Prostacyclin for pulmonary hypertension in adults
- PMID: 15846646
- PMCID: PMC7004255
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002994.pub2
Prostacyclin for pulmonary hypertension in adults
Abstract
Background: Primary pulmonary hypertension (PPH) is progressive, resulting in right ventricular failure. Pulmonary hypertension can be idiopathic or associated with other conditions. Prostacyclin is a potent vasodilator and inhibitor of platelet aggregation, and can be given orally, subcutaneously, intravenously or inhaled via a nebuliser.
Objectives: To determine the efficacy of prostacyclin or one of its analogues in idiopathic primary pulmonary hypertension.
Search strategy: Electronic searches were carried out with pre-specified terms. Searches were current as of July 2004.
Selection criteria: Two reviewers selected randomised controlled trials (RCTs) involving adults with pulmonary hypertension for inclusion.
Data collection and analysis: Study quality was assessed and data extracted independently by two reviewers. Outcomes were analysed as continuous and dichotomous outcomes. We sub-grouped data where possible by aetiology of PH (PPH, PH secondary to connective tissue disorder or mixed populations).
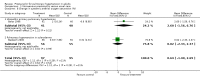
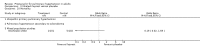
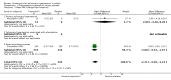
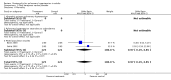
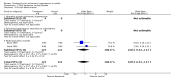
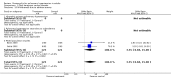
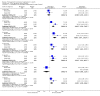
Main results: Nine RCTs of mixed duration (3 days-52 weeks), recruiting 1175 participants were included (NYHA functional classes II-IV). Intravenous prostacyclin versus usual care (four studies): There were significant improvements in exercise capacity of around 90 metres, cardiopulmonary haemodynamics and NYHA functional class over 3 days-12 weeks. Effects were consistent in primary and secondary pulmonary hypertension. Oral prostacyclin versus placebo (two studies): Short-term data (3-6 months) indicated that there was a significant improvement in exercise capacity, but data from one study of 52 weeks reported no significant difference at 12 months. No significant differences were observed for any other outcome. Subcutaneous treprostinil versus placebo (two studies, 8-12 weeks):One large study reported a significant median improvement in exercise capacity of around 16 metres. Cardiopulmonary haemodynamics and symptom scores favoured treprostinil. Infusion site pain and withdrawals due to adverse events were more frequent with treprostinil. Inhaled prostacyclin versus placebo (one study, 12 weeks):There was a significant increase in exercise capacity of approximately 36 metres. Treatment led to better symptom scores and functional class status than with placebo. Subgroup analyses reported by individual studies showed a better exercise capacity in participants with PPH, than those participants with PH secondary to other diseases. Side effects and adverse events were common in the studies.
Authors' conclusions: There is evidence that intravenous prostacyclin in addition to conventional therapy at tolerable doses optimised by titration, can confer some short-term benefits (up to 12 weeks of treatment) in exercise capacity, NYHA functional class and cardiopulmonary haemodynamics. There is also some evidence that patients with more severe disease based upon NYHA functional class showed a greater response to treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures








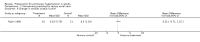



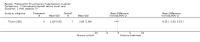































Update of
-
Prostacyclin for pulmonary hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(2):CD002994. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002994. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18;(2):CD002994. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002994.pub2. PMID: 12804447 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Badesch 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Badesch D, Tapson V, McGoon M, Brundage B, Rubin L, Wigley F, et al. Continuous intravenous epoprostenol for pulmonary hypertension due to the scleroderma spectrum of disease. Annals of Internal Medicine 2000;132(6):425‐34. - PubMed
Barst 1996 {published data only}
-
- Barst R, Rubin L, McGoon M, Caldwell E, Long W, Levy P. Survival in primary pulmonary hypertension with long‐term continuous intravenous prostacyclin. Annals of Internal Medicine 1994;121(6):409‐15. - PubMed
Barst 2003 {published data only}
-
- Barst RJ, McGoon M, McLaughlin V, Tapson V, Rich S, Rubin L, et al. Beraprost therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2003;41(12):2119‐25. - PubMed
Galiè 2002 {published data only}
-
- Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiéry JL, Vizza CD, Kneussl M, Manes A, et al. Effects of beraprost sodium, an oral prostacyclin analogue, in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: a randomized,double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2002;39(9):1496‐502. - PubMed
-
- Simmoneau G, Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiéry JL, Vizza C, Kneussl M, et al. Effects of beraprost sodium, an oral prostacyclin analogue in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2002;165(Suppl 8):A411. - PubMed
McLaughlin 2003 {published data only}
-
- McLaughlin VV, Gaine SP, Barst RJ, Oudiz RJ, Bourge RC, Frost A, et al. Efficacy and safety of treprostinil: an epoprostenol analogue for primary pulmonary hypertension. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 2003;41(2):293‐9. - PubMed
Olschewski 2002 {published data only}
-
- Olschewski H, Galie N, Higenbottam T, Naeije R, Rubin LJ, Simonneau G, et al. Positive outcome of the aerosolized iloprost randomised trial for treatment of severe pulmonary hypertension (AIR study) [Abstract]. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2002;165(8 Suppl):A411.
-
- Olschewski H, Simoneau G, Galie N, Higenbottam T, Naije R, Rubin LJ, et al. Inhaled Iloprost for severe pulmonary hypertension. New Egland Journal of Medicine 2002;347(5):322‐9. - PubMed
Rubin 1990 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Rubin L, Mendoza J, Hood M, McGoon M, Barst R, Williams W, et al. Treatment of primary pulmonary hypertension with continuous intravenous prostacyclin (Epoprostenol). Annals of Internal Medicine 1990;112(7):485‐91. - PubMed
Simonneau 2002 {published data only}
-
- McLaughlin V. Improvement in exercise tolerance with treprostinil is dose related for pulmonary arterial hypertension. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2002;165(Suppl 8):A570.
-
- Oudiz RJ, Schilz RJ, Barst RJ, Galiè N, Rich S, Rubin LJ, et al. Treprostinil, a prostacyclin analogue, in pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with collagen vascular disease. Chest 2004;126(2):420‐7. - PubMed
-
- Simonneau G, Barst R, Galie N, Naejie R, Rich S, Bourge RC, et al. Continuous subcutaneous infusion of treprostinil, a prostacyclin analogue, in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. American Journal of Respiratory Critical Care Medicine 2002;165(3):800‐4. - PubMed
Thurm 1991 {published data only}
-
- Thurm C, Wigley F, Dole W, Wise R. Failure of vasodilator infusion to alter pulmonary diffusing capacity in systemic sclerosis. The American Journal of Medicine 1991;90(5):547‐52. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Anonymous 2002 {published data only}
-
- Anonymous. Treprostinil (Remodulin) for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Medical Letter on Drugs & Therapeutics 2002;44(1139):80‐2. - PubMed
Badesch 2002 {published data only}
-
- Badesch DB, Bodin F, Channick RN, Frost A, Rainiso M, Robbins IM, et al. Complete results of the first randomised placebo‐controlled study of bosentan, a dual endothelin receptor antagonist, in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Current Therapeutic Research 2002;63(4):227‐46.
Barst 1994 {published data only}
-
- Barst R, Rubin L, McGoon M, Caldwell E, Long W, Levy P. Survival in primary pulmonary hypertension with long‐term continuous intravenous prostacyclin. Annals of Internal Medicine 1994;121(6):409‐15. - PubMed
Bartosik 1996 {published data only}
-
- Bartosik I, Eskilsson J, Scheja A, Akesson A. Intermittent Iloprost infusion therapy of pulmonary hypertension in scleroderma ‐ a pilot study. British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35(11):1187‐90. - PubMed
Bendayan 2002 {published data only}
-
- Bendayan D, Fink G, Aravot D, Ygla M, Bendov I, Bliden L, et al. Continuous intravenous epoprostenol in pulmonary hypertension. Israeli Medical Journal 2002;4:255‐8. - PubMed
Brenot 1995 {published data only}
-
- Brenot F, Sitbon O, Parent F, Benhamou D, Moszkowski J, Launay C, et al. Influence of long term continous infusion of epoprostenol on survival in patients wiht primary pulmonary hypertension: the French experience. European Respiratory Journal 1995;8(Suppl 19):195s.
Bresser 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bresser P, Fedullo PF, Auger WR, Channick RN, Robbins IM, Kerr KM, et al. Continuous intravenous epoprostenol for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. European Respiratory Journal 2004;23(4):595‐600. - PubMed
Budev 2004 {published data only}
-
- Budev MM, Minai OA, Arroliga AC. Overview of treprostinil sodium for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Drugs of Today 2004;40(3):225‐34. - PubMed
Castelain 2001 {published data only}
-
- Castelain V, Chemla D, Humbert M, Sitbon O, Simmoneau G, Lecarpentier Y, Hervé P. Pulmonary artery pressure‐flow relations after prostacyclin in primary pulmonary hypertension. American Journal of Respiratory Critical Care Medicine 2002;165:338‐40. - PubMed
Cea‐Calvo 2003 {published data only}
-
- Cea‐Calvo L, Escribano Subias P, Tello de Menesses R, Lazaro Salvador M, Gomez Sanchez MA, Delgado Jimenez JF, et al. Treatment of HIV‐associated pulmonary hypertension with treprostinil. Revista Espanola De Cardiologia 2003;56(4):421‐5. - PubMed
Chua 2005 {published data only}
-
- Chua R, Keogh A. Combining treprostinil and sildenafil in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Internal Medicine Journal 2005;35(11):684‐5. - PubMed
Cáneva 2002 {published data only}
-
- Cáneva J, Ossés J, Rours P, Visentini D, Gómez F, Mazzei M, et al. Comparison of the acute hemodinamics effects of oxygen 100% and inhaled iloprost in severe and refractory pulmonary hypertension. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2002;165(Suppl 8):A572.
Dandel 2003 {published data only}
-
- Dandel M, Kemper D, Weng Y, Hummel M, Mulahasanovic S, Kapell S, et al. Primary pulmonary hypertension: survival benefits of therapy with prostacyclin analogs and transplantation. Transplantation Proceedings 2003;35(6):2117‐20. - PubMed
de la Mata 1994 {published data only}
-
- Mata J, Gomez‐Sanchez MA, Aranza M, Gomez‐Reino J. Long‐term Iloprost infusion therapy for severe pulmonary hypertension in patients with connective tissue disease. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1994;37(10):1528‐33. - PubMed
Ewert 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ewert R. Iloprost in intensive medicine [Iloprost in der Intensivmedizin]. Journal für Anästhesie 2001, (3):66‐8.
Galiè 2003 {published data only}
-
- Galie N, Manes A, Branzi A. Prostanoids for pulmonary arterial hypertension. American Journal of Respiratory Medicine 2003;2(2):123‐37. - PubMed
Gerlach 2002 {published data only}
-
- Gerlach H. Intraoperative inhalation of nebulized iloprost during OLT reduces pulmonary hypertension after reperfusion. Journal Fur Anasthesie Und Intensivbehandlung 2002;9(2):226.
Gessler 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gessler T, Schmehl, Hoeper M, Rose F, Ghofrani H, Olschewski H, et al. Ultrasonic versus jet nebulisation of iloprost in severe pulmonary hypertension. European Respiratory Journal 2001;17:14‐9. - PubMed
Ghofrani 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ghofrani H, Wiedemann R, Rose F, Olschewski H, Schermuly RT, Weissmann N, et al. Combination therapy with oral sildenafil and inhaled iloprost for severe pulmonary hypertension. Annals of Internal Medicine 2002;136(7):515‐22. - PubMed
Ghofrani 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ghofrani HA, Seeger W, Grimminger F. Imatinib for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;353(13):1412‐3. - PubMed
Hache 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hache M, Denault A, Belisle S, Robitaille D, Couture P, Sheridan P, et al. Inhaled epoprostenol (prostacyclin) and pulmonary hypertension before cardiac surgery. Journal of Thoracic & Cardiovascular Surgery 2003;125(3):642‐9. - PubMed
Hallioglu 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hallioglu O, Dilber E, Celiker A. Comparison of acute hemodynamic effects of aerosolized and intravenous iloprost in secondary pulmonary hypertension in children with congenital heart disease. American Journal of Cardiology 2003;92(8):1007‐9. - PubMed
Higenbottam 1998 {published data only}
Higenbottam 2001 {published data only}
-
- Higgenbottam T, Siddons T. Trials of inhaled Iloprost and other new vasodilating prostaglandins. European Respiratory Journal 2001;17:6‐7. - PubMed
Highland 2003 {published data only}
-
- Highland KB, Strange C, Mazur J, Simpson KN. Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: a preliminary decision analysis. Chest 2003;124(6):2087‐92. - PubMed
Hoeper 2000 {published data only}
-
- Hoeper M, Schwarze M, Ehlerding S, Adler‐Schuermeyer A, Spiekerkoetter E, Niedermeyer J, et al. Long term tratment of primary pulmonary hypertension with aerosolized iloprost, a prostacyclin analogue. The New England Journal of Medicine 2000;342(25):1866‐70. - PubMed
-
- Hoeper MM, Schwarze M, Ehlerding S, Adler‐Schuermeyer A, Spiekerkoetter E, Niedermeyer J, et al. Long‐term treatment of primary pulmonary hypertension with Iloprost [Langfristige Behandlung der primären pulmonalen Hypertonie mit inhalvativen Iloprost]. Pneumologie 2001;55:38‐43. - PubMed
Hoeper 2002 {published data only}
-
- Hoeper MM. Pulmonary hypertension in collagen vascular disease. European Respiratory Journal 2002;19:571‐6. - PubMed
Humbert 1998 {published data only}
-
- Humbert M, Sacnhez O, Fartoukh M, Lagot JL, Gall C, Sitbon O, et al. Short‐term and long‐term epoprostenol (prostacyclin) therapy in pulmonary hypertension secondary to connective tissue diseases: results of a pilot study. European Respiratory Journal 1999;13:1351‐6. - PubMed
Humbert 2003 {published data only}
-
- Humbert M, Barst RJ, Robbins IM, Channick R, Manes A, et al. Safety & efficacy of bosentan combined with epoprostenol in patients with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension. American Thoracic Society 99th International Conference. 2003.
Jones 1987 {published data only}
Kramm 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kramm T, Eberle B, Oelert H, Mayer E. The use of inhaled iloprost in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension after pulmonary thromboendarterectomy ‐ a randomized double‐blind study. Journal für Anasthesie und Intensivbehandlung 2002;9(4):41‐42.
Langer 2003 {published data only}
-
- Langer F, Wilhelm W, Tscholl D, Schramm R, Lausberg H, Wendler O, et al. Intraoperative inhalation of the long‐acting prostacyclin analog iloprost for pulmonary hypertension. Journal of Thoracic & Cardiovascular Surgery 2003;126(3):874‐5. - PubMed
Langleben 2002 {published data only}
-
- Langleben D, Christman BW, Barst RJ, Dias VC, Galie N, Higenbottam TW, et al. Effects of the thromboxane synthetase inhibitor and receptor antagonist terbogrel in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. American Heart Journal 2002;143(5):E4. - PubMed
Leuchte 2002 {published data only}
-
- Leuchte H, Schaiblmair M, Baumgartner R, Ding I, Koczulla AR, Behr J. Acute hemodynamics effects of inhaled oxygen, nitric oxide and iloprost in patients with severe pulmonary hypertension. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2002;165(Suppl 8):A572.
McLaughlin 1998 {published data only}
-
- McLaughlin VV, Genthner DE, Panella MM, Rich S. Reduction in pulmonary vascular resistance with long‐term epoprostenol (prostacyclin) therapy in primary pulmoanry hypertension. The New England Journal of Medicine 1998;338(5):273‐7. - PubMed
McLaughlin 2005 {published data only}
-
- McLaughlin VV, Oudiz R, Frost A, Tapson V, Murali S, Channick R, et al. A randomsed, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of iloprost inhalation as add‐on therapy to Bosentan in pulmonary arterial hypertensions (PAH). Chest 2005;128(4):160s.
Menon 1998 {published data only}
-
- Menon N, McALpine L, Peacock AJ, Madhok R. The acute effects of prostacyclin on pulmonary haemodynamics in patients with pulmonary hypertension secondary to systemic sclerosis. Arthritis and rheumatism 1998;41(3):466‐9. - PubMed
Mikhail 1997 {published data only}
-
- Mikhail G, Gibbs JSR, Richardson M, Wright G, Khaghani A, Banner N, Yacoub M. An evaluation of nebulized prostacyclin in patients with primary and secondary pulmonary hypertension. European Heart Journal 1997;18:1499‐504. - PubMed
Mikhail 2002 {published data only}
-
- Mikhail GW, Gibbs JS, Yacoub M. Management of primary pulmonary hypertension. The British Journal of Cardiology 2002;9(6):330‐6.
Nagaya 2002 {published data only}
Nagaya 2004 {published data only}
-
- Nagaya N, Kyotani S, Uematsu M, Ueno K, Oya H, Nakanishi N, et al. Effects of adrenomedullin inhalation on hemodynamics and exercise capacity in patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation 2004;109(3):351‐6. - PubMed
Nakayama 2001 {published data only}
-
- Nakayama T, Ishikita T, Matsuura H, Tsutoma S. Effects of long‐term treatment with prostacyclin on plasma adrenomedullin in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Journal of Cardiology 2001;38(5):263‐71. - PubMed
Okano 1996 {published data only}
-
- Okano Y, Yoshioka T, Shimouchi A, Satoh T, Inagaka S, Itoh T, et al. Short‐term effect of continuous intravenous prostacyclin (Epoprostenol) in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Medical Book Information 1996;3:73‐9.
Olschewski 1996 {published data only}
-
- Olschewski H, Walmrath D, Schermuly R, Ghofrani A, Grimminger F, Seeger W. Aerosolized prostacyclin and iloprost in severe pulmonary hypertension. Annals of Internal Medicine 1996;124:820‐4. - PubMed
Olschewski 1999 {published data only}
-
- Olschewski H, Ghofrani A, Walmrath D, Schermuly R, Temmesfeld‐Wollbrück B, Grimminger F, et al. Inhaled prostacyclin and iloprost in severe pulmonary hypertension secondary to lung fibrosis. American Journal Critical Care Medicine 1999;160:600‐7. - PubMed
-
- Olschewski H, Ghofrani HA, Walmrath D, Schermuly R, Schulz R, Grimminger F, et al. Inhaled prostacyclin and iloprost in severe pulmonary hypertension secondary to lung fibrosis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 1998;157(Suppl 3):A595. - PubMed
Olschewski 2000 {published data only}
-
- Olschewski H, Ghofrani A, Scheml T, Winkler J, Wilkens H, Hoper M, et al. Inhaled iloprost to treat severe pulmonary hypertension. Annals of Internal Medicine 2000;132:435‐43. - PubMed
Olschewski 2003 {published data only}
-
- Olschewski H, Rohde B, Behr J, Ewert R, Gessler T, Ghofrani HA, et al. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of inhaled iloprost, aerosolized by three different devices, in severe pulmonary hypertension. Chest 2003;124(4):1294‐304. - PubMed
Olschewski 2004 {published data only}
-
- Olschewski H, Rose F, Schermuly R, Ghofrani HA, Enke B, Olschewski A, et al. Prostacyclin and its analogues in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2004;102(2):139‐53. - PubMed
Ono 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ono F, Nagaya N, Kyotani S, Oya H, Nakanishi N, Miyatake K. Hemodynamic and hormonal effects of beraprost sodium, an orally active prostacyclin analogue, in patients with secondary precapillary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation Journal 2003;67(5):375‐8. - PubMed
Ono 2003a {published data only}
-
- Ono F, Nagaya N, Okumura H, Shimizu Y, Kyotani S, Nakanishi N, et al. Effect of orally active prostacyclin analogue on survival in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension without major vessel obstruction. Chest 2003;123(5):1583‐8. - PubMed
Opitz 2005 {published data only}
-
- Opitz CF, Wensel R, Winkler J, Halank M, Bruch L, Kleber FX, et al. Clinical efficacy and survival with first‐line inhaled iloprost therapy in patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. European Heart Journal 2005;26(18):1895‐902. - PubMed
Robbins 2000 {published data only}
-
- Robbins I, Gaine S, Schilz R, Tapson V, Rubin L, Loyd J. Epoprostenol for treatment of pulmonary hypertension in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Chest 2000;117(1):14‐8. - PubMed
Rubin 2005 {published data only}
-
- Rubin L. Epoprostenol and nesiritide in pulmonary hypertension. Chest 2005;127(5):1870. - PubMed
Saadjian 1997 {published data only}
-
- Saadjian A, Philip‐Joet F, Paganelli F, Arnaud A, Levy S. Long‐term effects of cicletanine on secondary pulmonary hypertension. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1998;31:361‐71. - PubMed
Scorza 2001 {published data only}
-
- Scorza R, Caronni M, Mascagni B, Berruti V, Bazzi S, Micallef E, et al. Effects of long‐term cyclic iloprost therapy in systemic sclerosis with Raynaud's phenomenon. A randomized, controlled study. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2001;19(5):503‐8. - PubMed
Shapiro 1997 {published data only}
-
- Shapiro SM, Oudiz RJ, Cao T, Romano MA, Beckmann XJ, Georgiou D, et al. Primary pulmonary hypertension: Improved long‐term effects and survival with continuous intravenous epoprostenol infusion. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 1997;30(2):343‐9. - PubMed
Stiebellehner 2003 {published data only}
-
- Stiebellehner L, Petkov V, Vonbank K, Funk G, Schenk P, Ziesche R, et al. Long‐term treatment with oral sildenafil in addition to continuous IV epoprostenol in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chest 2003;123(4):1293‐5. - PubMed
Stricker 1999 {published data only}
-
- Stricker H, Domenighetti G, Fiori G, Mombelli G. Sustained improvement of performance and haemodynamics with long‐term aerosolised prostacyclin therapy in severe pulmonary hypertension. Schweizerische Medizinische Wochenschrift 1999;129(24):923‐7. - PubMed
Tapson 2006 {published data only}
-
- Tapson VF, Gomberg‐Maitland M, McLaughlin VV, Benza RL, Widlitz AC, Krichman A, et al. Safety and efficacy of IV treprostinil for pulmonary arterial hypertension: a prospective, multicenter, open‐label, 12‐week trial.. Chest 2006;129(3):683‐8. - PubMed
Vizza 2001 {published data only}
Voswinckel 2006 {published data only}
-
- Voswinckel R, Ghofrani HA, Grimminger F, Seeger W, Olschewski H. Inhaled trepostinil for treatment of chronic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Annals of Internal Medicine 2006;144(2):149‐50. - PubMed
Wilkens 2001 {published data only}
-
- Wilkens H, Guth A, König J, Forestier N, Cremers B, Hennen B, et al. Effect of inhaled Iloprost plus oral sildenafil in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 2001:1218‐22. - PubMed
Yap 2003 {published data only}
-
- Yap RL, Mermel LA. Micrococcus infection in patients receiving epoprostenol by continuous infusion. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 2003;22(11):704‐5. - PubMed
Additional references
ACCP 2004
-
- Badesch DB, Abman SH, Ahearn GS, Barst RJ, McCrory DC, Simonneau G, et al. Medical therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension: ACCP evidence‐based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2004;126(Suppl 1):35s‐62s. - PubMed
Bandolier 2000
-
- Bandolier. Bias. Bandolier 2000;October:80‐2.
Berkenboom 1982
Black 2001
-
- Black C. Personal communication 2001.
Brundage 1990
-
- Brundage BH. Pulmonary hypertension in collagen vascular disease. In: Fishman A editor(s). The Pulmonary Circulation. Philadelphia University of Pennsylvania Press, 1990:353‐8.
Christman 1992
-
- Christman BW, McPherson CD, Newman JH, King GA, Bernard GR, Groves BM, et al. An imbalance between the excretion of thromboxane and prostacyclin metabolites in pulmonary hypertension. New England Journal of Medicine 1992;327:70‐5. - PubMed
D'Alonzo 1986
-
- D'Alonzo GE, Gianotti L, Dantzker DR. Noninvasive assessment of haemodynamic improvement during chronic vasodilator therapy in obliterative pulmonary hypertension. American Review of Respiratory Disease 1986;133(3):380‐4. - PubMed
D'Alonzo 1991
-
- D'Alonzo GE, Barst RJ, Ayres SM, Bergofsky EH, Brundage BH, Detre KM, et al. Survival in patients with PPH. Results from a national prospective registry. Annals of Internal Medicine 1991;115(5):343‐9. - PubMed
Farber 1983
-
- Farber HW, Karlinsky JB, Faling LJ. Fatal outcome following nifedipine for pulmonary hypertension. Chest 1983;83(4):708‐9. - PubMed
Furst 1981
-
- Furst DE, Davis JA, Clements PJ, et al. Abnormalities of pulmonary vascular dynamics and inflammation in early progressive systemic sclerosis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1981;24(11):1403‐8. - PubMed
Grant 1992
-
- Grant S, Goa K. Iloprost. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in peripheral vascular disease, myocardial ischaemia and extracorporeal circulation procedures. Drugs 1992;43:889‐924. - PubMed
Higenbottam 1987
-
- Higenbottam T. The place of prostacyclin in the clinical management of primary pulmonary hypertension. American Review of Respiratory Disease 1987;136(3):782‐5. - PubMed
Higenbottam 1993
Higenbottam 1995
-
- Higenbottam TW. Prostacyclin. Bandolier 1995;14:3‐4.
Humbert 1999
-
- Humbert M, Sanchez O, Fartoukh M, Jagot JL, Gall C, Sitbon O, et al. Short‐term and long‐term epoprostenol (prostacyclin) therapy in pulmonary hypertension secondary to connective tissue diseases: results of a pilot study. European Respiratory Journal 1999;13:1351‐6. - PubMed
Jadad 1996
-
- Jadad AR, Moore A, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJM, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomised controlled trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17:1‐12. - PubMed
Kanthapillai 2004
Liu 2004
-
- Liu C, Chen J. Endothelin receptor antagonists for pulmonary arterial hypertension (Cochrane review). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2004, Issue 4. - PubMed
Loscalzo 1997
-
- Loscalzo J. Endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension. New England Journal of Medicine 1997;327:117‐9. - PubMed
Moncada 1976
-
- Moncada S, Gryglewski R, Bunting S, Vane JR. An enzyme isolated from arteries transforms prostaglandin endoperoxides to an unstable substance that inhibts platelet aggregation. Nature 1976;263:663‐5. - PubMed
Palmer 1988
-
- Palmer SM, Robinson LJ, Wang A, Gossage JR, Bashone T, Tapson VF. Massive pulmonary edema and death after prostacyclin infusion in a patient with pulmonary veno‐occlusive disease. Chest 1988;113(1):237‐40. - PubMed
Pope 2001
Rich 1987
-
- Rich S, Brindage BH. High dose channel blocking therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension: evidence for long‐term reduction in pulmonary arterial pressure and regression of right ventricular hypertrophy. Circulation 1987;76:135‐41. - PubMed
Robin 1982
-
- Robin ED. Some basic and clinical challenges in the pulmonary circulation. Chest 1982;81(3):357‐63. - PubMed
Rubin 1997
-
- Rubin LJ. Primary pulmonary hypertension. New England Journal of Medicine 1997;336:111‐2. - PubMed
Salerni 1977
-
- Salerni R, Rodnan GP, Leon DF, Shaver JA. Pulmonary hypertension in the CREST syndrome variant of progressive systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Annals of Internal Medicine 1977;86:394‐9. - PubMed
Stupi 1986
-
- Stupi AM, Steen VD, Owens GR, Barnes EL, Rodnan GP, Medsger TA Jr. Pulmonary hypertension in the CREST syndrome variant of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatism 1986;29:515‐24. - PubMed
Ungerer 1983
-
- Ungerer RG, Tashkin DP, Furst D, et al. Prevalence and clinical correlates of pulmonary arterial hypertension in progressive systemic sclerosis. American Journal of Medicine 1983;75:65‐74. - PubMed
Wells 2000
-
- Wells AU. Lung disease in association with connective tissue diseases. European Respiratory Monograph 2000;14:137‐64.
Yousem 1990
-
- Yousem SA. The pulmonary pathologic manifestations of the CREST syndrome. Human Pathology 1990;21(5):467‐74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

