086/377239. Epub 2003 Aug 11. J Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 12934187
-
A multiplex PCR method for the detection of all five individual genes of ica locus in Staphylococcus epidermidis. A survey on 400 clinical isolates from prosthesis-associated infections.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2005 Nov 1;75(2):408-13. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.30445. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2005. PMID: 16088896
-
ica and beyond: biofilm mechanisms and regulation in Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007 May;270(2):179-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00688.x. Epub 2007 Apr 10. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17419768 Review.
-
Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in biofilm: structural and regulatory aspects.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Feb 10;5:7. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00007. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25713785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Canine Staphylococcaceae circulating in a Kenyan animal shelter.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Feb 6;12(2):e0292423. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02924-23. Epub 2024 Jan 11. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38206027 Free PMC article.
-
Role of a putative polysaccharide locus in Bordetella biofilm development.J Bacteriol. 2007 Feb;189(3):750-60. doi: 10.1128/JB.00953-06. Epub 2006 Nov 17. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17114249 Free PMC article.
-
Accumulation-associated protein enhances Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation under dynamic conditions and is required for infection in a rat catheter model.Infect Immun. 2015 Jan;83(1):214-26. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02177-14. Epub 2014 Oct 20. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 25332125 Free PMC article.
-
Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus culture in chronic rhinosinusitis.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015 Mar;5(3):204-13. doi: 10.1002/alr.21439. Epub 2014 Nov 3. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015. PMID: 25367456 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for corneal infiltrative events during continuous wear of silicone hydrogel contact lenses.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Nov;51(11):5421-30. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-5456. Epub 2010 Jun 10. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 20538985 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Augustin, J., and F. Götz. 1990. Transformation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and other staphylococcal species with plasmid DNA by electroporation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 54:203-207. - PubMed
-
- Christensen, G. D., W. A. Simpson, J. J. Younger, L. M. Baddour, F. F. Barrett, D. M. Melton, and E. H. Beachey. 1985. Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: a quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. J. Clin. Microbiol. 22:996-1006. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Francois, P., P. H. Tu Quoc, C. Bisognano, W. L. Kelley, D. P. Lew, J. Schrenzel, S. E. Cramton, F. Götz, and P. Vaudaux. 2003. Lack of biofilm contribution to bacterial colonisation in an experimental model of foreign body infection by Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 35:135-140. - PubMed
-
- Galdbart, J. O., J. Allignet, H. S. Tung, C. Ryden, and N. El Solh. 2000. Screening for Staphylococcus epidermidis markers discriminating between skin-flora strains and those responsible for infections of joint prostheses. J. Infect. Dis. 182:351-355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

