Olanzapine for schizophrenia
- PMID: 15846619
- PMCID: PMC11781594
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001359.pub2
Olanzapine for schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: Olanzapine is an atypical antipsychotic reported to be effective without producing disabling extrapyramidal adverse effects associated with older, typical antipsychotic drugs.
Objectives: To determine the clinical effects and safety of olanzapine compared with placebo, typical and other atypical antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia and schizophreniform psychoses.
Search strategy: We updated the first search [Biological Abstracts (1980-1999), The Cochrane Library (Issue 2, 1999), EMBASE (1980-1999), MEDLINE (1966-1999), PsycLIT (1974-1999) and The Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's Register (October 2000)] in October 2004 using the Cochrane Schizophrenia's Group's register of trials. We also searched references of all included studies for further trials, and contacted relevant pharmaceutical companies and authors.
Selection criteria: We included all randomised clinical trials comparing olanzapine with placebo or any antipsychotic treatment for people with schizophrenia or schizophreniform psychoses.
Data collection and analysis: We independently extracted data and, for homogeneous dichotomous data, calculated the random effects relative risk (RR), the 95% confidence intervals (CI) and the number needed to treat (NNT) on an intention-to-treat basis. For continuous data we calculated weighted mean differences.
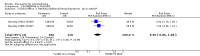
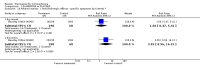
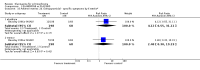
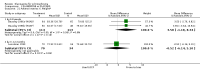
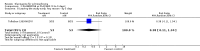
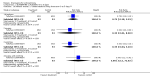
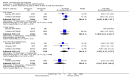
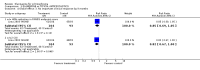
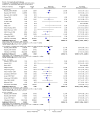
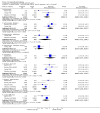
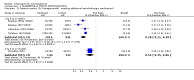
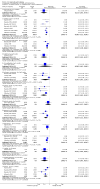
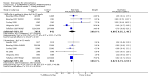
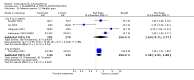
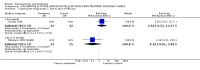
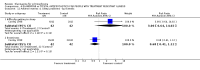
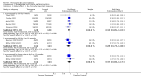
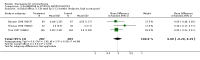
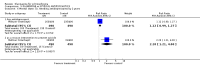
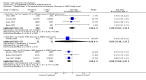
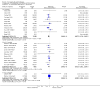
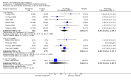
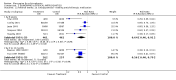
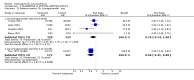
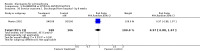
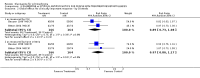
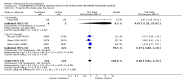
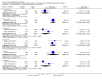
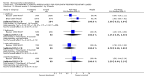
Main results: Fifty five trials are included (total n>10000 people with schizophrenia). Attrition from olanzapine versus placebo studies was >50% by six weeks, leaving interpretation of results problematic. Olanzapine appeared superior to placebo at six weeks for the outcome of 'no important clinical response' (any dose, 2 RCTs n=418, RR 0.88 CI 0.8 to 0.1, NNT 8 CI 5 to 27). Although dizziness and dry mouth were reported more frequently in the olanzapine-treated group, this did not reach statistical significance. The olanzapine group gained more weight. When compared with typical antipsychotic drugs, data from several small trials are incomplete. With high attrition in both groups (14 RCTs, n=3344, 38% attrition by six weeks, RR 0.81 CI 0.65 to 1.02) the assumptions included in all data are considerable. For the short term outcome of 'no important clinical response', olanzapine seems as effective as typical antipsychotics (4 RCTs, n=2778, RR 0.90 CI 0.76 to 1.06). People allocated olanzapine experienced fewer extrapyramidal adverse effects than those given typical antipsychotics. Weight change data for the short term are not statistically significant but results between three to 12 months suggest a clinically important average gain of four kilograms for people given olanzapine (4 RCTs, n=186, WMD 4.62, CI 0.6 to 8.64). Twenty three percent of people in trials of olanzapine and other atypical drugs left by eight weeks; 48% by three to12 months (11 RCTs, n=1847, RR 0.91 CI 0.82 to 1.00). There is little to choose between the atypicals, although olanzapine may cause fewer extrapyramidal adverse effects than other drugs in this category. Olanzapine produces more weight gain than other atypicals with some differences reaching conventional levels of statistical significance (1 RCT, n=980, RR gain at 2 years 1.73 CI 1.49 to 2.00, NNH 5 CI 4 to 7). There are very few data for people with first episode illness (1 RCT, duration 6 weeks, n=42). For people with treatment-resistant illness there were no clear differences between olanzapine and clozapine (4 RCTs, n=457).
Authors' conclusions: The large proportion of participants leaving studies early in these trials makes it difficult to draw firm conclusions on olanzapine's clinical effects. For people with schizophrenia it may offer antipsychotic efficacy with fewer extrapyramidal adverse effects than typical drugs, but more weight gain. There is a need for further large, long-term randomised trials with more comprehensive data.
Conflict of interest statement
Lorna Duggan ‐ has attended functions sponsored by Lundbeck, Janssen, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb and Zeneca and has accepted sponsorship from Eli Lilly for internal flights in the United States.
Mark Fenton ‐ has led Janssen, Lilly and Zeneca sponsored workshops for clinicians.
Ahmed El‐Dosoky ‐ has participated in Eli Lilly sponsored research (Loza 1999 (HGDT)).
John Rathbone ‐ no known conflicts of interest. The Cochrane Schizophrenia Group editorial base in Leeds has received general support funding from Eli Lilly during the years 1996‐1999 (see Group Module). This, along with some funds from other pharmaceutical companies, is used to support any ongoing work of the editorial base and is not linked to any particular review (annual report available on request).
Figures






















































































Update of
-
Olanzapine for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(1):CD001359. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001359. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18;(2):CD001359. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001359.pub2. PMID: 12535408 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Altamura 1999 (HGBQ) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Altamura AC, Eli Lilly Data Compilers. HGBQ ‐ Olanzapine verus haloperidol in partial responder schizophrenic patients. Supplied by Eli Lilly 2000.
-
- Altamura AC, Velona I, Curreli R, Bravi D. Olanzapine in the treatment of paranoid schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1999;9(Suppl 5):S297.
-
- Altamura AC, Velona I, Curreli R, Mundo E, Bravi D. Is olanzapine better than haloperidol in resistant schizophrenia? A double‐blind study in partial responders. International Journal of Psychiatry in Clinical Practice 2002;6(2):107‐11. [EMBASE 2002201401; CN‐00443300.] - PubMed
Avasthi 2001 {published data only}
Barak 2002 {published data only}
-
- Barak Y, Shamir E, Zemishlani H, Mirecki I, Toren P, Weizman R. Olanzapine vs. haloperidol in the treatment of elderly chronic schizophrenia patients. Progress in Neuro‐Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 2002;26:1199‐202. [MEDLINE: ; PMID 12452546] - PubMed
Beasley 1996a (HGAD) {published and unpublished data}
-
- *Beasley CM Jr, Tollefson G, Tran P, Satterlee W, Sanger T, Hamilton S. Olanzapine versus placebo and haloperidol: acute phase results of the North American double‐blind olanzapine trial. Neuropsychopharmacology 1996;14:111‐23. - PubMed
-
- Baker R W, Julier B, Stauffer V. Manic‐like symptoms in schizophrenic patients treated with olanzapine, haloperidol and placebo. 7th World Congress of Biological Psychiatry; 2001 Jul 1‐6; Berlin, Germany. 2001; Vol. 2, issue Suppl. 1.
-
- Baker RW, Ames D, Umbricht DSG, Chengappa KNR, Schooler NR. Obsessive‐compulsive symptoms in schizophrenia ‐ a comparison of olanzapine and placebo. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1996;32:89‐93. - PubMed
-
- Beasley CM Jr, Tollefson GD, Tran PV. Safety of olanzapine. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1997;58(Suppl 10):13‐7. - PubMed
-
- Beasley CM, Sayler ME, Kiesler GM, Potvin JH, Sanger TM, Tollefson GD. The influence of pharmacotherapy on self‐directed and externally‐directed aggression in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 1998;29(1‐2):28.
Beasley 1996b (HGAP) {published and unpublished data}
-
- *Beasley Jr CM, Sanger T, Satterlee W, Tollefson G, Tran P, Hamilton S. Olanzapine versus placebo ‐ results of a double‐blind, fixed‐dose olanzapine trial. Psychopharmacology 1996;124:159‐67. - PubMed
-
- Baker R W, Julier B, Stauffer V. Manic‐like symptoms in schizophrenic patients treated with olanzapine, haloperidol and placebo. 7th World Congress of Biological Psychiatry; 2001 Jul 1‐6; Berlin, Germany. 2001.
-
- Baker RW, Ames D, Umbricht DS, Chengappa KN, Schooler NR. Obsessive‐compulsive symptoms in schizophrenia: a comparison of olanzapine and placebo. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1996;32(1):89‐93. - PubMed
-
- Beasley C, Tran P, Satterlee W, Tollefson G, Lu Y, Kuntz A, Bradley P, Paul S. Olanzapine versus placebo, results of the United‐States double‐blind olanzapine trial. XXth Collegium Internationale Neuro‐psychopharmacologicum; June 23‐27; Melbourne; Australia. 1996.
-
- Beasley CM Jr, Dellva MA, Tamura RN, Morgenstern H, Glazer WM, Ferguson K, Tollefson GD. A randomized, double‐blind comparison of the incidence of tardive dyskinesia during long‐term treatment with olanzapine or haloperidol. British Journal of Psychiatry 1999;174:23‐30. - PubMed
Beasley 1997 (E003) {published and unpublished data}
-
- *Beasley CM Jr, Hamilton SH, Crawford AM, Dellva MA, Tollefson GD, Tran PV, Blin O, Beuzen JN. Olanzapine versus haloperidol: acute phase results of the international double‐blind olanzapine trial. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1997;7:125‐37. - PubMed
-
- Baker R W, Julier B, Stauffer V. Manic‐like symptoms in schizophrenic patients treated with olanzapine, haloperidol and placebo. 7th World Congress of Biological Psychiatry; 2001 Jul 1‐6; Berlin, Germany. 2001, issue Suppl. 1.
-
- Beasley CM Jr, Dellva MA, Tamura RN, Morgenstern H, Glazer WM, Ferguson K, Tollefson GD. A randomized, double‐blind comparison of the incidence of tardive dyskinesia during long‐term treatment with olanzapine or haloperidol. British Journal of Psychiatry 1999;174:23‐30. - PubMed
-
- Beasley CM Jr, Tollefson GD, Tran PV. Safety of olanzapine. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1997;58(Suppl 10):13‐7. - PubMed
-
- Beasley CM, Sayler ME, Kiesler GM, Potvin JH, Sanger TM, Tollefson GD. The influence of pharmacotherapy on self‐directed and externally‐directed aggression in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 1998;29(1‐2):28.
Bernardo 2001 (HGDD) {published data only}
-
- Bernardo M, Parellada E, Lomena F, Catafau AM, Font M, Gomez JC, Lopez‐Carrero C, Gutierrez F, Pavia J, Salamero M. Double‐blind olanzapine vs. haloperidol D2 dopamine receptor blockade in schizophrenic patients: a baseline‐endpoint. Psychiatry Research 2001;107:87‐97. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Beuzen 1998 (HGCF) {published and unpublished data}
-
- *Beuzen JN, Birkett M, Kiesler G, Wood A. Olanzapine versus clozapine in resistant schizophrenic patients ‐ results of an international double‐blind randomised clinical trial. Proceedings of XXIst Collegium Internationale Neuro‐psychopharmacologicum; 1998 July 12‐16; Glasgow, Scotland, UK. 1998.
-
- Beasley CM, Beuzen JN, Birkett MA. [Olanzapine versus clozapine: an international double‐blind study in the treatment of patients with treatment‐resistent schizophrenia]. NCDEU, Boca Raton, FL, USA. 1999.
-
- Beasley CM, Beuzen JN, Birkett MA. Olanzapine versus Clozapine: an international double‐blind study in the treatment of patients with treatment‐resistent schizophrenia. World Psychiatric Association. Hamburg, Germany. 1999.
-
- Beasley CM, Beuzen JN, Birkett MA. Olanzapine versus clozapine: an international double‐blind study in the treatment of patients with treatment‐resistent schizophrenia. American College of Neuropsychopharmacology Annual Meeting, Hawaii, USA. 1998.
-
- Beasley CM, Beuzen JN, Birkett MA. Olanzapine versus clozapine: an international double‐blind study in the treatment of patients with treatment‐resistent schizophrenia. American Psychiatric Association Meeting. Washington, DC, USA. 1999.
Bitter 2004 (HGCK) {published data only}
-
- *Bitter I, Dossenbach MRK, Brook S, Feldman PD, Metcalfe S, Gagiano CA, Furedi J, Bartko G, Janka Z, Banki CM, Kovacs G, Breier A. Olanzapine versus clozapine in treatment‐resistant or treatment‐intolerant schizophrenia. Progress in Neuro‐Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 2004;28:173‐180. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE 2003516387] - PubMed
-
- Bitter I, Brook S, Dossenbach M, Janka Z, Banki CsM, Selemani S, Grundy S, Martenyi F. Olanzapine versus clozapine in patients non‐responsive or intolerant to standard acceptable treatment of schizophrenia. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 1999;9:S288. [MEDLINE: ; Lilly study possible stands alone]
Casey 2003 {published data only}
-
- *Casey DE, Daniel DG, Wassef AA, Tracy KA, Wozniak P, Sommerville KW. Effect of divalproex combined with olanzapine or risperidone in patients with an acute exacerbation of schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2003;28:182‐92. [MEDLINE: ; PMID 12496955] - PubMed
-
- Citrome L, Casey DE, Daniel DG, Wozniak P, Kochan LD, Tracy KA. Adjunctive divalproex and hostility among patients with schizophrenia receiving olanzapine or risperidone. Psychiatric Services 2004;55(3):290‐4. - PubMed
-
- Citrome LL, Daniel DG, Wassef AA, Tracy KA, Wozniak P, Casey DE. Antipsychotic monotherapy versus combination treatment with valporate in hospitalized patients with acute schizophrenia: a double‐blind, multi‐center study. 155th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2002 May 18‐23; Philadelphia, PA, USA. 2002.
Chan 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chan HY, Chen CH, Chen JJ, Sun HJ, Chiu H‐J, Chang CJ. A comparison of olanzapine and risperidone for the schizophrenic patients intolerance of neuroleptic‐induced extrapyramidal syndromes (eps). Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2003;13(4):S316. [P.2.084]
Chang 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chang Fa wei, Wang Chang hong, Zhao Zheng. Clinical effects of olanzapine vs chlorpromazine in treating positive symptoms of schizophrenia. Chinese Journal of New Drugs and Clinical Remedies 2003;22(06):357‐59. [MEDI0306]
Chaudhry 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chaudhry HR, Kongsakon R, Ignacio JC, Raza SB, Leynes MCR, Hasanah CI, Chan B, Onate P, Brnabic AJM, Lowry AJ, Buenaventura R. Quality of life and clinical outcomes for asian outpatients with schizophrenia: a double‐blind randomised comparison of olanzapine and haloperidol. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2003;13(4):S309. [P.2.069]
Chen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chen Fei, Liang Ligui, Zhu Xianghua. A control study of elderly patients with schizophrenia treated with olanzapine or clozapine. Journal of Clinical Psychological Medicine 2003;13(05):298‐99. [MEDI0312]
Conley 1998 {published data only}
-
- *Conley RR, Tamminga CA, Bartko JJ, Richardson C, Peszke M, Lingle J, Hegerty J, Love R, Gounaris C, Zaremba S. Olanzapine compared with chlorpromazine in treatment‐resistant schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1998;155:914‐20. - PubMed
-
- Conley R, Gounaris C. Demographic differences in olanzapine responders with therapy‐refractory schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research ( The VIth International Congress on Schizophrenia Research;1997 April 12‐16; Colorado Springs; CO, USA 1997;24 Suppl.:189.
-
- Conley RR, Tamminga CA, Beasley C. Olanzapine vs chlorpromazine in therapy‐refractory schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research (The VIth International Congress on Schizophrenia Research; 1997 April 12‐16; Colorado Springs; CO, USA ) 1997;24 Suppl.:189.
-
- Conley RR, Tamminga CA, Beasley C. Olanzapine vs. Chlorpromazine in Treatment‐Resistant. Biological Psychiatry 1997;41:1S‐120S.
-
- Conley RR, Tamminga CA, Beasley C, Maryland Study Group. Olanzapine vs. chlorpromazine in treatment‐resistant schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry 1997;41:73S. [MEDLINE: ; PMID 22476629] - PubMed
Conley 2001 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Berry SA, Martinez RA, Gudelsky GA, Mahmoud R, Myers J. Serum prolactin levels in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research (8th International Congress on Schizophrenia Research; 2001 Apr 28 ‐ May 2; British Columbia, Canada). 2001, issue 1‐2 Suppl:280‐1. [MEDLINE: ; Probably Not Eli Lilly]
-
- Berry SA, Martinez RA, Gudelsky GA, Myers JE, Mahmoud RA. Serum prolactin in schizophrenia. 39th Annual Meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology; 2000; Dec 10‐14; San Juan; Puerto Rico. 2000.
-
- Brecher M. Risperidone versus olanzapine in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. 11th Congress of The European College of Neuropsychopharmacology; 1998 Oct 31‐ Nov 4; Paris, France. 1998.
-
- Brecher M. Risperidone versus olanzapine in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Proceedings of XXIst Collegium Internationale Neuro‐psychopharmacologicum; 1998 July 12‐16; Glasgow, Scotland, UK. 1998.
-
- Conley R, et al. Risperidone vs. Olanzapine in patients with schizophrenia and schizo‐affective disorder. International Drug Therapy Newsletter 2000;35(10):77‐8.
Corrigan 2004 {published data only}
-
- Corrigan MH, Gallen CC, Bonura ML, Merchant KM. Effectiveness of the selective D4 antagonist sonepiprazole in schizophrenia: a placebo‐controlled trial. Biological Psychiatry 2004;55(5):445‐51. [EMBASE: 2004123114] - PubMed
de Haan 2002 {published data only}
-
- Haan L, Beuk N, Hoogenboom B, Dingemans P, Linszen D. Obsessive‐compulsive symptoms during treatment with olanzapine and risperidone: a prospective study of 113 patients with recent‐onset schizophrenia or related disorders. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2002;63:104‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
de Hann 2003 {published data only}
-
- Haan L, Bruggen M, Lavalaye J, Booij J, Dingemans PM, Linszen D. Subjective experience and D2 receptor occupancy in patients with recent‐onset schizophrenia treated with low‐dose olanzapine or haloperidol: a randomized, double‐blind study. American Journal of Psychiatry 2003;160:303‐9. [MEDLINE: ; PMID 12562577] - PubMed
-
- Haan L, van‐Bruggen M, Lavalaye J, Booij J, Dingemans P, Linszen D. Subjective experience and d2 receptor occupancy in patients with schizophrenia, treated with low dose olanzapine or haloperidol; a randomized double‐blind study. Schizophrenia Research (Abstracts of the 11th Biennial Winter Workshop on Schizophrenia). Elsevier Science B.V, 2002, issue 3 Suppl.1:179.
Esel 2001 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Esel E, Basturk M, Saffet Gonul A, Kula M, Tayfun Turan M, Yabanoglu I, Sofuoglu S. Effects of olanzapine and haloperidol on serum prolactin levels in male schizophrenic patients. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2001;26(6):641‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
He 2003 {published data only}
-
- He Jin, An Qinghua. A comparative trial of olanzapine versus chlorpromazine in the treatment of schizophrenia. Shandong Archires of Psychiatry 2003;16(02):78‐80. [MEDI0307]
HGBJ (Finland) {unpublished data only}
-
- Eli Lilly. Data on file. Data supplied to the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group 1999.
-
- Naukkarinen H, Rimon R, Katila H, Riihikangas R, Heikkila L. Olanzapine and perhenazine in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 2000;41(1):190. [CSG NO. 4504]
HGBL 1997 {unpublished data only}
-
- Dittmann RW, Geuppert MS, Diehl A, Hubrich P, Maraz, Gattaz WF. Olanzapine versus flupentixol in the treatment of inpatients with schizophrenia: a randomised double‐blind trial. Schizophrenia Research (8th International Congress on Schizophrenia Research; 2001 Apr 28 ‐ May 2; British Columbia, Canada). 2001, issue 1‐2 Suppl:225.
-
- Eli Lilly. Data on file. Data supplied to the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group 1999.
HGCJ (Hong Kong) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Tran PV, Beasley CM, Tollefson GD, Creanga D, Zhang F, Wang J, Vangala S, Cousins L. Clinical experience with olanzapine in patients of African, Asian, and Hispanic descent. Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. Washington, DC, USA. 1999.
-
- Tran PV, Beasley CM, Tollefson GD, Creanga D, Zhang F, Wang J, Vangala S, Cousins L. Clinical experience with olanzapine in patients of African, Asian, and Hispanic descent. World Psychiatric Association; Hamburg, Germany. 1999.
-
- Tran PV, Cousins LM, Creanga D, Tollefson GD, Vangala S, Wang J, Zhang F. Clinical experience with olanzapine in patients of African, Asian, and Hispanic descent. ACNP. Hawaii, USA. 1998.
-
- Tran PV, Creanga D, Zhang F, Wang J, Vangala S, Cousins L, Tollefson GD. Clinical experience with olanzapine in ethnic subgroups. NCDEU. Boca Raton, FL, USA. 1999.
-
- Tran PV, Zhang F, Hwu HG, Liehmak F. Efficacy and safety study comparing olanzapine versus haloperidol in the treatment of Chinese patients with schizophrenia in Taiwan and Hong Kong. APA Annual Meeting, May 15‐20, Washington, DC. 1999. [CSG NO. 4118]
HGCQ (Turkey) 2000 {unpublished data only}
-
- Eli Lilly, Company. Study F1D‐VI‐HGCQ Olanzapine Versus Chlorpromazine in Turkey. Unpublished Document Internal to Eli‐lilly 2000:1‐560.
-
- Kostakoglu E, Alptekin K, Kivicik BB, Martenyi F, Tunca Z, Gogus A, Dossenbach M. [Sleep quality and early morning wakefulness of schizophrenia patients treated with olanzapine compared to chlorpromazine]. Errata, European Neuropsychopharmacology. 2000; Vol. 10, issue Suppl 3.
-
- Mraz K, Gogus A, Tunca Z, Martenyi F, Dossenbach M. Olanzapine versus chlorpromazine in Turkey. Schizophrenia Research (Abstracts of the Winter Workshop on Schizophrenia; 2000 Feb Davos; Switzerland). 2000.
HGCU (Taiwan) 1998 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Tran PV, Creanga D, Zhang F, Wang J, Vangala S, Cousins L, Tollefson GD. Clinical experience with olanzapine in ethnic subgroups. NCDEU. Boca Raton, FL, USA. 1999.
-
- Tran PV, Zhang F, Hwu HG, Liehmak F. Efficacy and safety study comparing olanzapine versus haloperidol in the treatment of Chinese patients with schizophrenia in Taiwan and Hong Kong. American Psychiatric Association Annual Meeting; 1999 May 15‐20; Washington DC; USA. 1999. [CSG NO. 4118]
-
- Zhang F, Tran PV, Taylor C, Hwu GH, Chen YS, Chang WH, Cheng J, Wang A, Chang S, Sze S, Chen RYK, Dunn E, Lieh Mak F. Efficacy and safety study comparing olanzapine versus haloperidol in the treatment of Chinese patients with schizophrenia in Taiwan and Hong Kong. World Psychiatric Association. Hamburg, Germany. 1999.
HGDV (Morocco) 1999 {unpublished data only}
-
- Eli Lilly. Study HGDV Olanzapine (Versus Chlorpromazine in Morocco). Unpublished Document Internal to Eli‐lilly 2001:1‐512.
-
- HGDV/Moroco. Data on file. Data supplied to the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group 1999.
HGFH (Korea) 1998 {unpublished data only}
-
- HGFH Korea. Data on file. Data supplied to the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group 1999.
Ishigooka 2001 {published data only}
-
- *Ishigooka J, Hirotsu C, Kurihara M, Inada T, Miura S. Olanzapine versus haloperidol in the treatment of patients with chronic schizophrenia: results of the japan multi‐center double‐blind olanzapine trial. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 2001;55(4):403‐14. - PubMed
-
- Inada T, Beasley CM, Yoko T, Walker D. Extrapyramidal symptom profiles assessed with the Drug‐Induced Extrapyramidal Symptom Scale: comparison with Western scales in the clinical double‐blind studies of schizophrenic patients treated with either olanzapine or haoperidol. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 2003;18:39‐48. - PubMed
-
- Inada T, Miura S. Favorable eps profiles of olanzapine measured by the diepss: predictive validity of this scale to differentiate the eps profiles of atypical antipsychotic drugs from conventional antipsychotic drugs in the clinical trial. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2000;3(Suppl 1):S147.
-
- Inada T, Yagi G, Miura S. Extrapyramidal symptom profiles in Japanese patients with schizophrenia treated with olanzapine or haloperidol. Schizophrenia Research 2002;57(2‐3):227‐38. - PubMed
Jakovljevic1999 HGCH {published and unpublished data}
-
- Dossenbach M, Friedel P, Jakovljevic M, Hotujac L, Folnegovic V, Uglesic B, Dodig G. Olanzapine versus fluphenazine ‐ six weeks' treatment of acute schizophrenia. 10th ECNP Congress; September 13 ‐ 17; Vienna; Austria. 1997.
-
- Dossenbach M, Jakovljevic M, Folnegovi V, Uglesic B, Dodig G, Friedel P, Hotujac L. Olanzapine versus fluphenazine ‐ six weeks of treatment of anxiety symptoms during acute schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 1998;29(1‐2):203.
-
- Ferenc M, Dossenbach M, Jakovljevic M, Metcalfe S. Predictive value of early anti anxiety effect on the acute antipsychotic outcome: a comparison of fluphenazine and olanzapine. 153rd Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2000 May 13‐18; Chicago, USA. 2000.
-
- Jakovljevic M, Dossenbach MRK. Olanzapine versus fluphenazine in the acute (six‐week) treatment of schizophrenia. Psychiatric Danubina 1999;11(1‐2):3‐10.
-
- Ljubin T, Milas DZ, Mimica N, Folnegovic Smalc V, Makaric G. A preliminary study of the comparative effects of olanzapine and fluphenazine on cognition in schizophrenic patients. Human Psychopharmacology 2000;15(7):513‐9. - PubMed
Jeste 2003 {published data only}
-
- *Jeste DV, Barak Y, Madhusoodanan S, Grossman D, Gharabawi G. International Multisite Double‐Blind Trial of the Atypical Antipsychotics Risperidone and Olanzapine in 175 Elderly Patients with Chronic Schizophrenia. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2003;11(6):638‐647. - PubMed
-
- Harvey PD, Napolitano JA, Mao L, Gharabawi G. Comparative effects of risperidone and olanzapine on cognition in elderly patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 2003;18(9):820‐9. - PubMed
-
- Jeste D, Madhusoodanan S, Barak Y, Martinez RA, Mahmoud R, Kershaw P. Risperidone and olanzapine in elderly patients with schizophrenia and schizopaffective disorder. International Psychogeriatrics 2003;13(2):295s. [N0546099389]
-
- Jeste DV, Madhusoodanan S, Barak F, Martinez RA. Risperidone versus olanzapine in elderly patients with schizophrenia. 154th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2001 May 5 ‐ 10; New Orleans, USA. Marathon Multimedia, 2001. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Jeste DV, Madhusoodanan S, Barak F, Martinez RA. Risperidone versus olanzapine in elderly patients with schizophrenia. 155th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2002 May 18‐23; Philadelphia, PA, USA. 2002. [NR754 Thursday, May 10, 12:00 p.m.‐2:00 p.m]
Jones 1998 (P022) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Canadian Cognition and Outcome Study Group. Neuropsychological change in early phase schizophrenia over twelve months of treatment with olanzapine, risperidone or haloperidol. Schizophrenia Research 1998;29:132‐3. - PubMed
-
- David SR, Purdon S, Jones BD, Stip E, Labelle A, Breier AF, Tollefson GD, Kutcher SP, Maclaren C, Hadrava V, Thompson PM, Leblanc. Olanzapine versus risperidone versus haloperidol in early illness schizophrenia. Education improves outcomes in MDD. 152nd Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 1999 May 15‐20; Washington, USA. 1999. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Jones B. Olanzapine versus risperidone and haloperidol in the treatment of schizophrenia. 151st Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association; May 30‐June 4; Toronto; ON, Canada. 1998.
-
- Jones B. Treatment of cognitive deficits with antipsychotic drugs. Neurobiology of Aging (Abstracts of 6th International Conference on Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders; 1998 Jul 18‐23; Amsterdam, the Netherlands). 1998, issue 4S:S152‐3.
-
- Jones B, Tollefson G. Olanzapine versus risperidone and haloperidol in the treatment of schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 1998;29:150‐1.
Kelly 2003 {published data only}
-
- Conley RR, Kelly DL, Richardson CM, Tamminga CA, Carpenter Jr WT. The Efficacy of High‐Dose Olanzapine Versus Clozapine in Treatment‐Resistant Schizophrenia: A Double‐Blind, Crossover Study [letter]. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2003;23(6):668‐71. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE 2003477898] - PubMed
-
- Kelly DL, Conley RR, Richardson CM, Tamminga CA, Carpenter Jr WT. Adverse effects and laboratory parameters of high‐dose olanzapine vs. clozapine in treatment‐resistant schizophrenia. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry 2003;15(3‐4):181‐6. [EMBASE: 2004064601] - PubMed
Kern 2001 {published data only}
-
- *Kern RS, Cornblatt B, Carson WH, Dunbar G, Ali M, Ingenito G, Green MF. An open‐label comparison of the neurocognitive effects of aripiprazole versus olanzapine in patients with stable psychosis. Schizophrenia Research 2001;1‐2:234. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Carson W, Cornblatt B, Saha A, Ali M, Kern R, Green M. Neurocognitive benefits of aripiprazole versus olanzapine in stable psychosis. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2002;Supplement 3:S291.
-
- Cornblatt B, Kern RS, Carson WH, Ali MW, Luo X, Green M. Neurocognitive effects of aripiprazole versus olanzapine in stable psychosis. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2002;Suppl. 1:s185.
-
- Cornblatt B, Kern RS, Carson WH, Stock E, Ali M, Ingenito G, Green MF. Neurocognitive effects of aripiprazole versus olanzapine in patients with stable psychosis. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2002;16(3):A15.
-
- Cornblatt B, Kern RS, Carson WH, Stock E, Ali M, Ingenito G, Green MF. Neurocognitive effects of aripiprazole versus olanzapine in patients with stable psychosis. Schizophrenia Research 2002;3(Suppl. 1):27. [MEDLINE: ]
Lecrubier 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Lecrubier Y, Bouhassira M, Olivier V, Lancrenon S, Crawford AM. Olanzapine versus amisulpride and placebo in the treatment of negative symptoms and deficit states of chronic schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1999;9(Suppl 5):S288.
Lieberman 2003 (HGDH {published data only}
-
- *Lieberman JA, Tollefson G, Tohen M, Green AI, Gur RE, Kahn R, McEvoy J, Perkins D, Sharma T, Zipursky R, Wei H, Hamer RM, HGDH Study= Group. Comparative efficacy and safety of atypical and conventional antipsychotic drugs in first‐episode psychosis: a randomized, double‐blind trial of olanzapine versus haloperidol. American Journal of Psychiatry 2003;160(8):1396‐404. [MEDLINE: ; PMID 12900300] - PubMed
-
- Breier A, Keefe RS, Young CA, Purdon SE, Gold JM, Davis KL. A one‐year double‐blind comparison of the neurocognitive efficacy of olanzapine, risperidone, and haloperidol in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 2003;60:274‐5. [EMBASE 2003496187] - PubMed
-
- Breier AF, Zipursky RB, Perkins DO, Addington JM, Tohen MF, David SR, McGlashan TH. A trial of olanzapine versus pbo in the prodrome: protocol and baseline sample. 155th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2002 May 18‐23; Philadelphia, PA, USA. 2002. [Lilly study possible stands alone not published]
-
- Centorrino F, Hamer RM, Tohen M, Lieberman JA. Drug attitudes and treatment adherence in a clinical trial comparing haloperidol and olanzapine in first episode schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 2003;60:277. [EMBASE: 2003241517]
-
- Green A, Tohen M, Strakowski SM, Lieberman JA, Glick D, Clarke SW. Comorbid substance use disorder and first episode schizophrenia: acute effects of olanzapine versus haloperidol. Schizophrenia Research (8th International Congress on Schizophrenia Research; 2001 Apr 28 ‐ May 2; British Columbia, Canada). 2001, issue 1‐2 Suppl:230. [MEDLINE: ]
Lima 2003 (HGHS) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Lima MS, Mari JJ, Costa AMN, Alexandrini N, Filho SR, Oliverira IR, Hotopf M. Quality of life of patients with schizophrenia: A Randomised, Naturalistic, Controlled Trial Comparing Olanzapine with Typical Antipsychotics in Brazil. Eli Lilly and Company.
-
- Lima MS, Jesus Mari J, Costa AMN, Alexandrini N, Filho SR, Oliveira IR, Hotopt M. Quality of life of patients with schizophrenia: a randomized, naturalistic, controlled trial comparing olanzapine with typical antipsychotics in Brazil. 156th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2003 May 17‐22; San Francisco, USA. 2003. [N0146103028]
-
- Mari JD, Lima MS, costa AN, Alexandrini N, Filho SR, Oliveira IR. A nine month naturalistic randomized controlled trial comparing olanzapine and conventional antipsychotics for schizophrenia and related disorders. Schizophrenia Research 2003;60:294. [EMBASE: 2003241517]
-
- Mari JdJ, Lima MS, Costa AMN, Alexandrini N, Filho SR, Oliveira IR. Olanzapine versus conventional antipsychotics: long‐term risk of tardive dyskinesia. 156th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2003 May 17‐22; San Francisco, USA. 2003. [[NR254]]
Littrell 1999 {published data only}
-
- Littrell KH. Patients switched from depot antipsychotics to oral risperidone or olanzapine:an open‐label randomized trial. APA Annual Meeting, May 15‐20, 1999, Washington, DC. 1999. [CSG NO. 4111]
Loza 1999 (HGDT) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Eli‐Lilly unpublished document. HGDT Olanzapine Versus Chlorpromazine in Egypt. Unpublished Document Internal to Eli‐lilly 2001:1‐513.
-
- Loza N, El‐Dosoky AM, Okasha TA, Khalil AH, Hasan NM, Dossenbach M, Kratky P, Okasha A. Olanzapine compared to chlorpromazine in acute schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1999;9(Suppl 5):S291.
Malyarov 1999 {published data only}
-
- Malyarov S, Dzub G. Comparative assessment of the positive and negative symptom dynamics in schizophrenic patients treated with atypical antipsychotics or haloperidol. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999:S296. [MEDLINE: ]
Martin 2002 {published data only}
-
- Fleurot O, Martins S, Loo H, Peuskens J, Rein W. Amisulpride vs olanzapine in schizophrenia. Preliminary results on short‐term analysis. European Psychiatry (11th Association of European Psychiatrists Congress, 2002 4‐8th May, Stockholm, Sweden). 2002, issue Suppl 1:107s. [data now published my Martin]
-
- Martin S, Loo H, Peuskens J, Rein W, Fleurot O. A six‐month, double‐blind, controlled trial in schizophrenic patients comparing amisulpride and olanzapine. Preliminary results on short‐term analysis. European Neuropsychopharmacology: The Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2002;12(Supplement 3):S329.
-
- Martin S, Loo H, Peuskens J, Thirumalai S, Giudicelli A, Fleurot O, Rein W. A Double‐blind, randomised, comparative trial of amisulpride versus olanzapine in the treatment of Schizophrenia: short‐term results at two months. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2002;18(6):355‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Martin SD, Loo H, Peuskens J, Rein W, Fleurot O. A six‐month, double‐blind, controlled trial in schizophrenic patients comparing amisulpride and olanzapine. Preliminary results on short‐term analysis. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (Abstracts of the 23rd Congress of the Collegium Internationale Neuro‐Psychopharmacologicum; 2002 Jun 23‐27; Montreal, Canada). 2002, issue Suppl 1:S119.
-
- Mortimer A. A six month international controlled trial of the therapeutic activity of amisulpride 200 to 800mg/day versus olanzapine 5 to 20 mg/day in patients with schizophrenic disorders' (The solianol study). National Research Register 2002; Vol. 1. [N0084096619]
McQuade 2003 {unpublished data only}
-
- Dubitsky GM, Harris R, Laughren T, Hardeman S. Abilify (aripiprazole) tablets, medical review part 3. www.fda.gov/cder/foi/nda/2002/21‐436_Abilify.htm. U.S. Food and Drug Administration CDER, 2002:111‐175.
-
- McQuade RD, Jody DN, Kujawa MJ, Carson WH, Iwamoto T, Archibald DG, et al. Long‐term weight effects of aripiprazole vs. olanzapine. 156th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2003 May 17‐22; San Francisco, USA 2003.
Meltzer (InterSept) {published data only}
-
- *Meltzer HY, Alphs L, Green AI, Altamura AC, Anand R, Bertoldi A, Bourgeois M, Chouinard G, Islam MZ, Kane J, Krishnan R, Lindenmayer JP, Potkin S, International Suicide Prevention Trial Study Group. Clozapine treatment for suicidality in schizophrenia: International Suicide Prevention Trial (InterSePT).. Archives of General Psychiatry 2003;60(1):82‐91. - PubMed
-
- Glick ID, Zaninelli R, Hsu C, Young FK, Weiss L, Gunay I, Kumar V. Patterns of concomitant psychotropic medication use during a 2‐year study comparing clozapine and olanzapine for the prevention of suicidal behavior.. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2004;65(5):679‐85. - PubMed
-
- Kane J, Alphs LD, Meltzer HY, Green AI, Hsu C, Anand R, Young F, Fahy T. The relationship between clinical response and changes in weight for clozapine and olanzapine‐treated patients. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (Abstracts of the 23rd Congress of the Collegium Internationale Neuro‐Psychopharmacologicum; 2002 Jun 23‐27; Montreal, Canada). 2002, issue Suppl 1:S171.
-
- Kerwin R. A prospective randomised international parallel‐group comparison of clozapine versus olanzapine in the reduction of suicide attempts in patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder at risk for suicide. National Research Register (N0042002860). 2000. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Meltzer H. Decreasing suicide in schizophrenia: the intersept study. European Psychiatry (11th Association of European Psychiatrists Congress, 2002 4‐8th May, Stockholm, Sweden). 2002, issue Suppl 1:26s.
Naber 2001 (HGBF) {published data only}
-
- Bender S, Balcar A, Dittmann‐Schall U, Klimke A, Riedel M, Vorbach U, Kuehn KU, Lambert M, Dittmann RW, Naber D. Effects of olanzapine versus clozapine on executive functions in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research (Abstracts of the 11th Biennial Winter Workshop on Schizophrenia). Elsevier Science B.V, 2002, issue 3 Suppl.1:194. [Probably Not Elli Lilly study]
-
- Dittmann‐Balcar A, Bender S, Schall U, Klimke A, Mueller N, Vorbach U, Kuehn KU, Dittmann RW, Naber D. Effects of olanzapine versus clozapine on executive functions in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 2003;60:131. [EMBASE: 2003241517]
-
- Naber D, Bandelow B, Bender S, Klimke A, Ku"hn K, Lambert M, Lemmer W, Dittmann M, Riedel ER. Subjective well‐being under neuroleptic treatment with olanzapine versus clozapine: first results from a double‐blind clinical trial using the swn self‐rating scale. Schizophrenia Research (8th International Congress on Schizophrenia Research; 2001 Apr 28 ‐ May 2; British Columbia, Canada). 2001, issue 1‐2 Suppl:240.
-
- Naber D, Degner D, Bender S, Klimke A, Kuhn KU, Lambert M, Lemmer W, Riedel M, Vorbach EU, Dittmann RW. Olanzapine vs. clozapine: findings on subjective well‐being from a double‐blind clinical trial. Schizophrenia Research (Abstracts of the 11th Biennial Winter Workshop on Schizophrenia). Elsevier Science B.V, 2002, issue 3 Suppl.1:176.
Namjoshi 2002 {unpublished data only}
-
- Namjoshi M, Young C, Huang L, Edgell ET, Breier A. Conical and quality‐of‐life outcomes associated with olanzapine, risperidone, and haloperidol treatment in patients with schizophrenia: results from a US random study. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (Abstracts of the 23rd Congress of the Collegium Internationale Neuro‐Psychopharmacologicum; 2002 Jun 23‐27; Montreal, Canada). 2002, issue Suppl 1:S127.
-
- Namjoshi M, Young CA, Huang L, Edgell E, Breier A. Cost‐effectiveness of olanzapine compared to risperidone and haloperidol in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia: Results from a U.S. randomized controlled trial. Schizophrenia Research 2003;60:296. [N0146099645]
-
- Namjoshi M, Young CA, Huang L, Edgell E, Breier A. Cost‐effectiveness of olanzapine compared to risperidone and haloperidol in the treatment of patients with schizophrenia: results from a U.S. randomized controlled trial. Schizophrenia Research International Congress on Schizophrenia Research, March29‐April 2, 2003, Colorado Springs, CO. 2003. [EMBASE 2003496187]
-
- Namjoshi M, Young Cm, Huang L, Edgell ET, Breier A. Hospitalization rates associated with olanzapine, risperidone, and haloperidol treatment in patients with schizophrenia: Results from a U.S. randomized controlled trial. European Neuropsychopharmacology: The Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002, issue Supplement 3:S315.
Ritchie 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ritchie CW, Chiu E, Harrigan S, Hall K, Hassett A, Macfarlane SMM, O'Connor DW, Opie J, Ames D. The impact upon extra‐pyramidal side effects, clinical symptoms and quality of life of a switch from conventional to atypical antipsychotics (risperidone or olanzapine) in elderly patients with schizophrenia. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2003;18(5):432‐40. [MEDLINE: ; PMID 12766921] - PubMed
Rosenheck 2003(HGFI) {published data only}
-
- Davis L, Sheikh J, Rosenheck R, Frecska E, Douyon R, Evans D, Smith‐Gamble V, Herz L, Grabowski J, Jasty V, Smelson D, Graeber D, Allan E, Corwin J, Dunn L, Kwon K, Caroff S, Gurklis JA. To determine if olanzapine is more cost effective than haloperidol for the treatment of schizophrenia. / The clinical and economic impact of olanzapine in the treatment of schizophrenia. National Institutes of Health (http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ accessed 16th Feb 2001). 2001.
-
- Glazer WM. Effectiveness and cost of olanzapine and haloperidol in the treatment of schizophrenia: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2004;291(9):1064‐5. [PsycINFO 2004‐11623‐005] - PubMed
-
- Rosenheck R, Perlick D, Bingham S, Liu‐Mares W, Collins J, Warren S, Leslie D, Allan E, Campbell EC, Caroff S, Corwin J, Davis L, Douyon R, Dunn L, Evans D, Frecska E, Grabowski J, Graeber D, Herz L, Kwon K, Lawson W, Mena F, Sheikh J, Smelson D, Smith‐Gamble V. Effectiveness and cost of olanzapine and haloperidol in the treatment of schizophrenia: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2003;290(20):2693‐702. - PubMed
Simpson 2004 {published data only}
-
- Fryburg DA, O'Sullivan RL, Siu C, Simpson G. Insulin resistance in olanzapine and ziprasidone treated subjects: interim results of a double‐blind controlled six‐week trial. 39th Annual Meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology; 2000; Dec 10‐14; San Juan; Puerto Rico. 2000.
-
- Glick ID, Fryburg D, O'Sullivan RL, Siu C, Simpson G. Ziprasidone's benefits versus olanzapine regarding weight and insulin resistance. European Neuropsychopharmacology (Abstracts of the 14th Congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology; 2001 Oct 13‐17; Istanbul, Turkey). 2001, issue 3:273.
-
- Harvey P, Simpson GM, Loebel A. Ziprasidone vs olanzapine for cognitive function in schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology: The Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2002;17(Supplement 3):S293.
-
- O'Sullivan R, Fryburg D, Siu C, Simpson G. Insulin resistance in olanzapine and ziprasidone treated subjects: interim results of a double‐blind controlled six‐week trial. Schizophrenia Research (8th International Congress on Schizophrenia Research; 2001 Apr 28 ‐ May 2; British Columbia, Canada). 2001, issue 1‐2 Suppl:241.
-
- Simpson G, Horne RL, Weiden PJ, Pigott T Bari M, Romano SJ. Ziprasidone vs olanzapine in schizophrenia: a double‐blind trial. European Psychiatry (11th Association of European Psychiatrists Congress, 2002 4‐8th May, Stockholm, Sweden). 2002, issue Suppl 1:101s.
Svestka 2003 {published data only}
-
- Svestka J, Synek O, Zourkova A. A double‐blind comparison of olanzapine and quetiapine in treatment of acute exacerbations of schizophrenic or schizoaffective disorders. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2003;13(4):S291. [P.2.031]
Thomas 1998 (HGBU) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Grainger, D, Gureje O, Lambert T, Tran PV, Andersen SW. Olanzapine versus risperidone in the management of schizophrenia: a randomized, double‐blind study in Australia and New Zealand. World Psychiatric Association Annual Meeting. 1999;Hamburg, Germany, August 6‐11. 1999. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Gregor K, Gureje O, Lambert T, Grainger D, Tran PV, Andersen SW, and the Australasian Olanzapine Study Group. Olanzapine versus risperidone in the management of schizophrenia: a randomized, double‐blind study in Australia and New Zealand. World Psychiatric Association. Hamburg, Germany. August 1999.
-
- Gureje O, Catts S, Fraser A, Hustig H, Keks N, Lambert Y, McGrath J, Miles W, Thomas A, Grainger D, Andersen S, Tollefson G. Olanzapine versus risperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia and related psychotic disorders. XXIst Collegium Internationale Neuro‐psychopharmacologicum. Glasgow, Scotland, UK. July 12‐16, 1998.
-
- Gureje O, Lambert T, Grainger D, Tran PV, Andersen SW. Olanzapine versus risperidone in the management of schizophrenia: a randomized, double‐blind study in Australia and New Zealand. 21st Congress of the Collegium Internationale Neuro‐psychopharmacologicum; 1998 Jul 12‐16; Glasgow, Scotland. 1998. [MEDLINE: ; published now (Thomas HGBU) Gureje]
-
- Gureje O, Miles W, Keks N, Grainger D, Lambert T, McGrath J, Tran P, Catts S, Fraser A, Hustig H, Andersen S, Crawford AM. Olanzapine vs risperidone in the management of schizophrenia: a randomized double‐blind trial in Australia and New Zealand. Schizophrenia Research 2003;61(2‐3):303‐14. - PubMed
Tollefson 1997(HGAJ) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Alan B, Hamilton SH. Comparative efficacy of olanzapine and haloperidol for patients with treatment resistant schizophrenia. 11th World Congress of Psychiatry; 1999 Aug 6‐11; Hamburg, Germany. 1999:144. - PubMed
-
- Almond S, O'Donnell O. Cost analysis of the treatment of schizophrenia in the UK: a comparison of olanzapine and haloperidol. Pharmacoeconomics 1998;13(5 part 2):575‐88. - PubMed
-
- Andersen S, Cohen L, Goldstein J, Tohen M, Tollefson G. Sex and neuroendocrine differences in response to treatment with olanzapine: a preliminary analysis. Schizophrenia Research 1998;29(1‐2):186‐7.
-
- Andersen SW, Tollefson GD, Sanger T. Depressive signs and symptoms in schizophrenia:a prospective blinded trial of olanzapine and haloperidol. APA Annual Meeting; May 15‐20; Washington DC; USA. 1999. [CSG NO. 4125] - PubMed
-
- Baker R W, Julier B, Stauffer V. Manic‐like symptoms in schizophrenic patients treated with olanzapine, haloperidol and placebo. 7th World Congress of Biological Psychiatry; 2001 Jul 1‐6; Berlin, Germany. 2001, issue Suppl. 1.
Tollefson 1997 Conti {published data only}
-
- Basson B, Kinon BJ, Gilmore JA, Taylor CC, Tollefson GD, Czekalla J. Factors influencing weight change in patients with schizophrenia treated with olanzapine verus haloperidol or risperidone. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2000;14(3 Suppl):A60. [MEDLINE: ; PMID 22476629] - PubMed
-
- Beasley CM. Safety of olanzapine. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1997;15(2):19‐21. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE 2003516387] - PubMed
-
- Goldstein JM, Cohen LS, Horton NJ, Lee H, Andersen S, Tohen M, Crawford A, Tollefson G. Sex differences in clinical response to olanzapine compared with haloperidol.. Psychiatry Research 2002;110(1):27‐37. [MEDLINE: ; CENTRAL CN‐00389114] - PubMed
-
- Jaton LA, Kinon BJ, Rotelli MD, Kaiser C, Kollack‐Walker S. Differential rate of weight gain present among patients treated with olanzapine. Schizophrenia Research 2003;60:S357. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE 2003516387]
-
- Kennedy JS, Jeste D, Kaiser CJ, Golsham S, Maguire GA, Tollefson G, Sanger T, Bymaster FP, Kinon BJ, Dossenbach M, Gilmore JA, Breier A. Olanzapine vs haloperidol in geriatric schizophrenia: analysis of data from a double‐blind controlled trial. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2003;18:1013‐20. [MEDLINE: ; PsycINFO 2003‐10341‐008; EMBASE 2003491563] - PubMed
Tollefson 1999(HGDY) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Burns P, Tollefson GD, Dellva MA, Mattler CA, Kinon BJ, Grundy SL. A controlled, double‐blind investigation of the clozapine discontinuation syndrome with conversion to either olanzapine or placebo. Presented at the 2nd Annual Meeting of the College of Psychiatric and Neurologic Pharmacists. March 25‐28, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA. 1999.
-
- Dellva MA, Tollefson GD, Mattler CA, Kinon BJ, Grundy SL. A controlled, double‐blind investigation of the clozapine discontinuation syndrome with conversion to either olanzapine or placebo. Presented at the ICSR. April 17‐21, Sante Fe, NM, USA. 1999. - PubMed
-
- Mallinckrodt C, David S, Burns P, Breier A. Long term efficacy and safety of olanzapine in patients with inadequate initial response to haloperidol or olanzapine. 11th Congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology, Paris, France. 1998. [CSG NO. 3360]
-
- Tollefson GD, Dellva MA, Mattler CA, Kinon BJ, Grundy SL. A controlled, double‐blind investigation of the clozapine discontinuation syndrome with conversion to either olanzapine or placebo. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1998;8(Suppl 2):229.
-
- Tollefson GD, Mattler CA, Dellva MA, et al. Controlled, double‐blind investigation of clozapine discontinuation syndrome and switching with conversion to either olanzapine or placebo. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology Accepted 1998, due to be published October 1999. - PubMed
Tran 1997 (HGBG) {published and unpublished data}
-
- *Tran PV, Hamilton SH, Kuntz AJ, Potvin JH, Andersen SW, Beasley C Jr, Tollefson GD. Double‐blind comparison of olanzapine versus risperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1997;17:407‐18. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed S, Zhang F, Lindborg S, Tohen M, Breier A. A comparison of olanzapine versus risperidone on improvement in negative symptoms and emotional discomfort in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 2003;60:270. [EMBASE: 2003241517]
-
- Ahmed S, Zhang F, Walker D, Beglinger L, Earley WR, Tran PV. Olanzapine versus risperidone for treatment of negative symptoms in schizophrenia. 156th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2003 May 17‐22; San Francisco, USA. 2003. [[NR247]]
-
- Basson B, Kennedy J, Tollefson G, Tran, Beasley C, Bymaster F. The comparative anti muscarinic like adverse event profiles of olanzapine and risperidone treatment in patients with schizophrenia spectrum psychosis. 11th World Congress of Psychiatry; 1999 Aug 6‐11; Hamburg, Germany. 1999:142.
-
- Basson B, Kinon BJ, Gilmore JA, Taylor CC, Tollefson GD, Czekalla J. Factors influencing weight change in patients with schizophrenia treated with olanzapine verus haloperidol or risperidone. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2000;14(3 Suppl):A60. [MEDLINE: ; PMID 22476629] - PubMed
Wang 2002 {published data only}
-
- Wang C, Feng Y, Wang L. A double‐blind randomized controlled study of olanzapine and clozapine on treatment of schizophrenia. Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry 2002;14(3):143‐5. [MEDI0312]
Wang 2003 {published data only}
-
- Wang Kangjian, Zhang Kai. A study of olanzapine and clozapine in the treatment of schizophrenia. Shandong Archives of Psychiatry 2003;16(03):141‐3. [MEDI0310]
References to studies excluded from this review
Addington 1998 {published data only}
-
- Addington DE, Addington JM. Costs of novel antipsychotics in clinical practice. 151st Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association. Toronto, ON, Canada. May 30‐June 4, 1998.
Allison 1998 {published data only}
-
- Allison DB, Mentor JL, Heo M, Weiden PJ, Chandler LP, Cappelleri J. Weight gain associated with conventional and newer antipsychotics: a meta‐analysis. 151st Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association. Toronto, ON, Canada. May 30‐June 4, 1998.
-
- Allison DB, Mentor JL, Heo M, Weiden PJ, Chandler LP, Cappelleri J. Weight gain associated with conventional and newer antipsychotics: a meta‐analysis. Proceedings of XXIst Collegium Internationale Neuro‐psychopharmacologicum. Glasgow, Scotland, UK. July 12‐16, 1998:american j of psychiatry 1999 vol 156, p1686‐96. [American J of Psychiatry 1999 vol 156, p1686‐96]
Apicella 2001 {published data only}
-
- Apicella A. National Alliance for Research on Schizophrenia ns Depression. www.mhsource.com/narsad/bd/studyops.html 2001.
Apiquian 2003 {published data only}
-
- Apiquian R, Fresan A, errera K, Ulloa RE, Loyzaga C, LaFuente‐Sandoval C, Gutierrez D, Nicolini H. Minimum effective doses of haloperidol for the treatment of first psychotic episode: a comparative study with risperidone and olanzapine. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2003;6(4):403‐8. [EMBASE: 2004054013] - PubMed
Aquila 2000 (HGEC) {published data only}
-
- Aquila R, Weiden PJ, Kinon BJ, Milton DR, Zygmunt A, Swindle RW, Stauffer VL. Effectiveness of olanzapine upon psychiatric and vocational rehabilitation outcomes. 153rd Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2000 May 13‐18; Chicago, USA. 2000.
Arango 2001 {published data only}
-
- Arango C, Summerfelt A, Buchanan RW. Olanzapine effects on auditory sensory gating in schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 2003;160(11):2066‐8. [PMID 14594761] - PubMed
-
- Arango C, Summerfelt AT, Buchanan RW. Lack of P50 changes in a randomized double blind study of olanzapine and haloperidol. Schizophrenia Research 2001;49(1‐2 Suppl):197. [MEDLINE: ]
Awad 2002b {published data only}
-
- Awad AG, Vourganti L, Dugar A. Patient attitude after switch to ziprasidone from other antipsychotics. European Psychiatry (11th Association of European Psychiatrists Congress, 2002 4‐8th May, Stockholm, Sweden) 2002;17(Suppl 1):102s. [probably Pfizzer study]
Baker 2003 {published data only}
-
- Baker R, Kinon BJ, Liu H, Richey A, Hill AL, Bergstrom RF, Schuh LM. Effectiveness of rapid initial dose escalation of oral olanzapine for acute agitation. Schizophrenia Research 2003;60:272. [EMBASE 2003496187]
-
- Baker RW, Kinon BJ, Maguire GA, Liu H, Hill AL. Effectiveness of rapid initial dose escalation of up to forty milligrams per day of oral olanzapine in acute agitation. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2003;23(4):342‐8. [PMID 12920409] - PubMed
Beasley 1996c {published data only}
-
- Beasley C, Tollefson G, Wood G, Tran P, Satterlee W, Beuzen J. Safety overview of Olanzapine. Xth World Congress of Psychiatry. Madrid, Spain. August 23‐28, 1996.
Beasley 2003 (HGGI) {published data only}
-
- Beasley CM, Hamilton SH, Dossenbach M. Relapse prevention with olanzapine. Schizophrenia Research 2000;41(1):196‐197. [CSG NO. 4512]
-
- Beasley CM, Sutton VK, Hamilton SH, Walker DJ, Dossenbach M, Taylor CC, Alaka KJ, Bykowski D, Tollefson GD. A double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial of olanzapine in the prevention of psychotic relapse. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2003;23(6):582‐94. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Beasley Jr C, Hamilton S, Dossenbach M. Relapse prevention with olanzapine. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2000;10(Suppl 3):S304.
Beuzen 1996 (HGCE) {published data only}
-
- Beuzen JN. Olanzapine ‐ cognitive and motor effects in healthy elderly. Xth World Congress of Psychiatry. Madrid, Spain. August 23‐28, 1996.
-
- Taylor N, Beuzen JN, Wesnes K, Wood A. The effect of olanzapine on cognition and psychomotor function in healthy elderly volunteers. Schizophrenia Research 1996;18(2‐3):VC2. - PubMed
Birkett 1994 {published data only}
-
- Birkett P. State of the Art ‐ Winter Workshop on Schizophrenia, Les Diablerets, Switzerland, January 1994. Journal of Psychopharmacology 1995;9(2):157‐60. - PubMed
Breier 2003 {published data only}
-
- Breier A, Young C, Purdon SE, Gold JM, Davis, KL, Keefe RSE. A one year Double‐blind Comparision of the Neurocognitive Efficacy of Olanzapine, Risperidone and Haloperidol in Patients with Schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research March 29 ‐ April 2003; Colorado Springs, CO. 2003. - PubMed
Britto 2002 {published data only}
-
- Britto D. Ziprasidone Quality of Life study in the treatment of chronic schizophrenia. National Research Register 2002; Vol. 1. [N0083099522]
Buchanan 2003 {published data only}
-
- Buchanan RW, Ball MP, Weiner E, Kirkpatrick B, Gold J, Carpenter WT. Olanzapine treatment of residual positive and negative symptoms. Schizophrenia Research 2003;60:275. [EMBASE: 2003241517] - PubMed
Burgoyne 1996 {published data only}
-
- Burgoyne K, Ananth J, Gadasally R, Smith M. Maintenance treatment with olanzapine for schizophrenic patients. Proceedings of XXIst Collegium Internationale Neuro‐psychopharmacologicum. Glasgow, Scotland, UK. July 12‐16, 1998.
-
- Burgoyne K, Ananth J, Smith M, Swartz JR, Gadasally R, Arns P. Olanzapine versus haloperidol: the results of a double‐blind study on acute psychotic patients. XXth Collegium Internationale Neuro‐psychopharmacologicum. Melbourne, Australia. June 23‐27, 1996.
Castilla 2002 {published data only}
-
- Castilla R. Early medication intervention in the treatment of psychosis in children. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (Abstracts of the 23rd Congress of the Collegium Internationale Neuro‐Psychopharmacologicum; 2002 Jun 23‐27; Montreal, Canada). 2002, issue Suppl 1:S51.
Clouth 1999 {published data only}
-
- Clouth J. Pharmacoeconomic evaluation of the treatment of schizophrenia in germany:a comparison of olanzapine and haloperidol. APA Annual Meeting, May 15‐20, 1999, Washington, DC. 1999. [CSG NO. 4109]
Corya 2002 (HGGA) {published data only}
-
- Corya S, Dubé S, Andersen SW, Sanger TM, Clemow D, Tohen M, Tollefson GD. Olanzapine‐fluoxetine combination for psychotic major depression. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (Abstracts of the 23rd Congress of the Collegium Internationale Neuro‐Psychopharmacologicum; 2002 Jun 23‐27; Montreal, Canada). 2002, issue Suppl 1:S144. [lilly data]
Cutler 2002 {published data only}
-
- Cutler NR, Simpson G, Weiden PJ, Romanoa SJ. Effects of oral ziprasidone on weight and serum lipids in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research (Abstracts of the 11th Biennial Winter Workshop on Schizophrenia). Elsevier Science B.V, 2002, issue 3 Suppl.1:160.
Dalheim 1997 {published data only}
-
- Dalheim LJ, Weiden PJ, Aquila R, Standard J, Emanuel M, Zygmunt A. Olanzapine crossover in stable outpatients. American Psychiatric Association, 150th Annual Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA. 1997.
Davis 1998 {published data only}
-
- Davis JM, Janicak PG, Sharma RP, Manav R. Comparisons of the effects of the newer atypical antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia: a meta‐analysis. 151st Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association. May 30‐June 4, Toronto, ON, Canada. 1998. [now published ‐ independent data not lilly]
-
- Davis JM, Sharma RP, Manav R. Comparisons of the effects of the newer atypical antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia: a meta‐analysis. 151st Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association. May 30‐June 4, Toronto, ON, Canada. 1998.
Devanand 1998 {published data only}
-
- Devanand DP. Classic neuroleptics in dementia. 151st Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association. Toronto, ON, Canada. May 30‐June 4, 1998.
-
- Devanand DP, Michaels K, Sackeim HA, Marder K, Mayeux RP. Antipsychotics in the treatment of dementia complicated by psychosis. 151st Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association. Toronto, ON, Canada. May 30‐June 4, 1998.
Docherty 2002 {published data only}
-
- Docherty JP, Napolitano J, Mahmoud RA, Martinez RA, Lasser RA, Pandina GJ, Gharabawi G. Anticholinergic effect of atypical antipsychotics in elderly patients. 155th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2002 May 18‐23; Philadelphia, PA, USA. 2002.
-
- Tune L, Mulsant B, Gharabawi G. Anticholinergic effect of atypical antipsychotics in elderly patients. European Neuropsychopharmacology: The Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2002;12(Supplement 3):S314.
Dolnak 2000 {published data only}
-
- Dolnak DR, Hyman Rapaport M, Caligiuri M, Lohr J, Golshan S. A prospective, randomized, double‐blind study contrasting motor dysfunction, negative symptoms and functioning in schizophrenic patients treated with olanzapine and risperidone.. 40th Annual Meeting of the New Clinical Drug Evaluation Unit (NCDEU); 2000 May 30 ‐ Jun 2; Boca Raton, Florida, USA. 2000:133.
-
- Dolnak DR, Minn K, Wieneke M, Watson, Espinoza S. Olanzapine versus haloperidol in the treatment of schizophrenia. American Psychiatric Association, 149th Annual Meeting. May 4‐9, 1996.
-
- Dolnak DR, Rapaport MH, Michael C, Shahrokh G. Motor dysfunction in schizophrenia. 153rd Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2000 May 13‐18; Chicago, USA. 2000.
-
- Dolnak DR, Rapaport MH, Michael C, Shahrokh G. Motor dysfunction in schizophrenia. 155th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2002 May 18‐23; Philadelphia, PA, USA. 2002.
-
- Dolnak R, Rapaport MH. A prospective, randomized, doubleblind study examining functioning in schizophrenic patients treated with olanzapine and risperidone. Schizophrenia Research (8th International Congress on Schizophrenia Research; 2001 Apr 28 ‐ May 2; British Columbia, Canada). 2001, issue 1‐2 Suppl:225‐6. [MEDLINE: ]
Dossenbach 1997 {published data only}
-
- Dossenbach M, Friedel P, Folnegovic V, Jackovljevic M, Hutujac L, Uglesic B, Dodig G. Olanzapine vs. fluphenazine ‐ 6 weeks treatment of acute schizophrenia. 10th European Colleague of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress 1997 September 13‐17 Vienna. 1997.
Finzen 2002 {published data only}
-
- Finzen A. Changing neuroleptics: From new to conventional ‐ And vice versa [Neuroleptikawechsel: von atypischen zu konventionellen und zuruck ‐ und ‐ umgekehrt]. Psychiatrische Praxis 2002;29(8):445‐6.
Fleming 1999 {published data only}
-
- Fleming K, Potkin SG, Alva G, Carreon D. Dissociation of improvement in neurocognition and negative symptomatology with olanzapine and clozapine conference abstract. Schizophrenia Research (Abstracts of The 7th International Congress on Schizophrenia Research; 1999 Apr 17‐21; Santa Fe, USA). 1999:279.
Gallinat 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gallinat J, Riedel M, Juckel G, Sokullu S, Frodl T, Moukhtieva R, Mavrogiorgou P, Nissle S, Muller N, Danker‐Hopfe H, Hegerl U. P300 and symptom improvement in schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 2001;158(1):55‐65. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gothelf 2003 {published data only}
-
- Gothelf D, Apter A, Reidman J, Brand‐Gothelf A, Bloch Y, Gal GKL, Tyano S, Weizman R, Ratzoni G. Olanzapine, risperidone and haloperidol in the treatment of adolescent patients with schizophrenia. Journal of Neural Transmission 2003;110(5):545‐60. [MEDLINE: ; PMID 12721815] - PubMed
Hrdlicka 2001 {published data only}
-
- Hrdlicka M, Rosillon D, Duchesne I. Czech results of the RODOS study: Comparison of Risperidone and Olanzapine from the point of view of efficacy, tolerability and treatment costs [Ceske vysledky studie RODOS: Porovnani risperidonu a olanzapinu z hlediska ucinnosti, snasenlivosti a nakladu lecby]. Ceska A Slovenska Psychiatrie 2001;97(7):343‐9. [should be 3 publications Janssen data]
Irwin 2003 {published data only}
-
- Irwin J, Moses SN, Edgar JC, Torres F, Thoma RJ, Hanlon FM, Anderson L, Weisend MP, Miller GA, Tuason VB, Canive JM. Olanzapine and risperidone in schizophrenia: A randomized double‐blind crossover study. Schizophrenia Research. 2003; Vol. 60:286. [EMBASE: 2003241517]
Jarboe 2001 {published data only}
-
- Jarboe KS, Lewine RR. Haloperidol versus olanzapine induced weight gain and clinical relevance, a double‐blind and open label comparison. Schizophrenia Research (8th International Congress on Schizophrenia Research; 2001 Apr 28 ‐ May 2; British Columbia, Canada). 2001, issue 1‐2 Suppl:232. [MEDLINE: ]
Javitt 2001 {published data only}
-
- Javitt DC, Silipo G, Cienfuegos A, Shelley AM, Bark N, Park M, Lindenmayer JP, Suckow R, Zukin SR. Adjunctive high‐dose glycine in the treatment of schizophrenia. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2001;4(4):385‐91. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jerrell 2002 {published data only}
-
- Jerrell JM. Cost‐effectiveness of risperidone, olanzapine, and conventional antipsychotic medications. Schizophrenia Bulletin 2002;28(4):589‐605. [EMBASE 2003196530] - PubMed
Kalali 2000 {published data only}
-
- Kalali A, Lasser R, Campbell B, Cucchiaro J, El‐Bizri H, Guven A, Matkovits‐Gupta T, Nann‐Vernotica E, Narurkar M, Pirozzi C, Gharabawi G. The management of cultural differences and the importance of safety monitoring in global studies: the realize clinical program. 39th Annual Meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology; 2000; Dec 10‐14; San Juan; Puerto Rico. 2000.
Kinon (HGFW) {published data only}
-
- Kinon BJ, Basson B, Wang J, Malcolm SK. Rapid reduction in hyperprolactinemia upon switching treatment to olanzapine from conventional antipsychotic drugs or risperidone. Schizophrenia Research 2000;41(1):194‐95. [CSG NO. 4510]
-
- Kinon BJ, Basson B, Wang J, Malcolm SK, Stauffer VL. Rapid reduction in hyperprolactinemia upon switching treatment to olanzapine from conventional antipsychotic drugs or risperidone. 40th Annual Meeting of the New Clinical Drug Evaluation Unit (NCDEU); 2000 May 30 ‐ Jun 2; Boca Raton, Florida. 2000. [N0146103028]
-
- Kinon BJ, Basson BR, Malcolm SK, Breier A. Strategies for switching from conventional antipsychotic drugs and risperidone to olanzapine. World Congress of Psychiatry (WPA). Hamburg, Germany. August 8‐11, 1999.
-
- Kinon BJ, Basson BR, Malcolm SK, Tollefson GD. Strategies for switching from conventional antipsychotic drugs and risperidone to olanzapine. 2nd Annual Meeting of the College of Psychiatric and Neurologic Pharmacists. Lake Tahoe, NV, USA. March 25‐28, 1999.
-
- Kinon BJ, Basson BR, Malcolm SK, Tollefson GD. Strategies for switching from conventional antipsychotic drugs and risperidone to olanzapine. American College of Neuropsychopharmacology (ACNP). Las Carabas, Puerto Rico. December 14‐18, 1998.
Kinon 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ahl J. Olanzapine reduces neuroleptic‐induced hyperprolactinemia in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 2003;60:350. [EMBASE: 2003241517]
-
- Kinon BJ, Liu H, Ahl J. Sexual dysfunction associated with neuroleptic‐induced hyperprolactinemia improves with reduction in prolactin levels. 156th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2003 May 17‐22; San Francisco, USA. 2003. [[NR552]] - PubMed
-
- Kinon BJ, Liu H, Ahl J, Baker RW. Longitudinal effects of olanzapine on fasting serum lipids: a randomized, prospective, four‐ month study. 156th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2003 May 17‐22; San Francisco, USA. 2003. [[NR553]]
-
- Kinon BJ, Milton DR, Hill AL, Williamson DJ. Effective resolution of acute presentation of behavioral agitation and positive psychotic symptoms in schizophrenia with olanzapine. Journal of Psychopharmacology. 2000; Vol. 14, issue 3:A60. [N0146103028]
Knegtering 2000 {published data only}
-
- Knegtering R, Boks M, Wiersma D, Blijd C, Bruggeman R, Oer RBV. Sexual dysfunctions in patients on antipsychotics. 155th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2002 May 18‐23; Philadelphia, PA, USA. 2002.
-
- Knegtering R, Boks M, Wiersma D, Blijd C, Bruggeman R, Oer RB. Sexual dysfunctions in patients on antipsychotics. 153rd Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2000 May 13‐18; Chicago, USA. 2000.
-
- Knegtering R, Castelein S, Bous H, Linde J, Bruggeman R, Kluiter H, Bosch RJ. A Randomized Open‐Label Study of the Impact of Quetiapine Versus Risperidone on Sexual Functioning. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2004;24(1):56‐61. [EMBASE: 2004050225] - PubMed
Kolff 2000 {published data only}
-
- Kolff M, Coenen A, Dis H, Duigemans P. Differential effects of antipsychotic drugs on clinical symptoms and cognitive functions in the treatment of schizophrenia. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2000, issue Suppl 2:S59.
Kucerova 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kucerova H. Olanzapine and improvement of tardive dyskinesia. European Psychiatry 2002;17(7):421‐4. - PubMed
Lahti 1999a {published data only}
-
- Lahti AC, Holcomb HH, Weiler MA, Parwani A, Michaelidis T, Medoff DR, Tamminga CA. Changes rcbf after acute challenge with haloperidol and olanzapine in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research (Abstracts of The 7th International Congress on Schizophrenia Research; 1999 Apr 17‐21; Santa Fe, USA). 1999:224. [MEDLINE: ]
Lahti 1999b {published data only}
-
- Lahti AC, Weiler MA, Parwani A, Holcomb HH, Michaelidis T, Warfel D, Tamminga CA. Blockade of ketamine‐induced psychosis with olanzapine. Schizophrenia Research (Abstracts of The 7th International Congress on Schizophrenia Research; 1999 Apr 17‐21; Santa Fe, USA). 1999:310. [MEDLINE: ]
Lilly (HGBM) 1999 {unpublished data only}
-
- Eli Lilly. Open‐label clinical trial on antipsychotic efficacy and safety of olanzapine in schizophrenic patients with positive or negative symptomatology. Data supplied to the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group 1999.
Lilly (HGCL) 1999 {unpublished data only}
-
- Eli Lilly. Efficacy and safety of olanzapine in the treatment of schizophrenic, schizophreniform and schizoaffective patients in Saudi Arabia. Data supplied to the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group 1999.
Lilly (HGCV) 1999 {unpublished data only}
-
- Eli Lilly. Olanzapine in schizophrenic patients intolerant of, or resistant to, clozapine. Data supplied to the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group 1999.
Lilly (HGDU) 1999 {unpublished data only}
-
- Eli Lilly. Safety and efficacy of olanzapine in patients with severe haloperidol side effects in Romania. Data supplied to the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group 1999.
Lilly (HGDZ) 1999 {unpublished data only}
-
- Eli Lilly. Efficacy and safety of olanzapine in the treatment of schizophrenic and schizoaffective patients in Russia. Data supplied to the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group 1999.
Lilly (HGEP) 1999 {unpublished data only}
-
- Eli Lilly. Open‐label olanzapine. Data supplied to the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group 1999.
Lilly (HGFM) 1999 {unpublished data only}
-
- Eli Lilly. Efficacy and safety of olanzapine in the treatment of schizophrenic patients in China. Data supplied to the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group. 1999.
Lindenmayer 1998 {published data only}
-
- Lindenmayer JP. Beyond symptoms: optimizing real‐world outcomes. 151st Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association. Toronto, ON, Canada. May 30‐June 4, 1998.
Loza 2001 {published data only}
-
- Loza B. Atypical antipsychotic treatment prognosis in first‐episode paranoid schizophrenia based on syllabic and language‐related dichotic listening scores. European Neuropsychopharmacology: The Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002, issue Supplement 3:S298.
-
- Loza B, Kucharska‐Pietura K, Debowska G. Atypical versus typical antipsychotic treatment prognosis in first‐episode paranoid schizophrenia based on wcst and dichotic listening scores. European Neuropsychopharmacology (Abstracts of the 14th Congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology; 2001 Oct 13‐17; Istanbul, Turkey). 2001, issue 3:285.
Mahmoud 1999 {published data only}
-
- Mahmoud RA, Engelhart LM, Janagap C, Awad G. Assessment of symptoms affecting quality of life and patient satisfaction with antipsychotic drugs:new insights for a trial of risperidone/olanzapine. APA Annual Meeting, May 15‐20, 1999, Washington, DC. 1999. [CSG NO. 4121]
-
- Mahmoud RA, Engelhart LM, Janagap C, Dogherty J. Symptoms commonly attributed to prolactin:a new assessment tool and findings from a trial of risperidone versus olanzapine. APA Annual Meeting, May 15‐20, 1999, Washington, DC. 1999. [CSG NO. 4122]
Marder 1998 {published data only}
-
- Marder SR. Newer antipsychotics: side‐effect profiles. 151st Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association. Toronto, ON, Canada. May 30‐June 4, 1998.
Mauri 2002 {published data only}
-
- Mauri MC, Steinhilber CPC, Laini V, Pavone F, Barale F. Olanzapine and quetiapine in the treatment of acute schizophrenia: a descriptive analysis. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (Abstracts of the 23rd Congress of the Collegium Internationale Neuro‐Psychopharmacologicum; 2002 Jun 23‐27; Montreal, Canada). 2002, issue Suppl 1:S119.
McElroy 1998 {published data only}
-
- McElroy SL. Atypical antipsychotics in women with bipolar and other psychiatric disorders. 151st Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association. Toronto, ON, Canada. May 30‐June 4, 1998.
McGurk 1998 {published data only}
-
- McGurk SR. The effects of atypical antipsychotic drugs on cognitive function in schizophrenia. 151st Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association. Toronto, ON, Canada. May 30‐June 4, 1998.
-
- McGurk SR, Meltzer HY. The affects of atypical antipsychotic drugs on cognitive functioning in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 1998;29(1‐2):160.
Meltzer 2003 {published data only}
-
- Meltzer HY, Sumiyoshi T, Carpenter WT, Gold JM. Atypical antipsychotic drugs improve cognition in schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry 2003;51(3):265‐8. - PubMed
Mintzer 1998 {published data only}
-
- Mintzer JE. Efficacy and safety of atypical neuroleptics in dementia. 151st Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association. Toronto, ON, Canada. May 30‐June 4, 1998.
Mitchell 2003 {published data only}
-
- Mitchell M, Earley W, Bari MA, Riesenberg RA, Marquez E, Kurtz D, Falk D, Taylor CC, Cavazzoni P. A preliminary study of the pharmacokinetics and tolerability of higher dose oral olanzapine (20, 30, or 40mg/day) in stable patients with serious mental disorders. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2003;13(4):S315. [P.2.081]
Mosolov 1998 {published data only}
-
- Mosolov SN. Biological treatment of mental disorders in Russia. 151st Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association. Toronto, ON, Canada. May 30‐June 4, 1998.
Mulqueen 2000 {published data only}
-
- Mulqueen AW, Wudarsky M, Nicolson RJ, Gochman P, Hamburger S, Lenane M, Rapoport JHL. Weight gain in pediatric patients on typical and atypical antipsychotics. 153rd Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2000 May 13‐18; Chicago, USA. 2000.
-
- Mulqueen AW, Wudarsky M, Nicolson RJ, Gochman P, Hamburger S, Lenane M, Rapoport JHL. Weight gain in pediatric patients on typical and atypical antipsychotics. 155th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2002 May 18‐23; Philadelphia, PA, USA. 2002.
Naber 1997 {published data only}
-
- Naber D. Evidence of efficacy of neuroleptics in effective versus negative symptoms. 10th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress. Vienna, Austria. September 13‐17, 1997.
Narendran 2003 {published data only}
-
- Narendran R, Young CM, Pristach CA, Pato MT, Valenti AM, Fass AR. Efficacy of clozapine in the treatment of atypical antipsychotic refractory schizophrenia: A pilot study. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2003;23(1):103‐4. - PubMed
Oliemeulen 2000 {published data only}
-
- Oliemeulen EAP, Jogems‐Kosterman BJM, Hoof JJM. Is olanzapine a subsitute for clozapine?. Schizophrenia Research (Abstracts of The 7th International Congress on Schizophrenia Research; 1999 Apr 17‐21; Santa Fe, USA). 1999:146‐7. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Oliemeulen EAP, Hoof JJM, Jogem‐Kosterman BJM, Hulsttijn W, Tuynman‐Qua HG. Is olanzapine a substitute for clozapine? The effects on psychomotor performance. Schizophrenia Research 2000;41(1):187. [CSG NO. 4502]
Ortega‐Solo (HGBS) {published data only}
-
- Nicolini H, Cruz C, Camarena B, Ortega H. 5HT2A and DRD4 molecular genotypes in a clinical trial of olanzapine versus risperidone in schizophrenic patients. European College of Neuropsychopharmacology, congress, Vienna, Austria, September 13‐17 1997.
-
- Ortega‐Solo HA, Apiquian R, Ullca RE, Loyzaga C, Mendiazabal A, Brunner E. Olanzapine versus risperidone a double blind trial in Mexican patients. Regional meeting of the Collegium Internationale Neuro‐Psychopharmacologicum and the Collegio Mexicano de Neuropsicofarmacologia. Acapulco, Mexico. August 21‐23, 1997.
Parellada 1999 {published data only}
-
- Parellada E, Lomena F, Catafau A, Font M, Gomez JC, Salamero M, Bernardo M. Olanzapine versus haloperidol d2 occupancy:a single photon emission tomography study. APA Annual Meeting, May 15‐20, 1999, Washington, DC. 1999. [CSG NO. 3999]
Perro 1999 {published data only}
-
- Lambert M, Moritz S, Karow A, Krausz M, Naber D. Quality of life in the treatment of schizophrenia‐ a randomised, open label comparison trial of amisulpride, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone and zotepine. Schizophrenia Research (Abstract of the 11th Biannial Winter Workshop on Schizophrenia). 2002.
-
- Perro C LMMSKMatAA. Depressive symptoms under atypical neuroleptic treatment in schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica (Abstracts of 13th International Symposium for the Psychological Treatment of Schizophrenia and Other Psychoses (ISPS); 2000 Jun 5‐9; Stavanger, Norway). 2000, issue Suppl.404:62‐3.
-
- Perro C, Lambert M, Moritz S, Krausz M, Naber D. A comparison of clinical outcome of four atypical neuroleptics in the treatment of schizophrenia. Pharmacopsychiatry (Abstracts of 21st Symposium of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Neuropsychopharmakologie Und Pharmakopsychiatrie (AGNP); 1999 Oct 6‐9; Nuremberg, Germany). 1999, issue 5:201.
-
- Perro C, Naber D, Lambert M, Moritz S, Krause M. A prospective clinical comparative‐study of four atypical antipsychotic agents in the treatment of schizophrenia. 11th World Congress of Psychiatry; 1999 Aug 6‐11; Hamburg, Germany. 1999:13.
Pivac 2002 {published data only}
-
- Pivac N, Muck‐Seler D, Jakovljevic M, Sagud M, Mihaljevic‐Peles A, Junaci S. The effects of olanzapine or fluphenazine on peripheral biochemical markers in schizophrenic patients. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (Abstracts of the 23rd Congress of the Collegium Internationale Neuro‐Psychopharmacologicum; 2002 Jun 23‐27; Montreal, Canada). 2002, issue Suppl 1:S184.
Ratakonda 1998 {published data only}
-
- Ratakonda S, Miller CE, Gorman JM, Sharif ZA. Efficacy of a 12 week trial of olanzapine in treatment refractory schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Schizophrenia Research 1998;29(1,2):150. [CSG NO. 4079]
Reus 1997 {published data only}
Sacchetti 2003 {published data only}
-
- Sacchetti E, Valsecchi P, Regini C, Galluzzo A, Cacciani P, Agrimi E, Mencacci C. Comparison of quetiapine, olanzapine and risperidone in patients with schizophrenia: interim results of a randomised, rater‐blinded study. 16th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology (ECNP), 2003 Sep 20‐24, Prague, Czech Republic. 2003. [EMBASE: 2003409683]
-
- Sacchetti E, Valsecchi P, Regini C, Galluzzo A, Cacciani P, Agrimi E, Mencacci C. Comparison of quetiapine, olanzapine and risperidone in patients with schizophrenia: interim results of a randomised, rater‐blinded study. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2003;13(4):S350. [P.2.162]
Sacristan (HGGS) {published data only}
-
- Sacristan JA. Doses of olanzapine, risperidone, and haloperidol in clinical practice: results of a prospective pharmaco‐epidemiological study (efeso). Schizophrenia Research (Abstracts of the 10th Biennial Winter Workshop on Schizophrenia; 2000 Feb 5‐11; Davos, Switzerland). 2000, issue 1:188‐9.
Sangar 1998 (HGEH) {published data only}
-
- Sanger T M, Tohen M, Tollefson G D, McElroy S L, Greaney M G, Toma V. Olanzapine VS Placebo in the Treatment of Acute Mania. Schizophrenia Research (9th Biennial Winter Workshop on Schizophrenia, 1998 Feb 7‐13, Davos, Switzerland). 1998, issue 1,2:152.
-
- Sanger T, Tohen M, Tollefson GD, Jacobs T. Olanzapine versus placebo in rapid‐cycling bipolar disorder. Proceedings of XXIst Collegium Internationale Neuro‐psychopharmacologicum. Glasgow, Scotland, UK. July 12‐16, 1998.
-
- Sanger TM, Tohen M, Vieta E, Dunner DL, Bowden CL, Calabrese JR, Feldman PD, Jacobs TG, Breier A. Olanzapine in the acute treatment of bipolar I disorder with a history of rapid cycling. Journal of Affective Disorders 2003;73(1‐2):155‐61. - PubMed
-
- Toben M, Zarate C Jr, Sanger IM. A placebo‐controlled trial of olanzapine in psychotic or non‐psychotic acute mania. Schizophrenia Research 1998;29(1,2):204. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Tohen M, Jacobs T, Gannon KS Sanger TM, Greaney M, Toma V, Tollefson G. Olanzapine: acute and long term efficacy in bipolar I patients. Schizophrenia Research 2000;41(1):192. [MEDLINE: ]
Sharma 2003 {published data only}
-
- Sharma M. Efficacy and safety of Olanzapine versus Haloperidol in Schizophrenic patients in India. http://www.kgmcindia.edu/departments/psychiatry/psychiatry_fac_res.htm 2003. [MEDLINE: ]
Sheitman 1997 {published data only}
-
- Sheitman BB, Lindgren JC, Early J, Sved M. High dose olanzapine for treatment‐refractory schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1997;154(11):1626. - PubMed
Sheitman 2000 {published data only}
-
- Sheitman B. Olanzapine versus risperidone for people with schizophrenia hospitalized after a relapse. Stanley Foundation Research Awards ‐ 2000 Research Award Recipients (http://www.stanleyresearch.org/ accessed February 2001) 2000.
Sikich 2004 {published data only}
-
- Sikich L, Hamer RM, Bashford RA, Sheitman BB, Lieberman JA. A pilot study of risperidone, olanzapine, and haloperidol in psychotic youth: a double‐blind, randomized, 8‐week trial. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004;29(1):133‐45. [EMBASE: 2004025276; 14583740 PMID] - PubMed
-
- Sikich L, Williamson K, Malekpour A, Bashford RA, Hooper S, Sheitman B, Lieberman JA. Interim results of a randomized controlled trial of haloperidol, risperidone, and olanzapine in psychotic youth.. 38th Annual Meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology; 1999 Dec 12‐16; Acapulco, Mexico. 1999.
Smelson 2003 {published data only}
-
- Smelson DA, Ziedonis DM, Williams JA, Losonczy MF, Williams J, Kaune M. A double‐blind trial of olanzapine reduces cue‐elicited cocaine craving and relapses. 156th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2003 May 17‐22; San Francisco, USA. 2003. [[NR692]]
Smith 1998 {published data only}
-
- Smith RC, Nigam S, Stern A, Infante M, Mehta R. Olanzapine in Chronic Nonresponding Schizophrenia:Effects on Psychopathology and Neurocognitive Function. 21st Congress of Collegium Internationale Neuro‐psychopharmacologicum, Glasgow, Scotland, UK. 1998. [CSG NO. 3628]
Smith 2001 {published data only}
-
- Smith RC, Lindenmayer J‐P, Khandat A, Infante M, Singh A. Olanzapine affects neurocognitive function in medication‐refractory schizophrenia. 155th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2002 May 18‐23; Philadelphia, PA, USA. 2002.
-
- Smith RC, Lindenmayer J‐P, Khandat A, Infante M, Singh A. Olanzapine affects neurocognitive function in medication‐refractory schizophrenia. Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2001 May 5‐10; LA, USA. Marathon Multimedia, 2001. [MEDLINE: ]
Soutullo 1998 {published data only}
-
- Soutullo CA, Sorter MT, Foster KD, McElroy SL, Keck PE. Olanzapine in the treatment of adolescent acute mania: preliminary report of seven cases. 151st Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association. Toronto, ON, Canada. May 30‐June 4, 1998.
Stephenson 2000 {published data only}
-
- Stephenson J. Delay in treating schizophrenia may narrow therapeutic window of opportunity. Journal of the American Medical Association 2000;283(16):2091‐92. - PubMed
Szafranski 1999 {published data only}
-
- Szafranski T, Jarema M, Olajossy M, Chrzanowski W, Araszkiewicz A, Landowski J, Rybakowski J, Bilikiewicz A, Bomba J. Subjective experiences of schizophrenic patients on atypical antipsychotic olanzapine and typical antipsychotic perphenazine. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999:S273. [MEDLINE: ]
Tamura 1996 (F1D‐JE) {published data only}
-
- Tamura RN, Tanaka Y, Satoh K, Takahashi M. Using the proportional odds model to assess the relationship between a multi‐item and a global item efficacy scale in a psychiatric clinical trial. Journal of Biopharmacological Statistics 1996;6:127‐37. - PubMed
Tang 2003 {published data only}
-
- Tang T, Meltzer HY. Olanzapine causes greater increases in serum lipids than risperidone. Schizophrenia Research 2003;60:367. [EMBASE: 2003241517]
Tohen 2000b (HGGW) {published data only}
-
- Tohen M, Jacobs T, Toma V, Francis J, Zhang F, Gannon KS, Sanger TM, Breier A. Is olanzapine a mood stabilizer?. Schizophrenia Research 2000;41(1):193‐4. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Tohen M, Jacobs TG, Grundy SL, McElroy SL, Banov MC, Janicak PG, Sanger T, Risser R, Zhang F, Toma V, Francis J, Tollefson GD, Breier A. Efficacy of Olanzapine in Acute Bipolar Mania: A Double‐blind, Placebo‐Controlled Study. Archives of General Psychiatry 2000;57(9):841‐9. - PubMed
Tran 1998 (HGEJ) {published data only}
-
- Tran PV, Tohen M, Mazzoti G, Silva C, Ospina J, Gattaz WF, Larach V. Switching psychotic patients with symptomatic extrapyramidal symptoms from haloperidol to olanzapine: results of a multi‐center, collaborative trial in Latin America. 151st Annual Meeting of American Psychiatric Association. Toronto, ON, Canada. May 30‐June 4, 1998.
Trandafir 1998 {published data only}
-
- Trandafir AI, Berk M, Brook S. Olanzapine versus haloperidol in cannabis induced psychosis: a randomised double‐blind trial. Proceedings of XXIst Collegium Internationale Neuro‐psychopharmacologicum. Glasgow, Scotland, UK. July 12‐16, 1998.
Uzun 2002 {published data only}
-
- Uzun S, Folnegovic‐Smalc V, Mimica N, Ljubin T, Makaric G, Ivezic S, Jelacic P, Vilibic M, Markan‐Sosic V. Ziprasidone clinical trials conducted in Croatia. Schizophrenia Research (Abstracts of the 11th Biennial Winter Workshop on Schizophrenia). Elsevier Science B.V, 2002, issue 3 Suppl.1:182.
Volavka 2002 {published data only}
-
- *Volavka J, Czobor P, Sheitman B, Lindenmayer JP, Citrome L, McEvoy JP, Cooper TB, Chakos M, Lieberman JA. Clozapine, olanzapine, risperidone, and haloperidol in the treatment of patients with chronic schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. American Journal of Psychiatry 2002;159:255‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Bilder RM, Goldman RS, Volavka J, Czobor P, Hoptman M, Sheitman B, Lindenmayer J‐P, Citrome L, McEvoy J, Kunz M, Chakos M, Lieberman JA. Neurocognitive effects of clozapine, olanzapine, risperidone, and haloperidol on treatment‐resistant patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Schizophrenia Research (Abstracts of the 11th Biennial Winter Workshop on Schizophrenia). Elsevier Science B.V, 2002, issue 3 Suppl.1:195.
-
- Bilder RM, Goldman RS, Volavka J, Czobor P, Hoptman M, Sheitman B, Lindenmayer JP, Citrome L, McEvoy J, Kunz M, Chakos M, Cooper TB, Horowitz TL, Lieberman JA. Neurocognitive effects of clozapine, olanzapine, risperidone, and haloperidol in patients with chronic schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. American Journal of Psychiatry 2002;159(6):1018‐28. [MEDLINE: ; Volavka study (hostility study)] - PubMed
-
- Bilder RM, Goldman RS, Volavka J, Czobor P, Hoptman M, Sheitman J‐PLB, Citrome L, McEvoy J, Kunz M, Chakos M//Lieberman JA. Neurocognitive effects of clozapine, olanzapine, risperidone, and haloperidol on treatment‐resistant patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. European Neuropsychopharmacology (Abstracts of the 14th Congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology; 2001 Oct 13‐17; Istanbul, Turkey). 2001, issue 3:256.
-
- Citrome L, Volavka J, Czobor P, Sheitman B, Lindenmayer J‐P, McEvoy J, Cooper TB, Chakos M, Lieberman JA. Effects of clozapine, olanzapine, risperidone, and haloperidol on hostility among patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatric Services 2001;52(11):1510‐4. - PubMed
Voruganti 2002 {published data only}
-
- Voruganti L, Cortese L, Owyeumi L, Kotteda V, Cernovsky Z, Zirul S, Awad A. Switching from conventional to novel antipsychotic drugs: Results of a prospective naturalistic study. Schizophrenia Research 2002;57(2‐3):201‐8. - PubMed
Woods 2002 (HGGF) {published data only}
-
- McGlashan TH, Miller TJ, Zipursky RB, Woods SW, Perkins DO, Hawkins KA, Addington JM. Intervention in the schizophrenic prodrome: the prevention through risk identification, management, and education initiative. 156th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2003 May 17‐22; San Francisco, USA. 2003. [[SYMPOSIUM]No. 39]
-
- McGlashan TH, Zipursky RB, Perkins D, Addington J, Miller TJ, Woods SW, Hawkins KA, Hoffman R, Lindborg S, Tohen M, Breier A. The PRIME North America randomized double‐blind clinical trial of olanzapine versus placebo in patients at risk of being prodromally symptomatic for psychosis. I. Study rationale and design. Schizophrenia Research. 2003; Vol. 61, issue 1:7‐18. [MEDLINE: ; PMID 12648731] - PubMed
-
- McGlashan TH, Zipursky RB, Perkins DO, Addington J, Woods SW, Miller TJ, Lindborg S, Marquez E, Hawkins K, Hoffman RE. Olanzapine versus placebo treatment of the schizophrenia prodrome: One year results. Schizophrenia Research. 2003; Vol. 60:295. [EMBASE: 2003241517]
-
- McGlashan TH, Zipursky RB, Perkins DO, Addington JM, Woods SW, Lindborg S, Breier AF. Olanzapine versus pbo for the schizophrenic prodrome: one‐year results. 156th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2003 May 17‐22; San Francisco, USA. 2003. [[NR584]]
-
- McGlashan TH, Zipursky RB, Perkins DO, Addington JM, Woods SW, Lindborg S, Breier AF. Olanzapine versus pbo for the schizophrenic prodrome: one‐year results. 156th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2003 May 17‐22; San Francisco, USA. 2003. [[NR584]]
Woodward 2001 {published data only}
-
- Woodward ND, Purdon SE, David SR, Stip E. Procedural learning over six months double blind treatment with haloperidol, risperidone or olanzapine. Schizophrenia Research (8th International Congress on Schizophrenia Research; 2001 Apr 28 ‐ May 2; British Columbia, Canada). 2001, issue 1‐2 Suppl:125. [MEDLINE: ]
Wright 2003 (HGAB) {published data only}
-
- King KG, Wright P, Meehan K, Birkett M, David SR, Taylor CC. Transition from intramuscular to oral olanzapine. XIIth World Congress of Psychiatry; 2002 Aug 24‐29; Yokohama, Japan. 2002. [now published lwad author wright part of (HGAB) clinical therapeutics 2003, vol 25, p420‐28]
-
- Padraig Wright, Karena Meehan, Martin Birkett, Stacy R. Lindborg, Cindy C. Taylor, Philip Morris, Alan Breier. A comparison of the efficacy and safety of olanzapine versus haloperidol during transition from intramuscular to oral therapy. Clinical Therapeutics 2003;25(5):1420‐28. - PubMed
-
- Wright P, Lindborg SR, Birkett M, Meehan K, Jones B, Alaka K, Ferchland I, Pickard A, Taylor CC, Roth J, Battaglia J, Bitter I, Chouinard G, Morris P, Breier A. Intramuscular olanzapine and intramuscular haloperidol in acute schizophrenia: antipsychotic efficacy and extrapyramidal safety during the first 24 hours of treatment. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry (submitted) 2003;48:11. [EMBASE: 2003409683] - PubMed
-
- Wright P, Lindborg SR, Birkett M, Meehan K, Jones B, Alaka KF‐HI Pickard A, Taylor CC, Roth J, Battaglia J, Bitter I, Chouinard G, Morris PL, Breier A. Intramuscular olanzapine and intramuscular haloperidol in acute schizophrenia: antipsychotic efficacy and extrapyramidal safety during the first 24 hours of treatment. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry ‐ Revue Canadienne de Psychiatrie 2003;48(11):716‐21. [PMID 14733451] - PubMed
-
- Wright P, Meehan K, Birkett M, Lindborg SR, Taylor CC, Morris PBA. A comparison of the efficacy and safety of olanzapine versus haloperidol during transition from intramuscular to oral therapy. Clinical Therapeutics 2003;25(5):1420‐8. [MEDLINE: ; PMID 12867218] - PubMed
Wudarsky 1999 {published data only}
-
- Wudarsky M, Nicolson R, Hamburger SD, Spechler L, Gochman P, Bedwell J, Lenane MC, Rapoport JL. Elevated prolactin in pediatric patients on typical and atypical antipsychotics. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology 1999;9(4):239‐45. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Yagdiran 2000 {published data only}
-
- Yagdiran O, Krausz M. Depressive symptoms under atypical neuroleptic treatment in schizophrenia.. Der Nervenarzt (Congress of the Deutsche Gesselschaft fur Psychiatrie, Psychotherapie und Nervenheilkunde: "Psychiatrie im Jahr 2000 ‐ die europaische Perspektive", 2000 September 20‐23, Aachen, Germany) 2000;71(Suppl.1):S135‐S136.
Zhang 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Zhang F, Tran PV, Taylor C, Hwu GH, Chen YS, Chang WH, Cheng J, Wang A, Chang S, Sze S, Chen RYK, Dunn E, Lieh Mak F. Efficacy and safety study comparing olanzapine versus haloperidol in the treatment of Chinese patients with schizophrenia in Taiwan and Hong Kong. World Psychiatric Association. Hamburg, Germany. 1999.
Ziherl (HGCZ) 1999 {unpublished data only}
-
- Ziherl S, Novak G, Kores‐Plesnicar B, Kosorok M, Juch H, Dossenbach M. Efficacy and safety of olanzapine in the treatment of schizophrenic, schizophreniform and schizoaffective patients in Slovenia. ECNP. London, England, UK. 1999.
References to ongoing studies
Centorrino 2001 {published data only}
-
- Centorrino F. A double‐blind, multi‐center controlled study comparing the safety and efficacy of ziprasidone and olanzapine in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder needing inpatient care. Clinical Research Net Psychiatry Clinical Trials (Massachusetts) (http://crnet.mgh.harvard.edu/home/home.asp accessed Feb 2001) 2001.
Hirsch 2000 {published data only}
-
- Hirsch S. Ziprasidone in the treatment of chronic schizophrenia (maintenance) versus olanzapine ‐ efficacy and side effects. National Research Register 2000.
Krakowski 2001 {published data only}
-
- Krakowski MI. Clozapine and olanzapine in violent schizophrenics. CRISP database (https://www‐commons.cit.nih.gov/crisp/index.html accessed 19th February 2001) 2001.
Ramamurthy 2000a {published data only}
-
- Palazidou E. A multicentre, double‐blind, randomised comparative study of aripiprazole and olanzapine in the treatment of patients with acute schizophrenia. National Research Register 2002; Vol. 1. [N0146099645]
-
- Ramamurthy 2000. A multi‐centre, double blind, randomised comparative study of aripiprazole and olanzapine in the treatment of patients with acute schizophrenia. National Research Register 2000.
Reveley 2000 {published data only}
-
- Reveley M. Effectiveness trials of antipsychotic drugs. National Research Register 2000.
Reynolds 2003 {published data only}
-
- Reynolds RF, Romano SJ, Stemhagen A, Dieck G. Ziprasidone observational study of cardiac outcomes (zodiac) large simple trial: rationale and design. Schizophrenia Research. 2003; Vol. 60:365. [EMBASE: 2003241517]
Singh 2000b {published data only}
-
- Singh V. A six month international controlled trial of the therapeutic activity of amisulpride 200 to 800mg/day verses olanzapine 5 to 20mg/day in patiients with schizophrenic disorders. National Research Register 2000.
Turner 2002 {published data only}
-
- Turner T. Quality of life ‐ Pfizer trial. National Research Register 2002; Vol. 1. [N0146103028]
Additional references
Alderson 2004
-
- Alderson P, Green S, Higgins JPT. Cochrane Reviewers' Handbook 4.2.2 [updated December 2003]. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2004, issue Issue 1.
Altman 1996
AMDP‐5 1981
-
- Arbeltsgemelnschaft fur methodik und dokumentation in der psychiatrie (AMDP) [Association for Methodology and Documentation in Psychiatry]. Das AMDP‐System: Manual zur dokumentation psychiatricher befunde. Berlin: Auflage, 1981.
Andreasen 1983
-
- Andreasen NC. Negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry 1982;39:784‐8. - PubMed
Anonymous 1997
-
- Anonymous. Olanzapine, sertindole and schizophrenia. Drugs and Therapeutics Bulletin 1997;35:11. - PubMed
APA 1994
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐IV). 4th Edition. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1994.
Barnes 1989
-
- Barnes TR. A rating scale for drug‐induced akathisia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1989;154:672‐6. - PubMed
Bland 1997
Breier 1994
-
- Breier A, Buchanan RW, Kirkpatrick B, Davis OR, Irish D, Summerfeldt A, et al. Effect of clozapine on positive and negative symptoms in outpatients with schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1994;151(1):20‐6. - PubMed
Carpenter 1984
-
- Heinrichs DW, Hanlon ET, Carpenter WT Jr. The quality of life scale: an instrument for rating the schizophrenic deficit syndrome. Schizophrenia Bulletin 1984;10:388‐96. - PubMed
Carpenter 1994
-
- Carpenter WT Jr, Buchanan RW. Schizophrenia. New England Journal of Medicine 1994;330:681‐90. - PubMed
Chalmers 1983
-
- Chalmers TC, Celano P, Sacks HS, Smith H Jr. Bias in treatment assignment in controlled clinical trials. New England Journal of Medicine 1983;309:1358‐61. - PubMed
Chouinard 1980
-
- Chouinard G, Ross‐Chouinard A, Annable L. Extrapyramidal symptom rating scale. Canadian Journal of Neurological Science 1980;7:233.
COSTART 1990
-
- US Food, Drug Administration. COSTART coding sysmbols for thesaurus of adverse reaction terms. 2nd Edition. Rockville MD: Food and Drug Administration, 1990.
de Haan 2002
-
- Haan L, Weisfelt M, Dingemans P.M.A.J, et al. Psychometric properties of the Subjective Well‐Being Under Neuroleptics scale and the Subjective Deficit Syndrome Scale. Psychopharmacology 2002;162:24‐28. - PubMed
de Haan 2002a
-
- Haan L, Weisfelt M, Dingemans PMAJ, Linszen DH, Wouters L. Psychometric properties of the Subjective Well‐Being Under Neuroleptics Scale (SWN) and the Subjective Deficit Syndrome Scale (SDSS). Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2002;162:24‐8. - PubMed
Divine 1992
-
- Divine GW, Brown JT, Frazier LM. The unit of analysis error in studies about physicians' patient care behavior. Journal of General Internal Medicine 1992;7(6):623‐9. - PubMed
Donner 2002
-
- Donner A, Klar N. Issues in the meta‐analysis of cluster randomized trials. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:2971‐80. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Fabre 1995
-
- Fabre LF, Arvanitis L, Pultz J, Jones VM, Malick JB, Slotnick VB. ICI 204,636, a novel, atypical antipsychotic ‐ early indication of safety and efficacy in patients with chronic and subchronic schizophrenia. Clinical Therapeutics 1995;17:366‐78. - PubMed
Fleischhacker 1989
-
- Fleischhacker WW, Bergmann KJ, Perovich R, Pestreich LK, Borenstein M, Lieberman JA, Kane JM. The Hillside Akathisia Scale: a new rating instrument for neuroleptic‐induced akathisia.. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1989;25(2):222‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Folstein 1975
-
- Folstein NF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. Mini‐Mental State: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician Folstein NF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. Mini‐Mental State: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1975;12:189‐98.. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1975;12:189‐98. - PubMed
Gulliford 1999
-
- Gulliford MC. Components of variance and intraclass correlations for the design of community‐based surveys and intervention studies: data from the Health Survey for England 1994. American Journal of Epidemiology 1999;149:876‐83 876‐83. - PubMed
Guy 1976
-
- Guy W. Early clinical drug evaluation (ECDEU) assessment manual for psychopharmacology. Washington, DC: National Institute of Mental Health, 1976:217‐22. [Publication No.76‐338.]
Hamilton 1960
Hamilton 1969
-
- Hamilton A. Diagnosis and Rating of Anxiety. British Journal of Psychiatry 1969;S3:76‐9.
Hamilton 1998
-
- Hamilton, S H, Revicki, D A, Genduso, L A, Beasley. CM Jr. Olanzapine versus placebo and haloperidol: quality of life and efficacy results of the North American double‐blind trial. Neuropsychopharmacology 1998;18:41‐9. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Hoadley 2004
-
- Hoadley JF. The continued need for independent research on prescription drugs. Health Affairs Jan/Feb 2004;23(1):244. - PubMed
Hogan 1983
-
- Hogan TP, Awad AG, Eastwood R. A Self‐report Predictive of Drug Compliance in Schizophrenia: Reliability and Discriminative Ability Psychological Medicine. Psychological Medicine 1983;13:177‐83. - PubMed
Hunter 2003
ICD‐10
-
- World Health Organization. The ICD‐10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1992.
Inada 1996
-
- Inada M. Evaluation and Diagnosis of Drug‐Enduced Extrapyramidal Symptoms: Commentary on the DIEPSS and guide to its usage. Tokyo: Seiwa Shoten, 1996.
Kane 1988
-
- Kane J, Honigfeld G, Singer J, Meltzer H, et al. Clozapine for the treatment‐resistant schizophrenic: a double‐blind comparison with chlorpromazine. Archives of General Psychiatry 1988;45:789‐96. - PubMed
Kay 1986
-
- Kay SR, Opler LA, Fiszbein A. Positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) manual. North Tonawanda (NY): Multi‐Health Systems, 1986.
Lehman 1983
-
- Lehman A. The well being of chronic mental patients: assessing their quality of life. Archives of General Psychiatry 1983;40:369‐73. - PubMed
Lieberman 1998
-
- Liebermann JA, Mailman RB, Duncan G, Sikich L, Chakos M, Nichols DE, Kraus JE. Serotonergic basis of antipsychotic effects in schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry 1998;44(11):1099‐117. - PubMed
Lingjaerde 1987
-
- Lingjaerde O, Ahlfors UG, Bech P, Dencker SJ, Elgen K. The UKU side effect rating scale. A new comprehensive rating scale for psychotropic drugs and a cross‐sectional study of side effects in neuroleptic‐treated patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 1987;76(334):100. - PubMed
Marshall 2000
-
- Marshall M, Lockwood A, Bradley C, Adams C, Joy C, Fenton M. Unpublished rating scales: a major source of bias in randomised controlled trials of treatments for schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 2000;176:249‐52. - PubMed
McEwan 1993
-
- McEwan GW. New antipsychotic medications: do research results relate to clinical practice?. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 1993;38(Suppl):75‐9. - PubMed
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman D. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomized trials. JAMA 2001;285:1987‐91. - PubMed
Montgomery 1979
-
- Montgomery SA, Asberg M. A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. Montgomery SA, Asberg M. A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. British Journal of Psychiatry 1979;134:382‐9. Montgomery 1979 Montgomery SA, Asberg M. A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. British Journal of Psychiatry 1979;134:382‐9.. British Journal of Psychiatry 1979;134:382‐9. - PubMed
Offerhaus 2004
-
- Offerhaus L. The pharmaceutical industry in scandal: Mercury or Aesculapius? [De geneesmiddelenindustrie in opspraak: Mercurius of Aesculapius?]. Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Geneeskunde 2004;148(51):2554‐6. - PubMed
Overall 1962
-
- Overall JE, Gorham DR. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psychological Reports 1962;10:799‐812.
Parrott 1980
-
- Parrott AC, Hindmarch I Parrott A.C, Hindmarch I. The Leeds Sleep Evaluation Questionnaire in psychopharmacological investigations ‐ a review. Psychopharmacology 1980;71:173‐79. - PubMed
Pocock 1975
-
- Pocock SJ, Simon R. Sequential treatment assignment with balancing for prognostic factors in the controlled clinical trial. Biometrics 1975;31(1):103‐15. - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias: dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273:408‐12. - PubMed
Seeman 1987
-
- Seeman P. Dopamine receptors and the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Synapse 1987;1:133‐52. - PubMed
Sellers 2003
-
- Sellers LJ. Fourth annual 50. Special Report. Pharmaceutical Executive. http://www.pharmexec.com/pharmexec/article/articleDetail.jsp?id=55215 May 2003:45‐52.
Simpson 1970
-
- Simpson GM, Angus JWS. A rating scale for extrpyramidal side‐effects. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 1970;212:11‐9. - PubMed
Srisurapanont 2004
Tamminga 1998
-
- Tamminga CA. Serotonin and schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry 1998;44:1079‐80. - PubMed
Thornley 2003
Tollefson 1997
-
- Tollefson GD, Beasley CM Jr, Tran PV, et al. Olanzapine versus haloperidol in the treatment of schizophrenia and schizoaffective and schizophreniform disorder: results of an international collaborative trial. American Journal of Psychiatry 1997;154:457‐65. - PubMed
Ukoumunne 1999
-
- Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JAC, Burney PGJ. Methods for evaluating area‐wide and organistation‐based intervention in health and health care: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment 1999;3(5):1‐75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

