Obesity and metabolic syndrome in circadian Clock mutant mice
- PMID: 15845877
- PMCID: PMC3764501
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1108750
Obesity and metabolic syndrome in circadian Clock mutant mice
Abstract
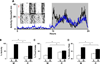
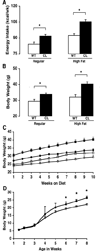
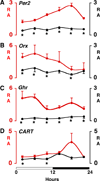
The CLOCK transcription factor is a key component of the molecular circadian clock within pacemaker neurons of the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus. We found that homozygous Clock mutant mice have a greatly attenuated diurnal feeding rhythm, are hyperphagic and obese, and develop a metabolic syndrome of hyperleptinemia, hyperlipidemia, hepatic steatosis, hyperglycemia, and hypoinsulinemia. Expression of transcripts encoding selected hypothalamic peptides associated with energy balance was attenuated in the Clock mutant mice. These results suggest that the circadian clock gene network plays an important role in mammalian energy balance.
Figures
References
-
- Van Cauter E, Turek FW. Roles of sleep-wake and dark-light cycles in the control of endocrine, metabolic, cardiovascular and cognitive function, Volume IV: Coping With the Environment: Neural and Endocrine Mechanisms. In: McEwen BS, editor. Handbook of Physiology, Section 7: The Endocrine System. New York: Oxford University Press; 2000. pp. 313–330.
-
- Reppert SM, Weaver DR. Coordination of circadian timing in mammals. Nature. 2002;418(6901):935–941. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi JS, Turek FW, Moore RY. Handbook of Behavioral Neurobiology. In: NT A, editor. Circadian Clocks. Vol. 12. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers; 2001. p. 770.
-
- Balsalobre A, Damiola F, Schibler U. A serum shock induces circadian gene expression in mammalian tissue culture cells. Cell. 1998;93:929–937. - PubMed
-
- Stokkan KA, Yamazaki S, Tei H, Sakaki Y, Menaker M. Entrainment of the circadian clock in the liver by feeding. Science. 2001;291(5503):490–493. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL075029/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL59598/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK002675/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- DK26356/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018200/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK02675/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AG18200/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG011412/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL75029/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059598/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK026356/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AG11412/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

